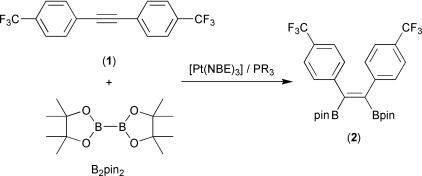
Automated parallel screening using a series of in situ generated platinum(0) phosphine complexes has allowed the identification of improved catalysts for the diboration of alkynes using bis(pinacolato)diboron (B2(pin)2, pin = OCMe2CMe2O). A selection of phosphines were added to [Pt(NBE)3] (NBE = norbornene), which contains only labile mono-olefin ligands, and the activity of the resulting solutions as catalysts for the diboration of 4-CF3C6H4C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CC6H4CF3-4′
1 by B2(pin)2 was investigated by in situ GC-MS and/or NMR spectroscopy. This allowed the optimum phosphine ∶ platinum stoichiometry to be identified as 1 ∶ 1, and the large differences in catalyst activity depending on the nature of the phosphine to be quantified. The best phosphines employed in the study, PCy3 and PPh2(o-Tol) (o-Tol = C6H4Me-o), give activities orders of magnitude greater than the worst, such as P(C6F5)3 and PBut3. The monophosphine catalysts function much more efficiently than previous catalysts for a range of alkynes allowing diborations to be performed at ambient temperatures. The diboration of strained cyclic alkenes and some vinyl- and allyl-arenes proceeded well, although the catalysts were inactive for other olefinic systems examined. As a result of these studies, the isolable and stable compound [Pt(PCy3)(η2-C2H4)2] was identified as an excellent catalyst for alkyne diboration even at room temperature.
CC6H4CF3-4′
1 by B2(pin)2 was investigated by in situ GC-MS and/or NMR spectroscopy. This allowed the optimum phosphine ∶ platinum stoichiometry to be identified as 1 ∶ 1, and the large differences in catalyst activity depending on the nature of the phosphine to be quantified. The best phosphines employed in the study, PCy3 and PPh2(o-Tol) (o-Tol = C6H4Me-o), give activities orders of magnitude greater than the worst, such as P(C6F5)3 and PBut3. The monophosphine catalysts function much more efficiently than previous catalysts for a range of alkynes allowing diborations to be performed at ambient temperatures. The diboration of strained cyclic alkenes and some vinyl- and allyl-arenes proceeded well, although the catalysts were inactive for other olefinic systems examined. As a result of these studies, the isolable and stable compound [Pt(PCy3)(η2-C2H4)2] was identified as an excellent catalyst for alkyne diboration even at room temperature.
p
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CC6H4CF3-4′
1 by B2(pin)2 was investigated by in situ
CC6H4CF3-4′
1 by B2(pin)2 was investigated by in situ 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...