 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleNon-noble metals as activity sites for ORR catalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs)
Jinjing
Tao
ab,
Xian
Wang
*ab,
Mingjun
Xu
ab,
Changpeng
Liu
 ab,
Junjie
Ge
ab,
Junjie
Ge
 *ab and
Wei
Xing
*ab and
Wei
Xing
 *ab
*ab
aState Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Jilin Province Key Laboratory of Low Carbon Chemistry Power, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022, China. E-mail: xwang@ciac.ac.cn; xingwei@ciac.ac.cn
bSchool of Applied Chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026, China. E-mail: gejunjie@ustc.edu.cn
First published on 20th April 2023
Abstract
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) have great potential to become the next generation green energy technique, but their application is limited by the slow kinetics of the cathode oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in acidic medium. Meanwhile, the high price of Pt-based catalysts, which are now widely used commercially, has raised the cost of PEMFCs. Therefore, non-noble metal ORR catalysts as alternatives to Pt-based group metals (PGM) have attracted much attention. However, there is still a big gap between the performance of non-noble metal catalysts and commercial Pt/C catalysts in acidic environment. Recently, it has been realized that the performance of catalysts is closely related to the structure of catalytically active sites. Inspired by this, in this review, we firstly introduced the development and breakthrough of non-noble metals as activity sites. We then briefly summarized their catalytic mechanisms, and put forward some suggestions on how to improve the activity and stability of non-noble metal ORR catalysts.
Keywords: ORR; Non-noble metal single atom catalysts; Active site; Fuel cell.
1 Introduction
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) can easily convert hydrogen energy to electricity without igniting, which has been widely studied because of its advantages of high energy conversion efficiency, no pollution, low noise and strong endurance.1 PEMFCs consist of two half reactions, i.e., the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR), respectively. The kinetics of the ORR at the cathode is much slower than that of the HOR at the anode. Therefore, it is essential to improve the ORR kinetics for promoting fuel cell performance.2 Commercial Pt-based catalysts are widely used in the cathodic ORR, however, their high price and low abundance lead to high catalyst cost and thereby limit the commercialization of PEMFCs. In order to meet the application requirements of PEMFCs, ORR catalysts that are highly efficient, stable, and low-cost (PGM-free) for use in acidic environments are urgently needed.3Macrocyclic-derived catalysts, as an alternative to Pt based catalysts, have been studied intensively since 1964, when Jasinski initially found phthalocyanine cobalt as a kind of macrocyclic compound showing promising activity toward the ORR.4 In the past few decades, non-noble metal-based catalysts have made tremendous progress towards the ORR. However, there is still a gap between non-noble metal catalysts and commercial Pt/C catalysts in terms of catalytic activity and stability, especially in the acid medium.3 Non-noble metals can be mainly divided into transition-group metals and main-group (s-block and p-block) metals. Generally, the outer electrons of the main-group metals are non-delocalized, so they lack the combination of empty and filled host-orbitals for multi-electron catalysis, resulting in poor catalytic activity.5 The atomic structure of transition-group metals, however, can provide unoccupied orbitals or lone pair electrons to reactants, which can successfully lower the activation energy and facilitate the reaction.2 To this end, great efforts have been devoted to transition metal catalysts. The major concern for non-noble metal catalysts is how to improve the catalytic activity and stability, which makes the catalyst's active site structure a key point to study. In the past few years, there has been an explosion of interest in non-noble metal carbide,6,7 nitride,8,9 oxide,10–12 and phosphide.13 However, the highest catalytic activity and most widely studied type is M–N–C, which is prepared by high temperature pyrolysis of carbon precursors containing nitrogen and metals.14,15
There are some effective approaches to enhance the activities of M–N–C catalysts for the ORR in the current study: (1) regulating the local coordination structure of center metals; (2) doping heteroatoms to adjust the electronic structures of active sites; (3) introducing bimetallic or polymetallic sites; (4) creating more defective-edge M–N–C; (5) increasing exposure of active sites and so on.3 Herein, we firstly summarized the recent work on the activity sites of non-noble metal catalysts for the acid ORR. Then, we discussed the design and construction of different activity sites and the catalytic mechanisms of these sites in acid medium. We finally concluded with a few suggestions about constructing effective activity sites to facilitate activity and stability for the ORR.
2 Mechanism of acid ORR
The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is a complex process that involves multielectron transfer. Nowadays, the ORR reaction paths are mainly divided into the four-electron pathway and two-electron pathway, as shown in Fig. 1.16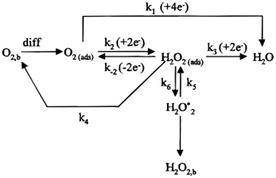 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the ORR process under acid conditions.16 | ||
The related reaction equation is as follows:
Four-electron pathway:
| O2 + 4H+ + 4e− → 2H2O | (1) |
Two-electron pathway:
| O2 + 2H+ + 2e− → H2O2 | (2) |
| H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e− → 2H2O | (3) |
| 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 | (4) |
For the above two reaction pathways, it is obvious that the two-electron pathway may produce hydrogen peroxide, which can destroy the stability of the catalysts and further reduce the reaction efficiency.2 In the four electron pathway, the ORR process mainly consist of the following elemental reactions (* represents the catalytically active site):17
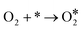 | (5) |
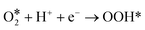 | (6) |
| OOH* + H+ + e− → H2O + O* | (7) |
| O* + H+ + e− → OH* | (8) |
| OH* + H+ + e− → H2O + * | (9) |
The whole process includes transfer and coupling of four electrons and four protons, activation and desorption of many reaction intermediates (such as 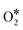 , OOH*, O*, and OH*). Generally, we call the slowest step in a reaction the rate determining step (RDS). Different catalysts with different coordination environments will show different RDS. As shown in Fig. 2, the center FeN4 model and defective-edge FeN4 model were proposed for DFT calculations (Fig. 2a and b). It clearly shows that several steps are endothermic at the equilibrium potential (U = 1.23 V), and the highest endothermic energy is the formation of OH* for the center FeN4 model, implying that the RDS is the third electron-transfer step (O* + H+ + e− → OH*). By contrast, the last electron-transfer step (OH* + H+ + e− → H2O + *) is the RDS for the defective-edge FeN4 model.18
, OOH*, O*, and OH*). Generally, we call the slowest step in a reaction the rate determining step (RDS). Different catalysts with different coordination environments will show different RDS. As shown in Fig. 2, the center FeN4 model and defective-edge FeN4 model were proposed for DFT calculations (Fig. 2a and b). It clearly shows that several steps are endothermic at the equilibrium potential (U = 1.23 V), and the highest endothermic energy is the formation of OH* for the center FeN4 model, implying that the RDS is the third electron-transfer step (O* + H+ + e− → OH*). By contrast, the last electron-transfer step (OH* + H+ + e− → H2O + *) is the RDS for the defective-edge FeN4 model.18
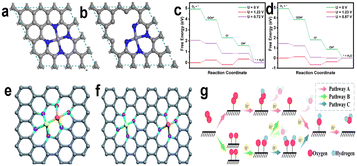 | ||
| Fig. 2 Model structures used in theoretical studies: (a) center and (b) defective-edge FeN4 structures. ORR free-energy diagrams of the (c) center and (d) defective-edge FeN4 structures.18 Model structure of dual-metal catalysts: (e) bonded dual-metal catalysts and (f) non-bonded dual-metal catalysts.19 (g) Schematic diagram of the reaction pathway of dual-metal catalysts.20 | ||
In recent years, in addition to single metallic catalysts, dual-metal catalysts have gradually shown their importance because of their excellent catalytic properties. Dual-metal catalysts can be further subdivided into: bonded dual-metal catalysts and non-bonded dual-metal catalysts. As shown in Fig. 2e and f,19 the former refers to the fact that the two metals are close enough to form a metal pair, and then coordinate with the surrounding N atoms, which can also be called dual-atomic catalysts (DACs). The latter shows that the two metals are coordinated with N atoms respectively, and the distance between the two metals is far to form metal bonds. Since the configuration of the latter can be simply seen as the combination of two single-metal sites, its reaction mechanism is similar to the mechanism described above. Next, we will focus on the reaction mechanism of bonded dual-metal catalysts. Due to the unique configuration of DACs, three different O2 adsorption models have been formed, which can be roughly divided into: associative adsorption models (end-on and side-on) and dissociative adsorption models (O2 decomposes). And it has been found that the adsorption model of oxygen largely determines the reaction pathway of the ORR and even affects the catalytic performance of the catalysts; the schematic diagram of the reaction pathway is shown in Fig. 2g.20 Obviously, in pathway A, a metal more likely acts as the main active center, while paths B and C show two metals participating in the reaction as active centers at the same time. This involves two reaction mechanisms, modulation mechanism and cooperation mechanism. In the modulation mechanism, one metal in the bimetallic acts as the active center, and the other metal only regulates the electronic structure of the active center. In the cooperation mechanism both metals can adsorb the relevant reaction intermediates, which is expected to break the scaling relationship and exceed the theoretical upper limit of electrocatalytic activity.21
Actually, according to the Sabatier principle, ideal catalysts should have a moderate binding energy to the reaction intermediates, which is neither too strong nor too weak. For the ORR, when the adsorption of the active sites to the intermediates is too weak, the proton and electron transfer of oxygen molecules will be restricted. However, if the adsorption is too strong, the product water molecules will closely bond with active sites and prevent oxygen molecules from further adsorption.22 Some research has demonstrated that the relationship between the catalytic activity of various metals for the ORR and the binding energy of oxygen atoms is represented by a “volcanic plot” curve. Pt locates near the peak of the volcanic plot, which exhibited much better catalytic performance than other non-noble metals for the ORR (Fig. 3a).23Fig. 3b shows the volcanic curve of single transition metals supported on graphene to form M–N–C catalytically active sites. The φ, as shown in Fig. 3b, is a descriptor that represents the free-energy for OOH*, O*, and OH* adsorption.24 The calculation results well matched the experimental results that Fe coordinated with four pyridine N possesses better performance than other transition metals. It further proves that the coordination environment has a great influence on the adsorption energy of intermediates, used for reasonably selecting and designing active sites. Similarly, there is a corresponding volcanic curve relationship for dual-metal catalysts. However, it should be clear that for the same bimetallic catalyst, the catalytic activity of the ORR is related to the choice of ORR pathway. From Zhou et al.'s theoretical research on bimetallic oxygen reduction catalysts, they selected two typical active site structures of DACs as simulation objects, and their structural diagrams are shown in Fig. 3c. From the theoretical calculation results, it is found that path C has the smallest limiting potential of 0.03 V by comparing the three reaction paths above (Fig. 3d–f), suggesting that path C is the most thermodynamically active. In addition, for the same bimetallic catalyst such as FeCoNC-4, it presents different overpotentials in path A and path B, which proves that the selection of reaction pathway is important for catalyst activity. Theoretical simulation calculation can help us understand the reaction mechanism simply, and can guide us to quickly design and manufacture catalysts with excellent performance.
