Biosynthesis of polyoxypeptin A: novel amino acid 3-hydroxy-3-methylproline derived from isoleucine
Abstract
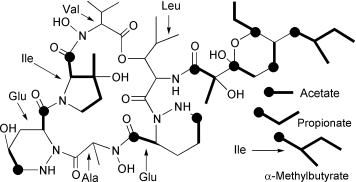
Polyoxypeptin A is a hexadepsipeptide, isolated from Streptomyces, containing the novel amino acid (2S,3R)-3-hydroxy-3-methylproline. Its biosynthetic pathway is studied by incorporation of stable isotope-labelled

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...