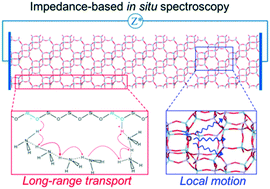
Integrated investigations combining experimental and theoretical methods have promoted significantly the fundamental understanding of zeolite-based ammonia selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR), a key technology for the abatement of automotive nitrogen oxide emissions. One representative finding is that site-isolated Cu ions within zeolite catalysts are solvated and mobilized in the NH3-SCR reaction at low temperatures. In this minireview, we highlight that impedance-based in situ spectroscopy (in situ IS), by monitoring the dielectric properties of zeolite catalysts, can be used to track directly the dynamic Cu ion motion under NH3-SCR reaction conditions. Further combining in situ IS with diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) allows us to monitor the dynamics of other mobile species involved in NH3-SCR catalysis, for example ammonium ion (NH4+) intermediates resulting from the redox of metal active sites.