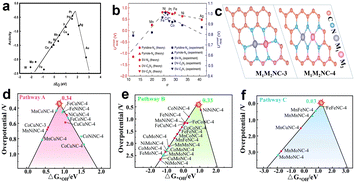 | ||
| Fig. 3 Volcanic plot relationship (a) between oxygen reduction activity and oxygen binding energy for various metals23 and (b) between theoretical and experimental onset potentials (UonsetRHE) versus the descriptor φ for single TM atoms supported on graphene.24 (c) Structural diagrams of M1M2NC-3 and M1M2NC-4.20 (d–f) Volcano plots of the three reaction pathways.20 | ||
3 Single metals as catalytically active site centers
In order to replace Pt-based precious metal electrocatalysts, some efficient active sites with non-noble metals as active centers were designed and synthesized. Combining experimental results and theoretical calculation, Fe and Co-doped carbon electrocatalysts are considered to have a greater competitive advantage compared to platinum-group metals (PGM). So, several typical metal active sites are summarized as follows:3.1 Fe as active center
Fe-based catalysts for the ORR in acid medium have been well developed after decades of research. Benefiting from characterization technology, we now have a deeper understanding of the configuration of active sites and catalytic mechanism.Deng et al.25 designed an active and stable catalyst which encapsulated Fe nanoparticles (NPs) into pea-pod like carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to be physically isolated from the acid environment to avoid leaching. The microstructure of the catalyst is shown in Fig. 4a. Even though Fe nanoparticles are wrapped by several layers of carbon sheets, the electrons can transfer from Fe to carbon, which contributes to the decrease of the local work function and strengthens the catalytic activity of the outer CNT shell to promote oxygen reduction.26 However, there are some questions that need to be solved for this type of catalyst, i.e., which are the real active sites and to what level do those active sites contribute to catalysis? These questions are valid because there are always small amounts of nitrogen and defect vacancies doped into the carbon matrix in the synthesized catalyst. According to previous studies, it can be confirmed that pyridine N and vacancy-type defects both exhibit an acidic ORR activity.27,28 Besides, some iron nanoparticles existed in the catalyst which also have some catalytic activity. In short, the ORR performance of the Fe3C type of catalyst is the result of multilayer factors and these factors make it difficult to define the specific mechanism of action of the ORR. For example, Sun et al.29 proposed an opposite view that Fe3C has no ORR catalytic activity. According to the above reports, the materials used to synthesize the catalysts all contain nitrogen sources, such as 1,8-diaminonaphthalene (DAN) and cyanamide. It led to the possibility of forming an Fe-based active center with N participating in the active site structure. The hypothesis was made because high-temperature pyrolysis of the coexisting N-containing source, iron salts and carbon substance can produce Fe/N/C catalysts with abundant Fe–Nx/C moieties.30–32 In order to explore the influence of the nitrogen source on catalytic performance, the author synthesized two catalysts with or without cyanamide, denoted as Fe3C–N/CNC and Fe3C/CNC, respectively. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra demonstrated that N species are present in Fe3C–N/CNC but not in Fe3C/CNC (Fig. 4b and c). The ORR performance of the catalysts, as shown in Fig. 4d, clearly shows that Fe3C–N/CNC is much better than Fe3C/CNC. The comparison results indicate that the catalytic activity of pure Fe3C is not good or even inactive, so, there must exist true active sites, i.e. the Fe–Nx/C moieties. Besides, the Fe3C nanoparticles were usually coated by several layers of carbon film, which may hinder the electron transfer from Fe3C to the outermost carbon shell and lead to catalyst inactivation. The different results may be derived from differences in synthesis procedures (i.e. original material, pyrolysis temperature) and the nature and sensitivity of the characterization techniques utilized.32 In conclusion, more theoretical calculations and more advanced material synthesis techniques are needed to better understand and enhance the activity of transition metal carbide-based ORR electrocatalysts.33
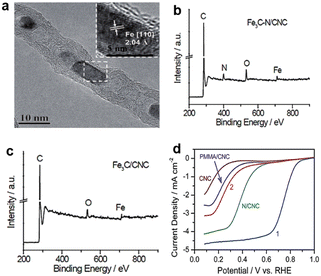 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) image of Pod-Fe with the inset showing the [110] crystal plane of Fe.25 XPS spectra of (b) Fe3C–N/CNC and (c) Fe3C/CNC.29 (d) ORR performance of Fe3C–N/CNC (curve 1) and Fe3C/CNC (curve 2).29 | ||
In the 1980s, Yeager's group produced a catalyst by heat-treating polyacrylonitrile (PAN), carbon (Vulcan XC-27) and cobalt/iron acetate which showed promising ORR activity in both alkaline and acid electrolytes.34 It opens a new way of making ORR catalysts by heat-treating precursors that are composed of the carbon support, nitrogen-containing polymers and metal salts. Since then, the M–N–C type active site has become a hot topic.35 Lefevre et al.36 synthesized a series of catalysts by pyrolyzing precursors between 400 and 1000 °C, with Fe salts adsorbed on the treated carbon matrix. According to the experimental results, two different catalytic sites simultaneously exist in this series of catalysts, i.e., FeN4/C and FeN2/C, and the most representative structures of these sites are FeN4C8 and FeN2C4, respectively. The formation of the different catalyst structures is temperature dependent. When the pyrolysis temperature is between 500 and 700 °C, N4-metal bound to the carbon support is easier to form. By contrast, if the pyrolysis temperature ranges from 700 to 900 °C, the quantity of FeN2/C reaches its maximum, as illustrated in Fig. 5a. The experimental results were measured by Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (ToF SIMS). It was concluded the variation tendency of three families (∑FeN1Cy+, ∑FeN3Cy+ and ∑FeN4Cy+) relative intensity with temperature changes, the author deduced the three families belonging to a catalytic site of the FeN4/C. Fig. 5b shows the possible structure of FeN2/C. The electrochemical performance was evaluated for these catalysts in H2SO4 solution (pH = 1), and the potential Vpr represents the maximum reduction occurring at 0 rpm, as shown in Fig. 5c. It demonstrated that the variation tendency of catalytic activity at different temperatures coincided with the change of relative abundance of FeN2/C. So it can be concluded that FeN2/C is more active than FeN4/C, but theoretical calculations reveal the order of ORR activity follows FeN4 > FeN3 > FeN2 > FeN1 > FeN5.37 The origin of the difference is that the characterization method is not advanced enough, as some experiments all proved that FeN4 is the most promising catalytic site.3 Liu et al.38 used sodium alginate with graphene to immobilize Fe3+ cations into a novel structure of “egg-box” (Fig. 5d); subsequent carbonization caused the formation of a N-doped porous carbon shell to encapsulate Fe2N nanoparticles (NPs). Fig. 5e and f demonstrate that the NPs are Fe2N, which is coated by a N-doped porous carbon shell with an average thickness of ≤5 nm. The catalyst presented an inferior catalytic activity (E1/2, 0.71 V vs. RHE) in 0.1 M HClO4 aqueous solution. After 10.5 h of chronoamperometric test, the initial current density had only 19% loss at 0.5 V vs. RHE in 0.1 M HClO4 electrolyte. Fruehwald et al.39 used a new way to produce a catalyst with FeN3/C acting as the active site. The synthetic methodology is shown in Fig. 5g. This method does not necessitate high-temperature pyrolysis to produce the catalyst, and experimental results show that the catalytic performance of materials with heat treatment was worse than the material without pyrolysis (Fig. 5h). The reason for this phenomenon may be the change of the conformation of the active FeN3/C sites to the inert FeN3+3/C sites, which corresponds with the FeN2 active sites transforming to another construction of FeN2+2 according to a previous report.32
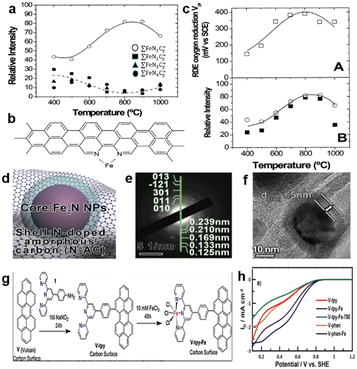 | ||
| Fig. 5 (a) Relative intensity of different ions of active sites as a function of the pyrolysis temperature.36 (b) Possible structure of FeN2/C.36 (c) The relationship between the catalytic activity (A) and the ToF SIMS relative intensity (B) as a function of the pyrolysis temperature.36 (d) The structure diagram of “egg-box”. (e) The SAED pattern.38 (f) The HRTEM of encapsulated Fe2N with thickness shell ≤5 nm.38 (g) Synthetic diagram of synthesis methodology.38 (h) RRDE ring currents of different catalysts in 0.1 M H2SO4 (the number 700 represents the pyrolysis temperature; phen represents phenanthroline as a raw material to produce N2/C sites).39 | ||
According to theoretic prediction and experimental verification, Fe–N–C shows the best catalytic performance among non-noble-metal based catalysts in acid medium.40 Researchers have synthesized many catalysts with high active site density and high activity by choosing different synthetic materials, regulating the morphology of catalysts, and optimizing the experimental parameters. In previous studies, Fe–N–C type catalysts were primarily synthesized by pyrolyzing a mixture which consists of a carbon substrate, nitrogen-rich materials, and iron salts, followed by complicated secondary processing.41 In 2010, Liu et al. started to use metal–organic framework (MOF) derived catalysts for the ORR. Employing MOFs as precursors has three main advantages: (1) the characteristic porosity of MOFs can disperse the active sites uniformly after pyrolysis. (2) The properties can be regulated and controlled through rationally designing the structure and morphology of MOFs. (3) MOFs take metals as nodes and are rich in a large number of uniformly distributed metals. In 2011, Dodelet et al. adopted ZIF-8 as a carbon and nitrogen source.42,43 Since then, ZIF-8 has become the most studied material in ORR non-noble metal based catalysts because Zn is easily volatilized at high temperature and can be eliminated during pyrolysis.44,45 For example, Wang et al.44 prepared a catalyst whose active sites were highly dispersed at the atomic level by doping Fe into ZIF-8 to partially replace Zn ions. They emphasized that an O2-free environment is crucial for improving the ORR performance, because iron is easily oxidized and aggregated in oxygen-containing environments and a uniform Fe distribution can be more easily achieved at an atomic level in inert Ar atmosphere than in air atmosphere (Fig. 6a). Iron is exchanged as an ion with Zn in ZIF-8 in the process of synthesizing precursors. Fe2+and Zn2+ have a similar ion radius (cation radii: Fe2+ 62 pm and Zn2+ 60 pm),46 but Fe3+ has a much smaller radius (49–55 pm), so Fe2+ can readily exchange with Zn2+. Besides, Fe3+ tends to hydrolyze more than Fe2+, which can be confirmed by similar experimental results for detection of Fe(III) oxide/hydroxide in XPS reported in previous studies (Fig. 6b).47,48 The catalyst treated in Ar gas has better catalytic performance, with E1/2 at 0.82 V vs. RHE and H2O2 yield as low as 1%. Unfortunately, the stability is poor, with the E1/2 negatively shifted by 40 mV after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles. Since Zhang and co-workers demonstrated a novel concept, “single-atom electrocatalysts (SACs)”, the high atomic utilization in theory and outstanding catalytic activity of SACs have made them a hot research topic in recent years.49 Owing to their unique electronic structure, SACs offer the chance to design and regulate the active sites to improve the catalytic performance.50 However, traditional synthesis methods have some problems in making SACs: (1) to achieve well-defined single-atom dispersion on the carbon support, the concentration of metal atoms must be extremely low, which means the density of active sites is low. (2) A high-temperature pyrolysis process usually leads to aggregation of metal atoms and production of low activity sites, and increasing the content of metal elements will lead to metal aggregation and the formation of low-activity metal nanoparticle aggregation. (3) In most cases, single-atom metals may be faced with the heterogeneous distribution of active sites and a poorly defined coordination environment.51 After recognizing these issues, great progress thereby has been made in designing Fe-based SACs. For instance, Liu et al.18 synthesized a catalyst with highly dense-FeN4 single-atom sites, as shown in aberration-corrected high-angle annular dark-field scanning TEM (AC HAADF-STEM) (Fig. 6d). The authors developed a clever method that uses the electrostatic interaction between Fe(II)-phenanthroline (positively charged) and poly-dopamine (PDA) chains (negatively charged) to attach Fe(II)-phenanthroline to PDA, forming the PDA/Fe(II)-phenanthroline complex coated ZIF-8 particles. After carbonization, the catalyst with high-density atomically dispersed Fe–N4 sites was achieved, as shown in Fig. 6e. PDA not only suppresses the formation of Fe-based aggregates, but also facilitates the formation of meso/macropores, creating abundant defective edge and Fe–N4 sites for the carbon matrix. Atomically dispersed Fe atoms can also be validated by Fourier-transformed extended X-ray absorption fine structure (FT-EXAFS) characterization (Fig. 6f). And the catalyst exhibits catalytic performance (E1/2, 0.828 V vs. RHE) which is comparable to commercial Pt/C in 0.1 M HClO4. Besides, there are many other methods to accomplish catalysts for single-atom dispersion of Fe–N4, such as the silica-protected strategy to realize extraordinary utilization efficiency of Fe,52 poly(acrylic acid–maleic acid) (P(AA–MA)) copolymer as a chelating agent to chelate with Fe(III) to inhibit iron aggregation,14 dual melt-salt-mediated template method to avoid rapid loss of nitrogen during pyrolysis and improve Fe–N4 single-atom site density,53 and so on.54–56
000 cycles. Since Zhang and co-workers demonstrated a novel concept, “single-atom electrocatalysts (SACs)”, the high atomic utilization in theory and outstanding catalytic activity of SACs have made them a hot research topic in recent years.49 Owing to their unique electronic structure, SACs offer the chance to design and regulate the active sites to improve the catalytic performance.50 However, traditional synthesis methods have some problems in making SACs: (1) to achieve well-defined single-atom dispersion on the carbon support, the concentration of metal atoms must be extremely low, which means the density of active sites is low. (2) A high-temperature pyrolysis process usually leads to aggregation of metal atoms and production of low activity sites, and increasing the content of metal elements will lead to metal aggregation and the formation of low-activity metal nanoparticle aggregation. (3) In most cases, single-atom metals may be faced with the heterogeneous distribution of active sites and a poorly defined coordination environment.51 After recognizing these issues, great progress thereby has been made in designing Fe-based SACs. For instance, Liu et al.18 synthesized a catalyst with highly dense-FeN4 single-atom sites, as shown in aberration-corrected high-angle annular dark-field scanning TEM (AC HAADF-STEM) (Fig. 6d). The authors developed a clever method that uses the electrostatic interaction between Fe(II)-phenanthroline (positively charged) and poly-dopamine (PDA) chains (negatively charged) to attach Fe(II)-phenanthroline to PDA, forming the PDA/Fe(II)-phenanthroline complex coated ZIF-8 particles. After carbonization, the catalyst with high-density atomically dispersed Fe–N4 sites was achieved, as shown in Fig. 6e. PDA not only suppresses the formation of Fe-based aggregates, but also facilitates the formation of meso/macropores, creating abundant defective edge and Fe–N4 sites for the carbon matrix. Atomically dispersed Fe atoms can also be validated by Fourier-transformed extended X-ray absorption fine structure (FT-EXAFS) characterization (Fig. 6f). And the catalyst exhibits catalytic performance (E1/2, 0.828 V vs. RHE) which is comparable to commercial Pt/C in 0.1 M HClO4. Besides, there are many other methods to accomplish catalysts for single-atom dispersion of Fe–N4, such as the silica-protected strategy to realize extraordinary utilization efficiency of Fe,52 poly(acrylic acid–maleic acid) (P(AA–MA)) copolymer as a chelating agent to chelate with Fe(III) to inhibit iron aggregation,14 dual melt-salt-mediated template method to avoid rapid loss of nitrogen during pyrolysis and improve Fe–N4 single-atom site density,53 and so on.54–56
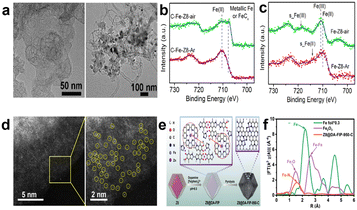 | ||
| Fig. 6 (a) TEM images of C–Fe-Z8-Ar (left) and C–Fe-Z8-air (right).44 (b) High resolution Fe 2p XPS spectra of C–Fe-Z8-Ar and C–Fe-Z8-air.44 (c) XPS spectra of Fe-Z8-Ar and Fe-Z8-air (without carbonization).44 (d) AC HAADF-STEM images of Z8@DA-FIP-950-C.18 (e) Illustration of the synthesis of Z8@DA-FIP-950-C.18 (f) FT Fe K-edge EXAFS spectra of Z8@DA-FIP-950-C and references.18 | ||
Although these active sites all displayed ORR catalytic performance under certain test conditions, there is still a big gap from practical application of these catalysts. Is there a better catalytic activity when two or more active sites combined their action? A number of studies have confirmed that the synergistic effect between the Fe-based nanoparticles and Fe–Nx configuration can profoundly affect the electron-density distribution of Fe atoms in the center of active sites, which is good for oxygen adsorption and further enhancing the catalytic activity.57 For example, transition-metal oxides have been studied as electrocatalysts because of their low-cost and chemical stability.58 Wang et al.59 synthesized a nanofiber catalyst which uniformly distributed Fe2O3/FeNx active sites (Fig. 7). It clearly demonstrates that Fe2O3 and metallic Fe were absent in the catalyst. According to the Fourier transform Fe k3-weighted EXAFS (FT-EXAFS) spectra of Fe2O3/FeNx@CNF, the fitting results show that the ratio of N to Fe atoms was 1.8 and O to Fe atoms was 0.2, indicating that the most likely active site of the structure was FeN2 surrounded by iron oxides. The electrocatalytic performance of the catalyst is much better in alkaline solution than in acid medium, whose E1/2 is 0.86 V vs. RHE. And the stability is noteworthy due to negligible decay of E1/2 which was only 10 mV after 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles. In short, the synergistic effect between Fe2O3 and FeNx has a certain impact on the catalytic activity, but the poor performance may be related to the weak conductivity and oxygen adsorption capacity of Fe2O3. Xu et al.60 used a cooperative protection strategy to create a catalyst which highly dispersed hyperfine Fe3C nanodots and abundant Fe–Nx sites (Fe-Nx/Fe3C@NC). Similarly, Fe3C nanoparticles are also wrapped by carbon layers as shown in Fig. 7d. The catalyst exhibits an inferior ORR activity; the E1/2 is only 0.72 V in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. The synergistic effect can be verified by an acid-leaching catalyst to remove Fe3C nanodots (Fig. 7e) and adding KSCN solution to poison Fe–Nx sites. These experiments demonstrate that Fe–Nx and Fe3C are essential for promoting the ORR activity. Fe3C nanoparticles do not directly participate in the ORR, but they can transfer electrons to the outer graphene shell, thus promoting the activation of oxygen molecules. Although the activity is not good for Fe–Nx/Fe3C@NC, it has excellent stability that the current density remained 94% after 20
000 cycles. In short, the synergistic effect between Fe2O3 and FeNx has a certain impact on the catalytic activity, but the poor performance may be related to the weak conductivity and oxygen adsorption capacity of Fe2O3. Xu et al.60 used a cooperative protection strategy to create a catalyst which highly dispersed hyperfine Fe3C nanodots and abundant Fe–Nx sites (Fe-Nx/Fe3C@NC). Similarly, Fe3C nanoparticles are also wrapped by carbon layers as shown in Fig. 7d. The catalyst exhibits an inferior ORR activity; the E1/2 is only 0.72 V in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. The synergistic effect can be verified by an acid-leaching catalyst to remove Fe3C nanodots (Fig. 7e) and adding KSCN solution to poison Fe–Nx sites. These experiments demonstrate that Fe–Nx and Fe3C are essential for promoting the ORR activity. Fe3C nanoparticles do not directly participate in the ORR, but they can transfer electrons to the outer graphene shell, thus promoting the activation of oxygen molecules. Although the activity is not good for Fe–Nx/Fe3C@NC, it has excellent stability that the current density remained 94% after 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 s of chronoamperometric test (Fig. 7f), which can be attributed to Fe3C nanoparticles. It has been reported that crystalline Fe3C can improve the graphitization degree of the carbon matrix and effectively mitigate carbon corrosion.61,62 Liu et al.62 heat-treated twice the iron-containing precursors in NH3 atmosphere to make a catalyst which includes two types of active sites namely FeNx and Fe2N, which can be labeled as Fe–N–C/HPC-NH3, and the morphology of the catalyst is shown in Fig. 7g. NH3 heat-treatment not only promoted the formation of the Fe2N nanoparticles, but also increased the porosity and surface area that facilitate the mass transport of reactants and products, further improving the ORR activity. The ORR activity of Fe–N–C/HPC-NH3 was evaluated in 0.1 M HClO4 solution, the E1/2 is 0.803 V and Jm is 1.98 A g−1. In order to investigate the role of Fe2N nanoparticles, they put the catalyst in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution at 80 °C for 12 h to remove Fe2N, and the E1/2 has shifted negatively by 21 mV (Fig. 7h). Besides, DFT calculations were also used to verify that Fe2N can boost the ORR activity of FeNx moieties, with results shown in Fig. 7i. An energy barrier of 0.74 eV needs to be overcome for FeN4–Fe2N at 1.23 V, which is lower than the single active site of FeN4 or Fe2N. This well explains the existence of Fe2N which lowers the reaction free energy and strengthens the ORR activity of FeN4.
000 s of chronoamperometric test (Fig. 7f), which can be attributed to Fe3C nanoparticles. It has been reported that crystalline Fe3C can improve the graphitization degree of the carbon matrix and effectively mitigate carbon corrosion.61,62 Liu et al.62 heat-treated twice the iron-containing precursors in NH3 atmosphere to make a catalyst which includes two types of active sites namely FeNx and Fe2N, which can be labeled as Fe–N–C/HPC-NH3, and the morphology of the catalyst is shown in Fig. 7g. NH3 heat-treatment not only promoted the formation of the Fe2N nanoparticles, but also increased the porosity and surface area that facilitate the mass transport of reactants and products, further improving the ORR activity. The ORR activity of Fe–N–C/HPC-NH3 was evaluated in 0.1 M HClO4 solution, the E1/2 is 0.803 V and Jm is 1.98 A g−1. In order to investigate the role of Fe2N nanoparticles, they put the catalyst in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution at 80 °C for 12 h to remove Fe2N, and the E1/2 has shifted negatively by 21 mV (Fig. 7h). Besides, DFT calculations were also used to verify that Fe2N can boost the ORR activity of FeNx moieties, with results shown in Fig. 7i. An energy barrier of 0.74 eV needs to be overcome for FeN4–Fe2N at 1.23 V, which is lower than the single active site of FeN4 or Fe2N. This well explains the existence of Fe2N which lowers the reaction free energy and strengthens the ORR activity of FeN4.
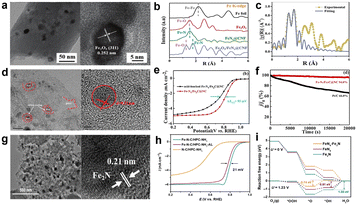 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a) TEM and HRTEM images of Fe2O3/FeNX@CNF.59 (b) XRD patterns.59 (c) FT-EXAFS spectra.59 (d) TEM and HETEM images of Fe–Nx/Fe3C@NC.60 (e) ORR polarization curves of Fe–Nx/Fe3C@NC and acid-leached Fe–Nx/Fe3C@NC.60 (f) Chronoamperometric curves of Fe–Nx/Fe3C@NC and 20 wt% Pt/C catalysts.60 (g) TEM images of Fe–N–C/HPC-NH3 and HRTEM image of the nanoparticle in Fe–N–C/HPC-NH3.62 (h) ORR polarization curves.62 (i) Energy profiles for the ORR over different catalytic sites.62 | ||
Moreover, Liu et al.63 synthesized a series of catalysts with close content of FeNx moieties but different contents of Fe NPs by heating different amounts of iron salts that were doped into pre-carbonized ZIF-8, which were labeled as Fe–N–C-100/300/500, respectively, with the number representing the amount of iron salt added. The morphology of Fe–N–C-300 is shown in Fig. 8a, and those marked with yellow circles represent atomically dispersed Fe atoms. The presence of Fe nanoparticles can be confirmed by XRD and scanning electron microscopy (SEM)/TEM characterization (Fig. 8a and b). The density of FeNx on the catalyst surface was detected by XPS and the total content of Fe determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES); the results are shown in Fig. 8c. It shows that FeNx contents are similar in the three samples, but the contents of Fe NPs have much difference, which led to different ORR performances. Appropriate content of Fe NPs may produce better activity, and the reason may be that (1) the strong interaction between FeNx and Fe NPs modifies the electron structure of active centers, which makes the adsorption energy of the reactants/products suitable. (2) Fe NPs assist FeNx in presenting single atom dispersion, improving the accessibility of FeNx active sites. (3) Excess Fe NPs may block the FeNx active sites and result in deceasing activity.63 However, Chen et al.64 proposed a novel strategy to effectively remove the encapsulated M-NPs by few carbon shells. The acid-leaching method can only remove the exposed M-NPs without carbon encapsulation, but these M-NPs are wrapped by single or few-layers which can't be removed during acid leaching and it is supposed to be active for the ORR. Therefore, it leads to an inability to accurately judge the role of various active sites. So, they used NH4Cl-treatment to etch out encapsulated M-NPs without destruction of co-existing M–Nx sites. HRTEM showed that the carbon layers of encapsulated Fe-NPs range from single to multiple-layers, but only more than six carbon layer encapsulated Fe-NPs can survive after NH4Cl-treatment (Fig. 8d and e). Previous theoretical simulations have verified that only less than three or four carbon layers could be modulated by encapsulated M-NPs and enhance the ORR performance.65,66 Even though there are some Fe-NPs in the catalyst after NH4Cl-treatment, the recovered Fe-NPs have no ORR activity, so the real catalytic role of M-NPs and M–NX sites in the ORR can be observed. Fig. 8f shows that the E1/2 positively shifted by 25 mV after NH4Cl treatment, implying that the effect of the encapsulated Fe-NPs was negligible, or even impeded the ORR performance of Fe–Nx sites when there are too many iron nanoparticles in the catalyst. They further researched the mechanism of NH4Cl-treatment promoting the ORR activity enhancement. Fig. 8g demonstrated that NH4Cl-treatment would not provide addition nitrogen to form new Fe–Nx sites, but it can remove some M-NPs to improve the specific surface area from 393 to 495 m2 g−1 and result in more exposed Fe–Nx active sites per unit of mass.
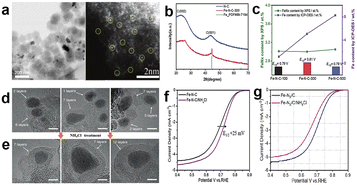 | ||
| Fig. 8 (a) TEM and HAADF-STEM image of Fe–N–C-300.63 (b) XRD patterns of the N–C and Fe–N–C-300 catalysts.63 (c) The data for FeNx and Fe content by XPS and ICP-OES detection, respectively, and E1/2 of Fe–N–C-100/300/500.63 HRTEM images of (d) the pristine Fe–N–C catalyst and (e) after NH4Cl-treatment Fe–N–C catalyst. ORR polarization plots of (f) the pristine and NH4Cl-treated Fe–N–C.64 (g) NP-free Fe–Nx/C before and after the NH4Cl treatment.64 | ||
There are many studies reporting that multiplex heteroatom-doped carbon-based catalysts can improve electrocatalytic activity for the ORR.50,51,67 The light heteroatoms in the nitrogenous carbon matrix, such as O, P, S and B with their suitable electron-donating properties, can generate a potential synergistic effect, which will change the electronic structure of the central metal and regulate the interaction between the metal sites and the ORR intermediates. Li and colleagues synthesized a N, S co-doped carbon-supported catalyst which presented Fe single-atom distribution by pyrolysis of the polyaniline hydrogels containing uniformly distributed Fe precursors.68 The high-resolution S 2p spectrum of N, S co-doped CPANI–TA–Fe Fe-SA-NC catalysts is shown in Fig. 9a, which shows two major peaks corresponding to C–S–C (S 2p3/2 at 163.8 eV and S 2p1/2 at 164.8 eV) and C–SOx–C (168.13 eV) respectively; there is also a weak peak for S![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–N. Previous studies have confirmed that the presence of C–S–C and S
C–N. Previous studies have confirmed that the presence of C–S–C and S![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–N species can enhance the ORR activity.69,70 But for the real coordination environment of Fe atoms in N, S co-doped CPANI–TA–Fe Fe-SA-NC catalysts, EXAFS spectroscopy can give the evidence (Fig. 9b). The simulation of the EXAFS reveals that Fe coordinates with four N atoms from the plane and two O atoms from the axial direction (Fig. 9c). The formation of this configuration is due to the chelation between Fe3+ and the hydroxyl groups (OH−) of tannic acid, and O atoms further coordinate with the Fe–N4 moiety to form Fe–O bonds with bridging O2. N, S co-doped CPANI–TA–Fe Fe-SA-NC exhibited a competitive catalytic activity (E1/2, 0.807 V), which can be attributed to the strongly electron-withdrawing N atoms changing the electronic structure of the N-doped carbon materials, making C atoms which are around the N atoms positively charged and promoting the adsorption of oxygen by the catalyst. At the same time, electrons are more easily transferred from the catalyst to the adsorbed oxygen, thereby weakening the oxygen–oxygen bond.71 Besides, doped S atoms can cause reconstruction of the charge density and spin density of C atoms, and these C atoms with high positive charge density or spin density can serve as catalytically active sites.72 Some studies demonstrated that the second shell coordination atoms can also impact the electronic structure of Fe–N–C active centers and improve the ORR activity.73 Yin and colleagues74 synthesized a catalyst with edge-type FeN4P2 sites, as shown in Fig. 9d. The charge density around FeN4 would be changed after introducing P atoms into the carbon-based matrix and the adsorption energy of intermediates regulated. FT-EXAFS curves show that no apparent peaks of Fe–Fe coordination (2.20 and 4.42 Å) have been found (Fig. 9e), confirming the iron single-atom distribution. Fig. 9e shows the Raman spectra of Fe–N–C–P/N, P–C and Fe–N–C/N–C; the D band (1350 cm−1) and G band (1585 cm−1) represent the degree of defect and graphitization of the carbon substrate, respectively. The value of ID/IG for Fe–N–C–P/N, P–C is higher than Fe–N–C/N–C, which revealed that the introduction of P created more defects. Besides, Fe–N–C–P/N, P–C has a smaller C–N content by comparing the results of XPS with Fe–N–C/N–C. Combining the experiments, doping P can help form single-atom Fe and generate more edge FeN4 moieties. Moreover, the DFT calculations reveal that the edge-type FeN4P2 site is more active than in-plane type FeN4P2. Similarly, Liu et al.75 synthesized a N, S-co-doped hierarchically ordered porous catalyst (FeSA/NSC) using thiourea as a sulfur source and dopamine as a nitrogen source. The active site construction of FeSA/NSC was confirmed by DFT calculations and EXAFS spectra (Fig. 9g), which attests that Fe only coordinates with N atoms, not with S atoms. The schematic diagram of the structure is shown in Fig. 9h, where Fe is the center atom, four N atoms are in the first coordination shell and two S atoms are in the second shell. Thiourea was introduced as a S source and nitrogen source to anchor more Fe atoms and increase the active site density. Besides, thiourea plays a pivotal role in improving the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and constructing the hierarchically ordered porous carbon structure during the process of high-temperature pyrolysis. The BET surface area of FeSA/NSC (1224.03 m2 g−1) is much higher than that of Fe/NC-UI (1091.34 m2 g−1) synthesized without a S source. Moreover, FeSA/NSC exhibits a wider pore size distribution than other catalysts (Fig. 9i), and the hierarchically porous structure is beneficial for boosting the performance of the ORR. It can be attributed to the fact that thiourea could break down and produce a large number of bubbles in the pyrolysis process. In summary, the introduction of sulfur atoms can tune the coordination environment of Fe–N4 and improve the catalytic activity. Besides, other heteroatoms (such as F and B) doped in the nitrogen-containing carbon support can also change the electronic structure of active sites, which benefits the ORR.76–79
C–N species can enhance the ORR activity.69,70 But for the real coordination environment of Fe atoms in N, S co-doped CPANI–TA–Fe Fe-SA-NC catalysts, EXAFS spectroscopy can give the evidence (Fig. 9b). The simulation of the EXAFS reveals that Fe coordinates with four N atoms from the plane and two O atoms from the axial direction (Fig. 9c). The formation of this configuration is due to the chelation between Fe3+ and the hydroxyl groups (OH−) of tannic acid, and O atoms further coordinate with the Fe–N4 moiety to form Fe–O bonds with bridging O2. N, S co-doped CPANI–TA–Fe Fe-SA-NC exhibited a competitive catalytic activity (E1/2, 0.807 V), which can be attributed to the strongly electron-withdrawing N atoms changing the electronic structure of the N-doped carbon materials, making C atoms which are around the N atoms positively charged and promoting the adsorption of oxygen by the catalyst. At the same time, electrons are more easily transferred from the catalyst to the adsorbed oxygen, thereby weakening the oxygen–oxygen bond.71 Besides, doped S atoms can cause reconstruction of the charge density and spin density of C atoms, and these C atoms with high positive charge density or spin density can serve as catalytically active sites.72 Some studies demonstrated that the second shell coordination atoms can also impact the electronic structure of Fe–N–C active centers and improve the ORR activity.73 Yin and colleagues74 synthesized a catalyst with edge-type FeN4P2 sites, as shown in Fig. 9d. The charge density around FeN4 would be changed after introducing P atoms into the carbon-based matrix and the adsorption energy of intermediates regulated. FT-EXAFS curves show that no apparent peaks of Fe–Fe coordination (2.20 and 4.42 Å) have been found (Fig. 9e), confirming the iron single-atom distribution. Fig. 9e shows the Raman spectra of Fe–N–C–P/N, P–C and Fe–N–C/N–C; the D band (1350 cm−1) and G band (1585 cm−1) represent the degree of defect and graphitization of the carbon substrate, respectively. The value of ID/IG for Fe–N–C–P/N, P–C is higher than Fe–N–C/N–C, which revealed that the introduction of P created more defects. Besides, Fe–N–C–P/N, P–C has a smaller C–N content by comparing the results of XPS with Fe–N–C/N–C. Combining the experiments, doping P can help form single-atom Fe and generate more edge FeN4 moieties. Moreover, the DFT calculations reveal that the edge-type FeN4P2 site is more active than in-plane type FeN4P2. Similarly, Liu et al.75 synthesized a N, S-co-doped hierarchically ordered porous catalyst (FeSA/NSC) using thiourea as a sulfur source and dopamine as a nitrogen source. The active site construction of FeSA/NSC was confirmed by DFT calculations and EXAFS spectra (Fig. 9g), which attests that Fe only coordinates with N atoms, not with S atoms. The schematic diagram of the structure is shown in Fig. 9h, where Fe is the center atom, four N atoms are in the first coordination shell and two S atoms are in the second shell. Thiourea was introduced as a S source and nitrogen source to anchor more Fe atoms and increase the active site density. Besides, thiourea plays a pivotal role in improving the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and constructing the hierarchically ordered porous carbon structure during the process of high-temperature pyrolysis. The BET surface area of FeSA/NSC (1224.03 m2 g−1) is much higher than that of Fe/NC-UI (1091.34 m2 g−1) synthesized without a S source. Moreover, FeSA/NSC exhibits a wider pore size distribution than other catalysts (Fig. 9i), and the hierarchically porous structure is beneficial for boosting the performance of the ORR. It can be attributed to the fact that thiourea could break down and produce a large number of bubbles in the pyrolysis process. In summary, the introduction of sulfur atoms can tune the coordination environment of Fe–N4 and improve the catalytic activity. Besides, other heteroatoms (such as F and B) doped in the nitrogen-containing carbon support can also change the electronic structure of active sites, which benefits the ORR.76–79
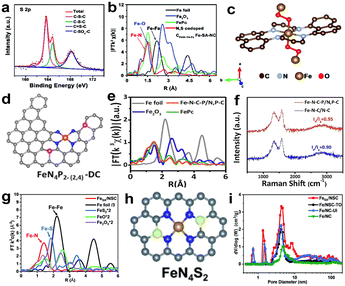 | ||
| Fig. 9 (a) High-resolution XPS spectra of S 2p.68 (b) Magnitudes of k3-weighted Fourier-transformed EXAFS data of Fe atoms.68 (c) The structure of the active site in N, S co-doped CPANI–TA–Fe Fe-SA-NC.68 (d) Schematic diagram of the edge-type FeN4P2 site.74 (e) FT-EXAFS curves of Fe–N–C–P/N, P–C and reference materials.74 (f) Raman spectra of Fe–N–C–P/N, P–C and Fe–N–C/N–C.74 (g) FT-EXAFS spectra of FeSA/NSC and other references.75 (h) Model of FeN4S2.75 (i) Pore size distribution curves of FeSA/NSC and other catalysts.75 | ||
3.2 Co as active center
Although Fe-based catalysts especially Fe–N4 are the most likely alternative to commercial Pt/C, their poor stability is still a big problem that needs to be overcome. The main factor affecting the stability of Fe-based catalysts is the Fe-related Fenton reaction that easily produces strong oxidizing radicals, which can cause carbon support oxidation and destroy Fe–N–C active sites. However, Co-based catalysts with a weak Fenton reaction can readily improve the stability, and the catalytic activity of Co–N–C catalysts is comparable to that of Fe–N–C catalysts, so Co is considered an ideal active center.Yan et al.80 synthesized a bamboo-like carbonitride nanotube catalyst which consists of multi-type active sites, such as encapsulated Co nanoparticles, intercalated CoO species, and Co–Nx coordination sites. Fig. 10a shows the XRD patterns of the CoO@Co–N-bCNT samples synthesized at different temperatures. They proved that melamine would decompose into NH3 and NO2 and at the same time, CoCl2 decomposes and forms cobalt oxides from 300 to 500 °C by using thermal analysis. When the temperature is above 600 °C, the cobalt oxides were restored to metallic Co and the Co catalyzed the decomposition of carbonaceous species to form carbon nanotubes.81–83 The main form of Co atoms in the catalyst is metallic Co, as shown in Fig. 10b. There is a dominant peak at 2.18 Å which demonstrates the Co–Co bond and two weak peaks at 1.53 Å and 1.12 Å, respectively, corresponding to Co–Nx and Co–O structures. Experiments shows that the half-wave potential is positively correlated with the content of Co–Nx sites (Fig. 10c), which demonstrates that Co–Nx sites play pivotal roles in all active sites for the ORR. But the content of Co–Nx sites is unconsidered, which ultimately leads to poor activity. He et al.84 achieved high density atomically dispersed Co doped into the carbon support via a surfactant-assisted metal–organic-framework approach. The surfactant coordinated with Co2+ and Zn2+ to form a protective layer around the surface of ZIF-8, and the surfactant layer first underwent carbonation, forming a carbon shell on the Co-ZIF-8 surface during the pyrolysis. The carbon shell led to a unique confinement effect, which prevented the aggregation of neighboring Co single atoms and mitigated the collapse of internal microporous structures derived from Co-ZIF-8.85,86 The authors proposed a more likely active site structure of CoN2+2 sites as shown in Fig. 10d for the Co–N–C@F127 catalyst. It's not likely that the general CoN4 moiety embedded in intact graphitic layer, CoN2+2 site is a CoN4 moiety bridging over two adjacent armchair graphitic edge. It can be proved by FT-EXAFS fitting results (Fig. 10e), and the fitted Co–N bond length was 1.94 ± 0.2 Å, but according to the theoretical calculations, the Co–N bond length is 1.85 Å and 1.88 Å of CoN4 and CoN2+2 sites, respectively. Besides, DFT calculations were also used to evaluate the possible structure (Fig. 10f). The free energy evolution diagram for CoN2+2 sites shows a downhill trend under a limiting electrode potential of U = 0.73 V, which indicates that CoN2+2 sites are thermodynamically capable of catalyzing the 4e− ORR. But for CoN4 sites, there is an energy barrier that needs to be overcome, and it suggests that CoN4 sites do not follow the four-electron path for the ORR. It can be verified that the Co–N–C@F127 catalyst follows the 4e− reduction pathway by electrochemical testing. So, the above experiments prove that the dominate active sites are CoN2+2. And the Co–N–C@F127 catalyst exhibited an E1/2 of 0.84 V vs. RHE in 0.5 M H2SO4, which is comparable most Fe–N–C catalysts. Moreover, some researchers used appropriate methods to synthesise catalysts with single-atom dispersed high-density CoN4 active sites, which also exhibit good activity in the acid environment.87,88
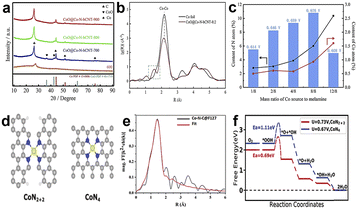 | ||
Fig. 10 (a) XRD patterns of CoO@Co–N-bCNT samples synthesized at different temperatures.80 (b) Co K-edge EXAFS spectra of CoO@Co–N-bCNT-8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 (8 2 (8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 is mass ratio of Co source to melamine) and Co foil.80 (c) Relationship among E1/2, N content and Co content of the CoO@Co–N-bCNT samples.80 (d) Structure of CoN2+2 and CoN4 active sites.84 (e) The fitted spectra of FT-EXAFS for the Co–N–C@F127 catalyst.84 (f) Free energy evolution diagram for the 4e− ORR pathway on the CoN2+2 and CoN4 active sites.84 2 is mass ratio of Co source to melamine) and Co foil.80 (c) Relationship among E1/2, N content and Co content of the CoO@Co–N-bCNT samples.80 (d) Structure of CoN2+2 and CoN4 active sites.84 (e) The fitted spectra of FT-EXAFS for the Co–N–C@F127 catalyst.84 (f) Free energy evolution diagram for the 4e− ORR pathway on the CoN2+2 and CoN4 active sites.84 | ||
Xiao et al.89 firstly detected binuclear Co2Nx sites and eventually confirmed the structure of Co2N5 by DFT calculation; the structure diagram of Co2N5/C is shown in Fig. 11a. The formation of binuclear Co2N5 sites can alter the atomic ratio of Zn/Co in the process of preparing the catalyst. For example, when the atomic ratio is 50, there are only single atom CoNx sites in Co–N–C-50, but for Co–N–C-10 (atomic ratio is 10), there are both single atom CoNx sites and binuclear Co2N5 sites with Co–Co distance at 2.1–2.2 Å, as shown in Fig. 11b. It can be noted that the Co–N coordination peak of Co–N–C-10 positively shifts compared with Co–N–C-50, which reveals that there are no pure CoNx sites in Co–N–C-10, but other sites. There is a special peak at 2.12 Å corresponding to the bimetallic atom structure, consistent with the aberration-corrected STEM in Co–N–C-10. These all confirmed the presence of special Co2N5 sites. The high activity was achieved on Co–N–C-10 with a half-wave potential of 0.79 V, and the catalytic activity of the Co2N5 site is approximately 12 times higher than the conventional CoN4 site by quantifying the atomic percentage of Co particles and simple calculations. This study demonstrated that the high activity of bimetallic sites has potential to further improve the catalytic performance, which inspired further exploration of bimetallic catalysts to improve the catalytic performance. Zhou et al.90 synthesized a single-atom distributed catalyst (CoSA–N–C) with active site structure of Co–N3C, as shown in Fig. 11d. The structure was verified by least-squares EXAFS fitting, the EXAFS fitting coordination number of Co was about 4, and one Co atom was coordinated with three N atoms and one C atom. Cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPc) as a reference also demonstrated that the active site structure in CoSA–N–C isn't like with Co–N4 (Fig. 11e). CoPc has a typical Co–N4 structure, and the characteristic peak is at 1.48 Å, but for CoSA–N–C, the dominant peak is at approximately 1.4 Å; the shorter length of CoSA–N–C can be attributed to the carbon atom replacing the nitrogen atom. The greater activity of Co–N3C sites than Co–N4 sites was proved by DFT calculation. Fig. 11f shows the free energy paths at U = 1.23 V, and the activation energy barrier is 0.94 eV for Co–N4, corresponding to the process of the reduction of *OOH to *O. It's much higher than Co–N3C (0.63 eV) to drive the reduction of *O to *OH, which suggests that Co–N3C can decrease the activation energy barrier of the rate determining step to accelerate the ORR process compared with conventional Co–N4. The linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves show that the E1/2 is 0.79 V of CoSA–N–C, which can compete with Pt/C (0.805 V) in 0.1 M HClO4. Moreover, Iqbal and colleagues91 used a novel strategy without the need for high temperature pyrolysis to synthesize a catalyst with high catalytic performance. The methodology was inspired by a computational study that indicated the pristine 2D metal hexahydroxybenzene framework as catalytic for the ORR in acid media.92 In addition, the pyrolysis method can damage the well-defined structure of the MOF and the pristine 2D MOF is highly conductive.93,94 So, the researchers created a novel cobalt based 2D conjugated MOF catalyst by a hydrothermal reaction, and the resulting catalyst is labeled as Co3(HADQ)2. There is also a novel active site structure of Co(NH)4, as shown in Fig. 11g. The catalyst exhibited good activity and stability, the E1/2 is 0.825 V and the current density degraded by only 5.4% after 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles. The high activity of Co3(HADQ)2 was also confirmed by DFT calculations (Fig. 11h), and the activation energy barrier of the RDS is only 0.37 eV at U = 1.23 V, which is smaller than other active sites. The reasons for the high performance of Co3(HADQ)2 can be summarized in the following aspects: (1) single Co atom distribution. The nearest distance between two Co atoms is 11.01 Å, which ensures that it's impossible for Co atoms to aggregate and improves the utilization ratio of active sites. (2) Porous structure. As shown in Fig. 11g, the pore size of Co3(HADQ)2 is 17.1 Å, and this unique construction increases the chance of the active site contact with the reactants and facilitates the ORR process. (3) High electrical conductivity. Because of the high electron delocalization between the CoN4 motifs, Co3(HADQ)2 is highly conductive as shown in Fig. 11i.
000 cycles. The high activity of Co3(HADQ)2 was also confirmed by DFT calculations (Fig. 11h), and the activation energy barrier of the RDS is only 0.37 eV at U = 1.23 V, which is smaller than other active sites. The reasons for the high performance of Co3(HADQ)2 can be summarized in the following aspects: (1) single Co atom distribution. The nearest distance between two Co atoms is 11.01 Å, which ensures that it's impossible for Co atoms to aggregate and improves the utilization ratio of active sites. (2) Porous structure. As shown in Fig. 11g, the pore size of Co3(HADQ)2 is 17.1 Å, and this unique construction increases the chance of the active site contact with the reactants and facilitates the ORR process. (3) High electrical conductivity. Because of the high electron delocalization between the CoN4 motifs, Co3(HADQ)2 is highly conductive as shown in Fig. 11i.
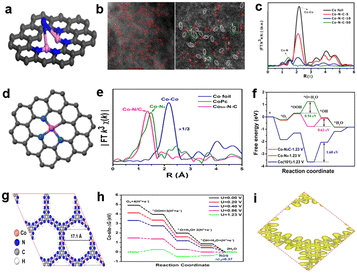 | ||
| Fig. 11 (a) Schematic structure of Co2N5/C, Co(purple), N(blue), C(gray).89 (b) Aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM images of Co–N–C-50 (left) and Co–N–C-10 (right).89 (c) FT-EXAFS spectra.89 (d) Schematic structure of CoSA–N–C, Co(pink), N(blue), C(grey).90 (e) FT-EXAFS curves of CoSA–N–C and references.90 (f) Free energy paths of the ORR on Co–N3C, Co–N4 and Co at U = 1.23 V.90 (g) The structure of Co3(HADQ)2.91 (h) The free energy diagrams of the ORR for Co3(HADQ)2 at different potentials.91 (i) Charge density distribution of Co3(HADQ)2.91 | ||
According to the DFT calculation, Co9S8 has catalytic activity similar to Pt/C via a four-electron pathway for the ORR, which suggests that cobalt sulfides have the potential to replace the commercial Pt/C. From this, Wang and colleagues95 synthesized a novel cobalt sulfide-graphene hybrid electrocatalyst (Fig. 12a). The catalyst was verified as Co1−xS nanoparticles grown on reduced graphene oxide (RGO) (Fig. 12b). Co1−xS acts as a connector to link RGO sheets together, and the Co1−xS/RGO hybrid catalyst forms a conducting network to accelerate the transfer of electrons and facilitate the ORR activity. Furthermore, Wang et al.96 synthesized a dual-shelled Co, N, S co-doped hollow carbon nanocage catalyst which includes Co9S8 nanoparticles, denoted as Co–N/S-DSHCN. There are other active sites except Co9S8, such as Co–Nx and metallic Co nanoparticles coated with several graphitic shells, which can also be proved by advanced characterization techniques and jointly drive the performance improvements for the ORR (Fig. 12c). According to the experiments, S doping can improve the catalytic performance, which can be attributed to the following aspects: (1) doping S into the nitrogen-containing carbon substrate increased the contents of the pyridinic-N, graphitic-N and Co–Nx, as shown in Fig. 12d. The pyridinic-N and Co–Nx are the key factors to reduce the ORR overpotential and graphitic-N has a great influence in limiting the current density, which has reached a broad consensus.97 (2) Doping of S introduces more sulfur-based active sites (Fig. 12e). These two prominent peaks belong to C–S–C (163.6 eV) and high-spin-density C–SOxn− (168.0 eV), and the other weaker peaks intrinsically originate from Co9S8. A previous study has shown that these S-containing species can facilitate the ORR performance.98 Combining the above analysis, Co–N/S-DSHCN is more active than Co–N–C. Some studies proved that the symmetrical planar structure may lead to limited ORR kinetics inhibiting the adsorption and activation of the ORR-related species.99,100 In order to explore better catalytic performance, Chen et al.101 estimated P and S co-doped ORR materials, which exhibited excellent ORR performance by DFT calculations. The result shows that the CoN3PS@PS model exhibits the best ORR performance, as shown in Fig. 12f. The curve shows that the CoN3PS@PS model exhibits the highest activity (η = 0.58 eV) and lowest ΔGO2 (0.02 eV). They then synthesized a catalyst with atomically dispersed Co species and the main active site is CoN3PS; the specific structure of the active site is shown in Fig. 12f. According to the least-squares EXAFS curve-fitting analysis, the number of N, P, and S that coordinate with Co is 3.1, 0.9, and 1.1, respectively, which verifies that the synthetic catalyst contains the CoN3PS moieties. Comparisons between theoretical simulation and experimental results of FT-EXAFS (Fig. 12g) and X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) (Fig. 12h) spectra were also presented. These figures all show that the experimental spectra are in good agreement with the theoretical simulation. As shown in Fig. 12i, the acidic ORR performance of CoN3PS/HC was evaluated, and the E1/2 of CoN3PS/HC similar to commercial Pt/C. But the kinetics current density (JK) of CoN3PS/HC is better than that of Pt/C, suggesting that the CoN3PS/HC catalyst has better kinetic activity than commercial Pt/C.
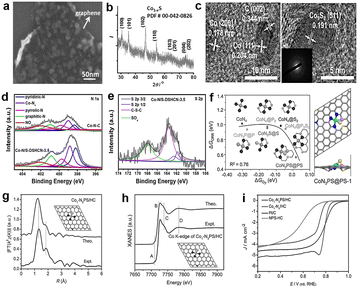 | ||
Fig. 12 (a) High-magnification SEM image of Co1−xS/RGO.95 (b) XRD spectra of Co1−xS/RGO.95 (c) HRTEM of Co–N/S-DSHCN, inset is the corresponding SAED pattern of Co-N/S-DSHCN.96 High-resolution XPS spectra of (d) N 1s. (e) S 2p.96 (f) The relationship between ORR activity (ΔGORR) and 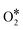 adsorption energy (ΔGO2) at U = 1.23 V and structural model of CoN3PS.101 (g) Comparison between the experimental and theoretically simulated FT-EXAFS spectra of CoN3PS/HC.101 (h) Comparison between the experimental and theoretically simulated XANES spectra of CoN3PS/HC.101 (i) Polarization curves of CoN3PS/HC and references in 0.5 M H2SO4.101 adsorption energy (ΔGO2) at U = 1.23 V and structural model of CoN3PS.101 (g) Comparison between the experimental and theoretically simulated FT-EXAFS spectra of CoN3PS/HC.101 (h) Comparison between the experimental and theoretically simulated XANES spectra of CoN3PS/HC.101 (i) Polarization curves of CoN3PS/HC and references in 0.5 M H2SO4.101 | ||
3.3 Other single-metals as active centers
Although Fe–N–C catalysts reflect excellent ORR activity in acid medium, their stability has always bothered investigators. It seems that Co–N–C catalysts are promising to replace Fe because of their lower Fenton reactivity, but actually the electrocatalytic performance of Co–N–C catalysts is usually inferior to that of Fe–N–C in acid medium. Besides, a big problem for Co–N–C catalysts is that Co-based catalysts tend to produce undesirable hydrogen peroxide by the two-electron transfer pathway. Many studies have reported that the selectivity of Co–N–C catalysts to hydrogen peroxide is more than 90%.102 In fact, the intermediate H2O2 of the two-electron pathway may damage the catalyst and proton exchange membrane, so the two-electron pathway is not expected to happen. Hence, seeking other non-noble metals as active centers is necessary.For example, Li et al.103 synthesized a single atom Mn–N–C catalyst which reached an E1/2 of 0.80 V in 0.5 M H2SO4, owing to the Mn–N4 active sites. The catalyst formed by Cr also has some catalytic activity. Luo et al.104 proposed a Cr–N–C single-atom catalyst where the active site is Cr–N4 configuration, displaying an E1/2 of 0.761 V. It can be seen that the catalysts with transition metal as the active center are mostly studied at present. Besides, recent attempts have been made to study catalysts with main group metals as active centers. However, main group metals are generally considered to have low catalytic activity or even inactive for the ORR. The reason for this is that main group metals lack empty host-orbitals for electrons to occupy, so it's hard for them to participate in the electron transfer process in the catalytic reaction, especially for the ORR which involves multi-electron transfer. The tunable electronic properties of single atom catalysts have provided tunable activities to the main group centers within the bounds of possibility. Liu et al.5 predicted that MgN2C is a promising active site because the MN2C model is located near the top of the volcano map with moderate oxygenated species adsorption strength (Fig. 13a). It can be clearly seen that MN4C (M = Mg, Al, Ca) is located at the left side of the volcano map, which suggests strong adsorption of OH*. The coordination environment can adjust the electron filling of the 3p orbital of Mg centers, as shown in Fig. 13b. It is clear that the p-band center position (εp) of MgN2C sites is the highest and the density of states (DOS) of OH (especially 1π) after interaction with the p-state of Mg is higher, which means weak adsorption and higher catalytic activity. Therefore, main-group metals can also have catalytic properties similar to those of d-band metals by appropriate coordination environment regulation. According to this prediction, they synthesized a catalyst with MgN2C moieties (Fig. 13c), which exhibited good electrocatalyst activity and better stability than Pt/C. Fig. 13d shows the XANES of Mg K-edge curves, and the pre-edge of Mg–N–C coincides with MgPc, which means that the valance state of Mg is between 0 and +2, but the edge of Mg–N–C is left shifted compared to MgPc, suggesting that the coordination number of Mg–N in Mg–N–C should be less than 4. DFT calculation results show MgN1C is unstable and MgN3C is less reactive, so the most likely structure is MN2C. Moreover, Luo et al.105 prepared Sn–N–C which exhibited inferior activity and selectivity for the four-electron reduction pathway to Fe–N–C, but the turn-over frequency (TOF) is similar, which demonstrates that the intrinsic reactivity of Sn–N–C is comparable to that of Fe–N–C (Fig. 13e and f). According to the Fourier-transformed EXAFS spectrum (Fig. 13g), the Sn atom coordinated with four in-plane N atoms and one axial O atom. These research studies demonstrated the main-group metals are likely to be catalytically active centers, which broadens the design idea of non-precious metal catalysts for the ORR.
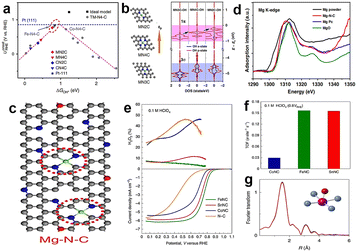 | ||
| Fig. 13 (a) The relationship between the onset potential and ΔGOH* of different catalysts.5 (b) The structure of different Mg–N–C coordination environments which tune the εp of Mg atoms and the corresponding density of state changes of OH after interaction with the p-state of Mg.5 (c) Microstructural diagram of Mg–N–C.5 (d) The XANES of Mg K-edge of Mg–N–C and references.5 (e) The yield of H2O2 (top) and ORR polarization curves of different catalysts (bottom).105 (f) Comparison of TOF values at 0.8 VRHE.105 (g) Fourier-transform EXAFS spectrum of SnNC; the black curve is the experimental spectra and the red curve is the theoretical spectra.105 | ||
4 Dual metals as catalytically active site centers
Since single atomic sites have such good properties, would adding another metal improve their properties? It has been found that the O2 molecule is attached to a single-atom site through the side-on or end-on model. But different from single-metal doping, O2 tends to adsorb on a dual-metal site by the bridge-cis model, thus the strength of the oxygen bond will be weakened.106,107 If dual-metals are introduced, the synergistic catalytic effect between metals can adjust the electronic structure of active sites and further improve the performance for the ORR. Inspired by the above discovery, designing and synthesizing dual-metal site catalysts have aroused great interest. Dual-metal catalysts can be divided into two main types: one is where the active part consists of a simple superposition of two kinds of active sites with different center metals, because the two metals are far enough apart that they are not bonding. The other is where the two metal atoms are close to form a bond and generate electronic interaction, which can promote the intrinsic catalytic activities.2,3,504.1 Fe–Co dual-metal as active center
Hu et al.108 studied the catalytic activity and stability of different active sites by density function theory calculations, including three types of sites: FeCoN6, FeCoN7 and FeCoN8. It can be verified that introducing the second metal atom can greatly improve the stability and ORR activity. These studied catalysts are all stable, but the catalytic activity of type FeCoN6 is lower than that of FeCoN7 and FeCoN8, which is attributed to the excessive adsorption strength between active sites and reaction intermediates. In theory, the top site of the Co atom is more likely to be the active center, as the overpotentials of the top site of Co atoms are all lower than the top site of Fe atoms. The internal mechanism of improving the performance of Fe–Co–N–C is that the introduction of the second Fe atom can increase the binding strength between Co and atomic O. Therefore, Fe–Co–N–C catalysts are a promising alternative for Pt-based catalysts.Wang et al.109 prepared a new catalyst which concludes two types of sites, Co2N6 and FeN4, and the configuration of the catalyst is shown in Fig. 14a. The aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM verified the coexistence of the two types of sites, and it clearly shows that single-atom sites and dual-atom sites correspond to the configurations of FeN4 and Co2N6, respectively (Fig. 14b). Moreover, they employed Fourier-transformed EXAFS to further investigate the coordination environment of Co and Fe in Co2/Fe–N@CHC, as shown in Fig. 14c. The spectrum of Co K-edge in Co2/Fe–N@CHC shows a weak peak at about 2.1 Å, which confirms the existence of Co–Co coordination. On the contrary, the spectrum of Fe K-edge in Co2/Fe–N@CHC does not have a special peak associated with Fe–Fe. And the Co and Fe K-edge EXAFS fitting result also indicated that the Co species have three N and one Co neighbor, while the Fe species coordinate with four N atoms, which also demonstrated the coexistence of Co2N6 and FeN4. There is no doubt that Co2/Fe–N@CHC exhibited good activity, and the E1/2 reached 0.812 V in 0.1 M HClO4, which is better than Co2–N6@CHC (0.770 V) and Fe–N4@CHC (0.787 V). This result suggests that the coexistence of two different active sites can greatly improve the catalytic performance. In order to explore the internal mechanism of activity enhancement, they next carried out DFT theoretical simulation calculation. The calculation results displayed that the property of Co2–N6 sites was inferior to that of Fe–N4 sites, so Co2–N6 sites play an auxiliary role to Fe–N4 sites. It is obvious from Fig. 14d that there is a significant negative shift in the d-band center of Fe after introducing Co2–N6 sites, resulting in an increased antibonding orbital filling, which weakens the adsorption strength of the Fe-center and reaction intermediates. Moreover, Yin et al.110 prepared a new FeCo–N–C catalyst (M/FeCo-SAs-N–C) which contains metal nanoparticles (M-NPs) and M–N4 composite sites. The special structure of composite sites is shown in Fig. 14e; the bigger cluster represents FeCo NPs, which can be confirmed by the lattice distance of 0.205 nm (inset of Fig. 14e). Single Fe/Co atom sites were marked in red circles. The specific coordination environment was evaluated by Fe K-edge EXAFS fitting results (Fig. 14f), and the coordination numbers of Fe–N and Fe–Fe were about 4 and 2, respectively, which suggests the coexistence of M-NPs and M–N4. It exhibited the best catalytic performance compared with Co-SAs-N–C, Fe-SAs-N–C and FeCo-SAs-N–C in 0.1 M HClO4, which can be attributed to the synergistic effect between M-NPs and M–N4, owing to the lower dissociation barrier of O2 on composite sites than Fe–N4 (Fig. 14g). The internal synergistic effect mechanism can be summarized as follows: a partial electron transfer from M-NPs to Fe–N4 increases the charge density of the adsorbed O2 molecule, which leads to the O–O bond length being elongated and reduces the barrier of O2 dissociation.
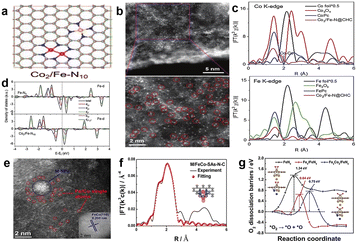 | ||
| Fig. 14 (a) The structure diagram of Co2/Fe–N@CHC.109 (b) Aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM images of Co2/Fe–N@CHC.109 (c) FT-EXAFS spectra of Co K-edge (top) and Fe K-edge (bottom) of Co2/Fe–N@CHC and references.109 (d) The projected density of states (PDOS) of Fe-d orbitals in FeN4 (top) and Co2/Fe–N@CHC (bottom).109 (e) Aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM images of M/FeCo-SAs-N–C, inset is the HR-STEM of an individual particle.110 (f) Fe K-edge EXAFS experimental and fitting curves.110 (g) O2 dissociation barriers on Fe–N4, Fe4/Fe–N4 and Fe2Co2/Fe–N4.110 | ||
In the case where Fe and Co atoms are close enough to produce a synergistic effect, Jiang et al.111 proposed a new active site structure of N3–Fe–Co–N3, as shown in Fig. 15a. The special structure can be proved by FT-EXAFS and corresponding fitting results; the FT-EXAFS of Fe K-edge and Co K-edge are presented in Fig. 15b and c, respectively. It is notable that there are two obvious peaks respectively corresponding to Fe–N (1.50 Å) and Co–N (1.32 Å) coordination environment, and a peak at about 2.30 Å that indicates the existence of Fe–Co bonds.112 The distance is in agreement with HAADF-STEM images, which is about 0.23 nm between Fe and Co atoms. The concrete coordination paths of Fe–N, Co–N and Fe–Co can be calculated by FT-EXAFS fitted curves based on DFT simulations. Eventually, the coordination numbers of Fe–N, Co–N, Fe–Co and Co–Fe are approximately 2.84, 2.89, 0.86 and 0.8, respectively. These results well verify the correctness of the N3–Fe–Co–N3 configuration. The catalyst achieved an unremarkable performance in the acidic solution, but its performance exceeds commercial Pt/C in alkaline environment. The reason for the ORR catalytic performance may be the synergetic effect of Fe–Co dual-atom sites and abundant atomically dispersed N3–Fe–Co–N3 sites. Xiao et al.15 then constructed an Fe–Co dual-atom centered site to greatly enhance the ORR activity. Firstly, they carried out DFT calculations to investigate the thermodynamic stability and intrinsic mechanism of the catalytic activity of the dual-metal center. The Fe 3d partial density of states (PDOS) is shown in Fig. 15d and e, and it can be clearly seen that the d-band center of dual-atom centered structures has undergone a slight positive shift compared with the single-atom centered site, which means stronger adsorption of ORR intermediates on the dual-atom centered sites. It indicates that intermediates are more likely to adsorb stably onto dual-atom centered sites. In the process of the ORR, water will spontaneously decompose and the OH* generated can be stabilized on FeCoN5 to form a new FeCoN5–OH site; the structure is shown in Fig. 15f. The d-band center of the new FeCoN5–OH site has a significant negative shift compared to the FeN4 site (Fig. 15e). According to the d-band center theory, the d-band center's negative shift can lead to an increase in the filling degree of anti-bonding orbitals, which weakens the binding strength between the active sites and intermediates and improves the catalytic performance. Guided by theoretical calculations, a catalyst with the FeCoN5 site was synthesized intentionally. The coordination configuration of the synthesized catalyst (FeCoNx/C) was researched by least-squares EXAFS fitting analysis. Actually, the M–N coordination number is less than 4, meaning that the configuration of FeCoNx/C isn't a simple superposition of FeN4 and CoN4. Besides, there are particular Fe-X and Co-X paths (2.1–2.2 Å), which can be attributed to the Fe–Co contribution, and the Fe–Co bond length agrees well with the distance of two atoms observed from the AC-HAADF-STEM image (Fig. 15g). FeCoNx/C reached an extraordinary E1/2 of 0.86 V in 0.1 M HClO4, and this performance exceeds the current state-of-the-art non-precious metal catalysts, which can be attributed to the extremely high intrinsic activity of the FeCoN5–OH site. Chen et al.113 then proposed the doping of Co atoms in the Fe–N–C catalyst (FeCo–NC-3), which not only boosts the catalytic activity, but also improves the stability of the catalysts. The HAADF-STEM and FT-EXAFS together proved the existence of Fe–Co binuclear sites, and the fitting Fe K-edge EXAFS confirmed that the coordination numbers of Fe–N and Co–N are both close to 4, so the most likely structure of active sites is shown in Fig. 15h. After testing, the E1/2 of FeCo–NC-3 is 0.842 V in 0.1 M HClO4 and the E1/2 decreased by only 11 mV after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles. The reason for the improvement in catalytic performance is the introduction of Co atoms that increases the electron density of Fe center sites, which can be attested by experimental results of XPS and Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy; the results of Mössbauer spectroscopy are summarized in Fig. 15i. The D1, D2 and D3 respectively represent the signature active low-spin FeII–N4 structure, inactive low-spin N–(FeII–N4)–N structure and mid-spin FePc-like FeII–N4 species. After introduction of Co, the content of inactive D2 is reduced while D1 is significantly increased, so the valence of Fe changes from +3 to +2, resulting in increased activity. A study demonstrated that two *OH adsorbing on the same side of Fe to form *Fe(OH)2 will lead to Fe site leaching and subsequent performance degradation.114 Inspired by experiments, the author used DFT calculation to prove the good stability of FeCo–NC-3. The reason is that *OH is difficult to adsorb stably on the FeCoN6 site to form *Fe(OH)2, thus avoiding damage of Fe sites.
000 cycles. The reason for the improvement in catalytic performance is the introduction of Co atoms that increases the electron density of Fe center sites, which can be attested by experimental results of XPS and Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy; the results of Mössbauer spectroscopy are summarized in Fig. 15i. The D1, D2 and D3 respectively represent the signature active low-spin FeII–N4 structure, inactive low-spin N–(FeII–N4)–N structure and mid-spin FePc-like FeII–N4 species. After introduction of Co, the content of inactive D2 is reduced while D1 is significantly increased, so the valence of Fe changes from +3 to +2, resulting in increased activity. A study demonstrated that two *OH adsorbing on the same side of Fe to form *Fe(OH)2 will lead to Fe site leaching and subsequent performance degradation.114 Inspired by experiments, the author used DFT calculation to prove the good stability of FeCo–NC-3. The reason is that *OH is difficult to adsorb stably on the FeCoN6 site to form *Fe(OH)2, thus avoiding damage of Fe sites.
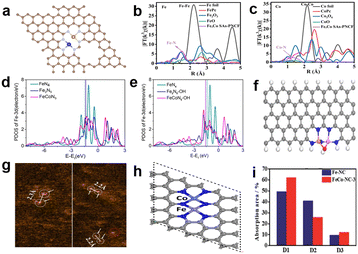 | ||
| Fig. 15 (a) The schematic structure of Fe, Co SAs-PNCF.111 FT-EXAFS spectra of (b) Fe K-edge and (c) Co K-edge.111 Fe 3d PDOS (d) before and (e) after absorption of OH*.15 (f) The structure of FeCoN5-OH site.15 (g) AC HAADF-STEM images of FeCoNx/C.15 (h) The main active site structure of FeCo–NC-3.113 (i) The content of three Fe moieties which comes from the analysis of Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy.113 | ||
4.2 Other dual-metals as active centers
Aside from the usual Fe–Co bimetals, other dual-metals as active centers were also researched. In recent years, researchers have discovered that the spin states of Fe are related to the catalytic activity and stability, which stimulated the research on the regulation of Fe spin states. Yang et al.115 prepared a catalyst containing Fe–Mn dual-metal (Fe,Mn/N–C), the structure of the active site is shown in Fig. 16a, and the structure was verified by K-edge XANES and K-edge FT-EXAFS of Fe and Mn. This catalyst reached an E1/2 of 0.804 V in 0.1 M HClO4, and the good performance can be attributed to the single-atom dispersed Mn–N moieties effectively adjusting the electron configuration and spin states of FeIII (from the low spin state to the ideal intermediate spin state), which allows the active sites to have a suitable adsorption strength with oxygen intermediates. Moreover, Cai et al.116 synthesized a catalyst with FeN4 and MnN4 species, and FeN4 and MnN4 are linked together by an oxygen atom, forming a new active site (FeN4–O–MnN4), as shown in Fig. 16b. According to the fitting FT EXAFS, the coordination numbers of Fe–N/O and Mn–N/O are 4.6 and 5.1, respectively. Combined with O 1s XPS spectral results, the presence of the metal–O bond demonstrated the rationality of the structure of O as a bridge connecting FeN4 and MnN4. The catalyst exhibited an E1/2 of 0.781 V, slightly lower than 20% Pt/C. The introduction of Mn can not only increase the content of Fe, but also reduce the energy barrier of the ORR (Fig. 16c). He and colleagues117 then discovered that introduction of Cu can also regulate the spin-state of FeN4, especially near the nanopore edge. The possible structure of NCAG/Fe–Cu is shown in Fig. 16d. DFT calculations show that the introduction of Cu can regulate the Fe 3d density of states (DOS), making the DOS closer to the Fermi energy level than without Cu (Fig. 16e), which can improve the catalytic performance. Du et al.118 and Song et al.119 also synthesized catalysts which contain two metallic elements, Fe and Cu, and the structure of the active sites is mostly a simple combination of FeN4 and CuN4. These articles both proved that trace amounts of Cu atoms doped in the carbon matrix that is close to Fe can facilitate the formation of FeN4 and promote the catalytic activity and stability. Aiming at solving the problem of the stability of M–N–C catalysts being affected by the destruction of the active site caused by the protonation of nitrogen, Li et al.120 screened an Fe–Zn based bimetal catalyst with high stability through theoretical calculations. Fe and Zn K-edge EXAFS show a weak peak at 2.36 Å which demonstrated the interaction between Fe and Zn, and the fitting data proved the structure of FeZnN6; the structure is shown in Fig. 16f (Fe/Zn–N–C). Fe/Zn–N–C reached an E1/2 of 0.808 V, and the E1/2 lost only 12 mV after 5000 potential cycles in 0.1 M HClO4. The good performance of Fe/Zn–N–C can be attributed to the FeZnN6 moieties showing high protonation free energy, and the breaking of the Zn–N bond to protect the active structure of FeN4 during protonation. | ||
| Fig. 16 (a) The structure of Fe,Mn/N6.115 (b) The model of active site FeN4–O–MnN4.116 (c) The free energy evolution diagram on FeN4–O–FeN4 and FeN4–O–MnN4 sites for the ORR.116 (d) The structure of NCAG/Fe–Cu near the nanopore edge.117 (e) Fe 3d DOS of Fe1/Fe1-2 and Cu1/Fe1-2.117 (f) The structure of FeZnN6 moieties.120 | ||
In addition to the bimetallic-site catalysts mentioned above, bimetal site catalysts formed by Co and other metals have also been studied by many people. For example, Li and colleagues121 prepared a catalyst which contained carbon-coated CoNi alloy and M–N4 sites (CoxNi–N/C). XRD patterns exhibit three identified peaks, which correspond to the (111), (200), and (220) lattice planes of metallic Ni and Co, respectively (Fig. 17a). However, the position of these peaks is offset from the standard position recorded in the database, which reflects the presence of CoNi alloys. High-resolution XPS spectra of Co 2p and Ni 2p demonstrated the coordination environment of Co–Nx and Ni–Nx. Experiments showed that introduction of Ni increased the amount of pyridine-N and Co–N moieties, and the interaction between CoNi alloys and M–N–C moieties can adjust the electron density of M–N–C moieties, facilitating the catalytic activity. Moreover, Zhang et al.122 prepared a novel catalyst that encapsulated a thin Cu layer and Co nanoparticles in graphitic carbon layers, forming abundant M-NPs and M–Nx atomic sites. The electron-donating effect of M-NPs can regulate the electron density of M–Nx. DFT calculations show that about 0.05 e− are transferred from a Cu slab to the CoN4 sites. So, the interaction of Co and Cu enhances the ORR activity toward both H2O and H2O2 (Fig. 17b). In addition, Shah et al.123 produced porous N-doped carbon nanostructures with Mn-/Co–Nx dual moieties (MnCo–NC/CNT) which exhibited excellent catalytic activity and stability in acid environment. The high-resolution Mn 2p and Co 2p spectra demonstrated the presence of Co–Nx and Mn–Nx moieties, which act as the most important active sites to catalyze the ORR, as shown in Fig. 17c and d. The doping of Mn improved the selectivity of the four-electron ORR pathway of Co–N–C catalysts, and the H2O2 yield was less than 5% in acid medium. It can be seen that the synergistic effect of bimetallic sites can improve the performance of catalysts. In addition to experimental studies, the stability and activity of active sites can also be predicted by theoretical calculations. Wang et al.124 systematically studied the intrinsic nature of the Zn–Co bimetallic catalyst in the oxygen reduction reaction by DFT calculations. In order to better understand the effect of the structure of the active site on the catalytic activity and stability, the authors simulated a variety of configurations, labeled as ZnCoNx-gra (x = 1–6). Calculation results show that when x < 4, the structures are thermodynamically unstable, and the stability of the active site increases with the increase of x value. The most stable configuration is shown in Fig. 17e. Besides, this research discovered that the catalytic activity of the ORR was enhanced when the active sites were combined with electron-withdrawing functional groups, especially with two *OH (Fig. 17f). The conclusion is consistent with the research of Cao et al.125 And Zn tends to sacrifice itself to protect the Co active center during the catalytic reaction, which is conducive to stabilization.
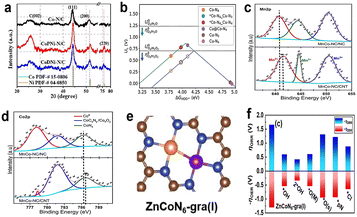 | ||
| Fig. 17 (a) XRD patterns of Co–N/C, CoXNi–N/C (X = P and D).121 (b) The volcano plots for the four-electron ORR to H2O (solid circles) and two-electron ORR to H2O2 (empty circles).122 High-resolution (c) Mn 2p and (d) Co 2p spectra of MnCo–NC/NC and MnCo–NC/CNT.123 (e) The most stable configuration of ZnCoNx-gra.124 (f) The overpotential of the ORR and OER for ZnCoN6-gra (1) with or without electron-withdrawing functional groups.124 | ||
5 Conclusions and outlook
Developing low-cost and high-efficiency PGM-free ORR catalysts in acidic media is important for application of PEMFCs. After decades of development, the performance of catalysts has been greatly improved. However, we also need to clearly recognize that the catalysts currently studied are not enough to be used in practical production, especially in acidic environment, and there is still a big gap between their performance and state-of-the-art Pt/C. Therefore, how to effectively improve the catalytic activity and stability of non-noble metals is still a hot research issue. Next, we will summarize the challenges and some common strategies for improving the activity and stability of non-noble metal oxygen reduction catalysts.As one of the important parameters for evaluating oxygen reduction catalysts, the half-wave potential can initially determine the activity of catalysts. However, the activity of most non-precious metals in the three-electrode test is about 50 mV lower than that of commercial Pt/C, which is mainly due to (1) the low intrinsic activity of non-precious metals. As shown in Fig. 3a, compared with other non-precious metals, Pt is closer to the peak of the volcanic curve, which means that Pt has appropriate adsorption energy for the intermediate of the oxygen reduction reaction, and therefore presents the best activity, while most transition metals such as Fe and Co often show weak reactivity due to their strong adsorption. (2) Insufficient density of active sites. Since Zhang et al. proposed SACs,49 people began to study single-atom oxygen reduction catalysts extensively and proved their superiority. But SACs often mean low metal content, because increasing the metal content causes the metal atoms to gather together and become less active.84,126 Therefore, monatomic catalysts with high intrinsic activity face the problem of insufficient active sites. (3) Insufficient exposure of active sites. At present, most catalysts use a metal organic frame and other materials with fence function to restrict metal aggregation and form monatomic catalysts. The typical precursor is ZIF-8, but the catalyst formed by this is mainly composed of micropores, which hinders the diffusion of O2 and makes it difficult for O2 to approach the active site, thus reducing the utilization rate of the active site.67 These reasons all lead to insufficient activity expression of non-precious metals. Understanding these reasons can help us design catalysts reasonably. The following are some common strategies for improving catalyst activity:
The improvement in catalytic activity is mainly achieved via the following techniques: (1) increasing the density of active sites. Many studies have proved that the number of active sites is positively correlated with catalytic activity. Increasing the active site density means increasing the number of species reacting per unit time, simultaneously increasing the reaction rate. (2) Designing catalysts with high-intrinsic activity. In order to achieve this goal, it's necessary to define the main active site and determine the main factors affecting the performance. The completion of these steps can't be separated from the guidance of theoretical calculations. With the development of computer technology, using DFT to design the catalyst has a good guiding significance. (3) Improving the utilization rate of the active center. In recent years, the development of single-atom site catalysts has efficiently improved the utilization rate, but a major problem of such catalysts is the low metal loading, which leads to a low density of active sites. Therefore, efforts should be made in the future to increase the number of single atomic metal sites as much as possible without causing metal aggregation. (4) Increasing the exposure of active sites. The catalytic activity of metal sites covered by carbon layers is lower than that of sites exposed to carbon layers. The hierarchical porous structure of the catalyst is favorable for exposing more active sites and increases the mass transfer rates of reactants and products.
Now, it's found that the main reasons for the poor stability of catalytic include: (1) demetallization of the active site. (2) H2O2 or hydroperoxyl radical oxidative species attack. (3) Corrosion of carbon substrates. (4) Micropore flooding. According to the previous introduction, Fe has been widely studied as a non-noble metal with the highest oxygen reduction reactivity. However, current studies have shown that Fe has strong Fenton activity and reacts with H2O2 to form highly active oxygen-containing radicals during the reaction. These free radicals attack the active center and carbon substrate of the catalyst, resulting in demetallization and carbon corrosion of the catalyst. This is the main factor contributing to the inactivation of the catalyst. In addition, because the product of the oxygen reduction reaction is water, and the active site is concentrated in the micropores, it is difficult for the product water to be discharged in time, resulting in the active site being buried, thus resulting in a decrease in catalyst activity. Some strategies have made great progress in improving stability, such as incorporation of activated biomasses in catalysts to enhance stability,127 improving the graphitization degree of the carbon substrate128 and so on. There are several ways to improve the stability of catalysts by changing the active site: (1) change the electronic structure near the active site to improve the M–N bond strength. (2) Look for alternative metals to Fe. According to the reasons for the decline in catalyst performance described above, we can replace Fe with non-precious metals with weak Fenton activity or even no Fenton activity, such as Co, Mn, etc. to improve the stability of the catalyst. (3) Exploring suitable dual-metal catalysts. The synergistic effect between bimetals can effectively regulate the electronic structure around the active sites, thus affecting the stability of the catalysts.3 (4) Construction of catalysts with micro–meso-composite pore structures. Materials with rich mesopores are selected as carbon substrates to promote the transport of substances in the reaction process and reduce the harm caused by micropore flooding.
At present, the methods for preparing high-performance ORR non-noble metal catalysts can be summarized as the template method, chemical vapor deposition method, heteroatom modification method, etc. (1) Template method. By adding an additional substance as a template to limit the shape and size of the carbon substrate, a carbon substrate with a porous structure can be obtained by removing the template in a subsequent step. Using its porous structure, the active site density of the catalyst can be increased, thus improving the activity of the catalyst. For example, Wan et al. used SiO2 as a template to construct ZIF-8 with a concave surface through high-temperature pyrolysis and subsequent steps to remove the template, thereby forming a single-atom Fe–N–C catalyst with high active site density, and its Fe content can reach 3 wt%.129 In addition, because the catalyst is concave, its external surface area is large, which also promotes the exposure of the active site. Experiments show that the template method is an effective method for constructing high-performance catalysts, but this method usually faces the dilemma that the template is difficult to remove. In addition, there are reports of using molten salts such as KCl and NaCl as templates; using the melting characteristics of the molten salt under high temperature conditions, the molten salt can be removed by simple washing to form a porous carbon substrate. For example, Wang et al. used NaCl as a template, NaCl melted and coated on the surface of ZIF-8 under high temperature conditions, and a N-containing carbon substrate with a porous structure could be obtained after NaCl was removed by subsequent water washing.130 Similarly, this method increases the active site density and effectively improves the performance of the catalyst. (2) Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method. Chemical vapor deposition refers to the reaction of chemical gases or vapors on the substrate surface to synthesize coatings or nanomaterials. A typical example of the chemical vapor deposition method is when Jiao et al. used anhydrous FeCl3 as an iron source and ZIF-8 as a C source containing N. FeCl3 was adsorbed on ZIF-8 by the method of CVD. Under the condition of high temperature, Fe and Zn exchanged to form Fe–N4 sites with high activity. In addition, because Fe is mostly located on the surface of the catalyst, the active site utilization rate of the catalyst is extremely high, reaching 100%.131 Although this method has not been studied much in the preparation of ORR non-precious metal catalysts, according to the high-performance catalyst prepared by this method, the CVD method will be a potential method to be further explored. (3) Heteroatom modification method. Heteroatom doping is usually the doping of atoms such as P, S, B and F into the N-containing carbon substrate through high-temperature pyrolysis to regulate the electron density near the active site, so as to achieve the purpose of improving the activity of the catalyst. Although these methods can improve the performance of catalysts to a certain extent, there are still some problems in the preparation of non-noble metal oxygen reduction catalysts, such as the high temperature pyrolysis method takes a long time, the catalyst is difficult to be prepared in batch, and the organic matter used in the preparation process causes great pollution to the environment. These problems have seriously hindered the commercial application of ORR non-precious metal catalysts. Therefore, the development of other efficient and clean preparation methods is the direction of our future efforts.
In summary, improving the performance of ORR catalyst is of great significance to the wide application of PEMFCs. In fact, the structure of the catalyst active site is closely related to the performance of the catalyst, so it is necessary to determine the structure of the active site through advanced characterization techniques and reasonable simulation calculations in the study of catalysts. The application process of PEMFCs can be effectively accelerated by combining theoretical calculation with experimental techniques to design and manufacture efficient catalysts.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Key R&D Program (2022YFB4004100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21875243, 21673221, 22209168), Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Program (20200201001JC, 20190201270JC, 20180101030JC) and Special Funds for Guiding Local Scientific, Technological Development by the Central Government (Grant No. 2020JH6/10500021).References
- J. Lian, J. Y. Zhao and X. M. Wang, Recent Progress in Carbon-based Materials of Non-Noble Metal Catalysts for ORR in Acidic Environment, Acta Metall. Sin., 2021, 34, 885–899 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Song, Y. Feng, W. Zhang and W. Zheng, MOFs fertilized transition-metallic single-atom electrocatalysts for highly-efficient oxygen reduction: Spreading the synthesis strategies and advanced identification, J. Energy Chem., 2022, 67, 391–422 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. H. He, S. W. Liu, C. Priest, Q. R. Shi and G. Wu, Atomically dispersed metal-nitrogen-carbon catalysts for fuel cells: advances in catalyst design, electrode performance, and durability improvement, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 3484–3524 RSC.
- R. Jasinski, New fuel cell cathode catalyst, Nature, 1964, 201, 1212–1213 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Liu, Z. Li, C. Wang, W. Tao, M. Huang, M. Zuo, Y. Yang, K. Yang, L. Zhang, S. Chen, P. Xu and Q. Chen, Turning main-group element magnesium into a highly active electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 938 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Iida, M. Shetty, K. Murugappan, Z. Wang, K. Ohara, T. Wakihara and Y. Roman-Leshkov, Encapsulation of Molybdenum Carbide Nanoclusters inside Zeolite Micropores Enables Synergistic Bifunctional Catalysis for Anisole Hydrodeoxygenation, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 8147–8151 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Xiao, J. Zhu, L. Feng, C. Liu and W. Xing, Meso/Macroporous Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Architectures with Iron Carbide Encapsulated in Graphitic Layers as an Efficient and Robust Catalyst for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Both Acidic and Alkaline Solutions, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 2521–2527 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Patniboon and H. A. Hansen, Acid-Stable and Active M–N–C Catalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction: The Role of Local Structure, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 13102–13118 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Yang, X. Chen, W. T. Chen, Q. Wang, N. C. Cuello, A. Nafady, A. M. Al-Enizi, G. I. N. Waterhouse, G. A. Goenaga, T. A. Zawodzinski, P. E. Kruger, J. E. Clements, J. Zhang, H. Tian, S. G. Telfer and S. Ma, Tunable Synthesis of Hollow Metal-Nitrogen-Carbon Capsules for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Catalysis in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells, ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 8087–8098 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Behera, S. P. Mantry, B. D. Mohapatra, R. K. Behera and K. S. K. Varadwaj, Functional molecule guided evolution of MnOx nanostructure patterns on N-graphene and their oxygen reduction activity, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 27945–27952 RSC.
- J. Liu, L. Jiang, B. Zhang, J. Jin, D. S. Su, S. Wang and G. Sun, Controllable Synthesis of Cobalt Monoxide Nanoparticles and the Size-Dependent Activity for Oxygen Reduction Reaction, ACS Catal., 2014, 4, 2998–3001 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Xu, P. Gao and T. S. Zhao, Non-precious Co3O4 nano-rod electrocatalyst for oxygenreduction reaction in anion-exchange membranefuelcells, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 5333–5339 RSC.
- K. P. Singh, E. J. Bae and J. S. Yu, Fe-P: a new class of electroactive catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 3165–3168 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Miao, X. Wang, Z. Zhao, W. Zuo, S. Chen, Z. Li, Y. He, J. Liang, F. Ma, H. L. Wang, G. Lu, Y. Huang, G. Wu and Q. Li, Improving the Stability of Non-Noble-Metal M-N-C Catalysts for Proton-Exchange-Membrane Fuel Cells through M-N Bond Length and Coordination Regulation, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, e2006613 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Xiao, Y. Chen, J. Zhu, H. Zhang, X. Zhao, L. Gao, X. Wang, J. Zhao, J. Ge, Z. Jiang, S. Chen, C. Liu and W. Xing, Climbing the Apex of the ORR Volcano Plot via Binuclear Site Construction: Electronic and Geometric Engineering, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 17763–17770 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Prakash, D. A. Tryk and E. B. Yeager, Kinetic investigations of oxygen reduction and evolution reactions on lead ruthenate catalysts, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1999, 146, 4145–4151 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Sun, S. Mitchell, J. Li, P. Lyu, X. Wu, J. Perez-Ramirez and J. Lu, Design of Local Atomic Environments in Single-Atom Electrocatalysts for Renewable Energy Conversions, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, e2003075 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Liu, L. Shi, X. Lin, D. Yu, C. Zhang, R. Xu, D. Liu, J. Qiu and L. Dai, Site-density engineering of single-atomic iron catalysts for high-performance proton exchange membrane fuel cells, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 302, 120860–120871 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yan, H. Y. Cheng, Z. H. Qu, R. Yu, F. Liu, Q. W. Ma, S. Zhao, H. Hu, Y. Cheng, C. Y. Yang, Z. F. Li, X. Wang, S. Y. Hao, Y. Y. Chen and M. K. Liu, Recent progress on the synthesis and oxygen reduction applications of Fe-based single-atom and double-atom catalysts, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 19489–19507 RSC.
- W. Zou, R. Lu, X. Liu, G. Xiao, X. Liao, Z. Wang and Y. Zhao, Theoretical insights into dual-atom catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction: the crucial role of orbital polarization, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 9150–9160 RSC.
- J. Wang, C. X. Zhao, J. N. Liu, Y. W. Song, J. Q. Huang and B. Q. Li, Dual-atom catalysts for oxygen electrocatalysis, Nano Energy, 2022, 104, 107927–107940 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Stamenkovic, B. S. Mun, K. J. Mayrhofer, P. N. Ross, N. M. Markovic, J. Rossmeisl, J. Greeley and J. K. Norskov, Changing the activity of electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction by tuning the surface electronic structure, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 2897–2901 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. K. Norskov, J. Rossmeisl, A. Logadottir, L. Lindqvist, J. R. Kitchin, T. Bligaard and H. Jonsson, Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 17886–17892 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Xu, D. Cheng, D. Cao and X. C. Zeng, A universal principle for a rational design of single-atom electrocatalysts, Nat. Catal., 2018, 1, 339–348 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Deng, L. Yu, X. Chen, G. Wang, L. Jin, X. Pan, J. Deng, G. Sun and X. Bao, Iron encapsulated within pod-like carbon nanotubes for oxygen reduction reaction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 371–375 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Xiao, J. Zhu, C. Liu, J. Ge and W. Xing, Recent Progress in Non-Precious Metal Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalysts with an Encapsulation Structure, J. Electrochem., 2016, 22, 101–112 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Guo, R. Shibuya, C. Akiba, S. Saji, T. Kondo and J. Nakamura, Active sites of nitrogen-doped carbon materials for oxygen reduction reaction clarified using model catalysts, Science, 2016, 351, 361–365 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Jia, L. Zhang, L. Zhuang, H. Liu, X. Yan, X. Wang, J. Liu, J. Wang, Y. Zheng, Z. Xiao, E. Taran, J. Chen, D. Yang, Z. Zhu, S. Wang, L. Dai and X. Yao, Identification of active sites for acidic oxygen reduction on carbon catalysts with and without nitrogen doping, Nat. Catal., 2019, 2, 688–695 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Sun, Y. Jiang, Q. Wu, L. Du, Z. Zhang, L. Yang, X. Wang and Z. Hu, Is iron nitride or carbide highly active for oxygen reduction reaction in acidic medium?, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7, 51–55 RSC.
- C. Zhu, H. Li, S. Fu, D. Du and Y. Lin, Highly efficient nonprecious metal catalysts towards oxygen reduction reaction based on three-dimensional porous carbon nanostructures, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 517–531 RSC.
- J. Masa, W. Xia, M. Muhler and W. Schuhmann, On the Role of Metals in Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 10102–10120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Chen, D. Higgins, A. Yu, L. Zhang and J. Zhang, A review on non-precious metal electrocatalysts for PEM fuel cells, Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4, 3167–3192 RSC.
- X. L. Tian, X. F. Lu, B. Y. Xia and X. W. Lou, Advanced Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Energy Conversion Technologies, Joule, 2020, 4, 45–68 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Gupta, D. Tryk, I. Bae, W. Aldred and E. Yeager, Heat-treated polyacrylonitrile-based catalysts for oxygen electroreduction, J. Appl. Electrochem., 1989, 19, 19–27 CrossRef CAS.
- U. Martinez, S. Komini Babu, E. F. Holby, H. T. Chung, X. Yin and P. Zelenay, Progress in the Development of Fe-Based PGM-Free Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, e1806545 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Lefevre, J. P. Dodelet and P. Bertrand, Molecular oxygen reduction in PEM fuel cells: Evidence for the simultaneous presence of two active sites in Fe-based catalysts, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106, 8705–8713 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, X. Liu, L. Zheng, J. Shang, X. Wan, R. Hu, X. Guo, S. Hong and J. Shui, Preparation of Fe–N–C catalysts with FeNx (x = 1, 3, 4) active sites and comparison of their activities for the oxygen reduction reaction and performances in proton exchange membrane fuel cells, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 26147–26153 RSC.
- L. Liu, X. Yang, N. Ma, H. Liu, Y. Xia, C. Chen, D. Yang and X. Yao, Scalable and Cost-Effective Synthesis of Highly Efficient Fe2N-Based Oxygen Reduction Catalyst Derived from Seaweed Biomass, Small, 2016, 12, 1295–1301 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. M. Fruehwald, I. I. Ebralidze, O. V. Zenkina and E. B. Easton, Fe-N-3/C Active Catalytic Sites for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Prepared with Molecular-Level Geometry Control through the Covalent Immobilization of an Iron-Terpyridine Motif onto Carbon, ChemElectroChem, 2019, 6, 1350–1358 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Qin, S. Zhu, L. Zhang, S. Sun and M. Shao, Theoretical Studies of Metal-N-C for Oxygen Reduction and Hydrogen Evolution Reactions in Acid and Alkaline Solutions, J. Electrochem., 2021, 27, 185–194 CAS.
- G. Wu and P. Zelenay, Nanostructured Nonprecious Metal Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction, Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46, 1878–1889 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Proietti, F. Jaouen, M. Lefevre, N. Larouche, J. Tian, J. Herranz and J. P. Dodelet, Iron-based cathode catalyst with enhanced power density in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells, Nat. Commun., 2011, 2, 416–424 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Liu, G. Goenaga, S. Ma, S. Yuan and J. Shui, New Approaches to Non-PGM Catalysts through Rational Design, ECS Trans., 2011, 30, 97–104 CrossRef.
- X. Wang, H. Zhang, H. Lin, S. Gupta, C. Wang, Z. Tao, H. Fu, T. Wang, J. Zheng, G. Wu and X. Li, Directly converting Fe-doped metal–organic frameworks into highly active and stable Fe-N-C catalysts for oxygen reduction in acid, Nano Energy, 2016, 25, 110–119 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Xu, J. Liu, J. Ge, C. Liu and W. Xing, Research Progress of Metal-Nitrogen-Carbon Catalysts toward Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Dianhuaxue, 2020, 26, 464–473 CAS.
- J. G. Speight, Lange's handbook of chemistry, McGraw-hill New York, 2005 Search PubMed.
- S. Poulin, R. Franca, L. Moreau-Belanger and E. Sacher, Confirmation of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Peak Attributions of Nanoparticulate Iron Oxides, Using Symmetric Peak Component Line Shapes, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 10711–10718 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Yamashita and P. Hayes, Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2008, 254, 2441–2449 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Qiao, A. Wang, X. Yang, L. F. Allard, Z. Jiang, Y. Cui, J. Liu, J. Li and T. Zhang, Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt-1/FeOx, Nat. Chem., 2011, 3, 634–641 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Qu, S. Ji, Y. Chen, D. Wang and Y. Li, Design and structural engineering of single-atomic-site catalysts for acidic oxygen reduction reaction, Trends Chem., 2021, 3, 954–968 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Ren, H. Wang, X. F. Lu, Y. X. Tong and G. R. Li, Recent Progress on MOF-Derived Heteroatom-Doped Carbon-Based Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction, Adv. Sci., 2018, 5, 1700515 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Deng, L. Qiu, R. Hu, L. Yao, Z. Zheng, X. Ren, Y. Li and C. He, Restricted diffusion preparation of fully-exposed Fe single-atom catalyst on carbon nanospheres for efficient oxygen reduction reaction, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 305, 121058–121067 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Xu, D. Wang, P. Yang, L. Du, X. Lu, R. Li, L. Liu, J. Zhang and M. An, A hierarchically porous Fe-N-C synthesized by dual melt-salt-mediated template as advanced electrocatalyst for efficient oxygen reduction in zinc-air battery, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 305, 121040–121051 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, C. Yang, X. Wang, H. Zhu, L. Cao, A. Chen, L. Gu, Q. Zhang, L. Zheng and H.-P. Liang, Green Synthesis of a Highly Efficient and Stable Single-Atom Iron Catalyst Anchored on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanorods for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 9, 137–146 CrossRef.
- L. Li, Y. Wen, G. Han, Y. Liu, Y. Song, W. Zhang, J. Sun, L. Du, F. Kong, Y. Ma, Y. Gao, J. Wang, C. Du and G. Yin, Tailoring the stability of Fe-N-C via pyridinic nitrogen for acid oxygen reduction reaction, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 437, 135320–135327 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Xiang, X. Zhang, B. Yan, K. Wang, Y. Wang, D. Lyu, S. Xi, Z. Qun Tian and P. Kang Shen, Atomic iron coordinated by nitrogen doped carbon nanoparticles synthesized via a synchronous complexation-polymerization strategy as efficient oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts for zinc-air battery and fuel cell application, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 440, 135721–135733 CrossRef CAS.
- W. J. Jiang, L. Gu, L. Li, Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, L. J. Zhang, J. Q. Wang, J. S. Hu, Z. Wei and L. J. Wan, Understanding the High Activity of Fe-N-C Electrocatalysts in Oxygen Reduction: Fe/Fe3C Nanoparticles Boost the Activity of Fe-N(x), J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 3570–3578 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhang, M. Chen, X. Zhao, J. Cai, W. Yan, J. C. Yen, S. Chen, Y. Yu and J. Zhang, Advanced Noncarbon Materials as Catalyst Supports and Non-noble Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells and Metal–Air Batteries, Electrochem. Energy Rev., 2021, 4, 336–381 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Wang, T. Liao, X. Zhang, J. Cao, S. Xu, H. Tang and Y. Wang, Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers Loaded with Atomic FeNx/Fe2O3 Active Sites for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Both Acidic and Alkaline Media, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 9, 2101904–2101914 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xu, L. Chen, Y. Wen, S. Qin, H. Li, Z. Hou, Z. Huang, H. Zhou and Y. Kuang, A co-operative protection strategy to synthesize highly active and durable Fe/N co–doped carbon towards oxygen reduction reaction in Zn–air batteries, Mater. Today Energy, 2021, 21, 100721–100731 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Xu, J. Ma, M. Shi, Y. Xie and C. Feng, Biomass based iron and nitrogen co-doped 3D porous carbon as an efficient oxygen reduction catalyst, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2018, 523, 144–150 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, H. Liu, C. Chen, L. Zou, Y. Li, Q. Zhang, B. Yang, Z. Zou and H. Yang, Fe2N nanoparticles boosting FeNx moieties for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction in Fe-N-C porous catalyst, Nano Res., 2019, 12, 1651–1657 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Liu, Q. Meyer, Y. Li, T. Zhao, Z. Su, K. Ching and C. Zhao, Fe–N–C/Fe nanoparticle composite catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells, Chem. Commun., 2022, 58, 2323–2326 RSC.
- M. X. Chen, M. Zhu, M. Zuo, S. Q. Chu, J. Zhang, Y. Wu, H. W. Liang and X. Feng, Identification of Catalytic Sites for Oxygen Reduction in Metal/Nitrogen-Doped Carbons with Encapsulated Metal Nanoparticles, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 1627–1633 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-A. Chen, C.-L. Hsin, Y.-T. Huang, M. L. Tang, S. Dhuey, S. Cabrini, W.-W. Wu and S. R. Leone, Measurement of Interlayer Screening Length of Layered Graphene by Plasmonic Nanostructure Resonances, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 22211–22217 CrossRef CAS.
- D. H. Deng, L. Yu, X. Q. Chen, G. X. Wang, L. Jin, X. L. Pan, J. Deng, G. Q. Sun and X. H. Bao, Iron Encapsulated within Pod-like Carbon Nanotubes for Oxygen Reduction Reaction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 371–375 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-W. Ye and L. Xu, Recent advances in the design of a high performance metal–nitrogen–carbon catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 22218–22247 RSC.
- H. Li, K. Du, C. Xiang, P. An, X. Shu, Y. Dang, C. Wu, J. Wang, W. Du, J. Zhang, S. Li, H. Tian, S. Wang and H. Xia, Controlled chelation between tannic acid and Fe precursors to obtain N, S co-doped carbon with high density Fe-single atom-nanoclusters for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction in Zn–air batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 17136–17149 RSC.
- Y. Y. Meng, D. Voiry, A. Goswami, X. X. Zou, X. X. Huang, M. Chhowalla, Z. W. Liu and T. Asefa, N-, O-, and S-Tridoped Nanoporous Carbons as Selective Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction and Alcohol Oxidation Reactions, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 13554–13557 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. B. Zhu, K. Li, M. L. Xiao, C. P. Liu, Z. J. Wu, J. J. Ge and W. Xing, Significantly enhanced oxygen reduction reaction performance of N-doped carbon by heterogeneous sulfur incorporation: synergistic effect between the two dopants in metal-free catalysts, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 7422–7429 RSC.
- X. Hu, Y. Wu, H. Li and Z. Zhang, Adsorption and activation of O2 on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 9603–9607 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, J. Niu, M. Li and Z. Xia, Catalytic mechanisms of sulfur-doped graphene as efficient oxygen reduction reaction catalysts for fuel cells, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 3545–3553 CrossRef CAS.
- C. X. Zhao, B. Q. Li, J. N. Liu and Q. Zhang, Intrinsic Electrocatalytic Activity Regulation of M-N-C Single-Atom Catalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 4448–4463 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yin, P. Yuan, B.-A. Lu, H. Xia, K. Guo, G. Yang, G. Qu, D. Xue, Y. Hu, J. Cheng, S. Mu and J.-N. Zhang, Phosphorus-Driven Electron Delocalization on Edge-Type FeN4 Active Sites for Oxygen Reduction in Acid Medium, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 12754–12762 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, X. Zhai, W. Sheng, J. Tu, Z. Zhao, Y. Shi, C. Xu, G. Ge and X. Jia, Isolated single iron atoms anchored on a N, S-codoped hierarchically ordered porous carbon framework for highly efficient oxygen reduction, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 10110–10119 RSC.
- F. Xiao, G.-L. Xu, C.-J. Sun, M. Xu, W. Wen, Q. Wang, M. Gu, S. Zhu, Y. Li, Z. Wei, X. Pan, J. Wang, K. Amine and M. Shao, Nitrogen-coordinated single iron atom catalysts derived from metal organic frameworks for oxygen reduction reaction, Nano Energy, 2019, 61, 60–68 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Tao, R. Lu, L. Ni, V. Gridin, S. H. Al-Hilfi, Z. Qiu, Y. Zhao, U. I. Kramm, Y. Zhou and K. Mullen, Facilitating the acidic oxygen reduction of Fe-N-C catalysts by fluorine-doping, Mater. Horiz., 2022, 9, 417–424 RSC.
- M. Fan, Q. Yuan, Y. Zhao, Z. Wang, A. Wang, Y. Liu, K. Sun, J. Wu, L. Wang and J. Jiang, A Facile “Double-Catalysts” Approach to Directionally Fabricate Pyridinic NB-Pair-Doped Crystal Graphene Nanoribbons/Amorphous Carbon Hybrid Electrocatalysts for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, e2107040 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Hu, L. Tao, D. Liu, J. Huo and S. Wang, Sulfur-Doped Fe/N/C Nanosheets as Highly Efficient Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 19379–19385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yan, Y. Liu, R. Wang, M. Xia, J. Wang, F. Gao and Y. Tang, Bamboo-like carbonitride nanotubes with multi-type active sites for oxygen reduction reaction in both alkaline and acid mediums, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47, 7949–7960 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Cheng, J.-M. Chen, Q.-J. Li, C.-Y. Su, A.-N. Chen, J.-X. Zhang, Z.-Q. Liu and Y. Tong, Modified molecular framework derived highly efficient Mn-Co-carbon cathode for a flexible Zn-air battery, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 11596–11599 RSC.
- Z. Wang, S. Peng, Y. Hu, L. Li, T. Yan, G. Yang, D. Ji, M. Srinivasan, Z. Pan and S. Ramakrishna, Cobalt nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon nanotube-grafted nitrogen and sulfur co-doped multichannel carbon fibers as efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 4949–4961 RSC.
- S. K. Mishra and S. B. Kanungo, Thermal Dehydeation and Decomposition of Cobalt Chloride Hydrate (CoCl2·xH2O), J. Therm. Anal., 1992, 38, 2437–2454 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. He, S. Hwang, D. A. Cullen, M. A. Uddin, L. Langhorst, B. Li, S. Karakalos, A. J. Kropf, E. C. Wegener, J. Sokolowski, M. Chen, D. Myers, D. Su, K. L. More, G. Wang, S. Litster and G. Wu, Highly active atomically dispersed CoN4 fuel cell cathode catalysts derived from surfactant-assisted MOFs: carbon-shell confinement strategy, Energy Environ. Sci., 2019, 12, 250–260 RSC.
- G. Yang, F. Li, L. Wang, K. H. Row, H. Liu, L. Bai, W. Cao and T. Zhu, Synthesis, characteristics and evaluation of a new monolithic silica column prepared from copolymer pluronic F127, Chromatographia, 2008, 68, 27–31 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhao, Y. Wang, W. Dong, Y. Wu, D. Li, B. Liu and Q. Zhang, A new surfactant-introduction strategy for separating the pure single-phase of metal-organic frameworks, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 9479–9482 RSC.
- Y. He, H. Guo, S. Hwang, X. Yang, Z. He, J. Braaten, S. Karakalos, W. Shan, M. Wang, H. Zhou, Z. Feng, K. L. More, G. Wang, D. Su, D. A. Cullen, L. Fei, S. Litster and G. Wu, Single Cobalt Sites Dispersed in Hierarchically Porous Nanofiber Networks for Durable and High-Power PGM-Free Cathodes in Fuel Cells, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, e2003577 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Miao, Y. Xia, J. Liang, L. Xie, S. Chen, S. Li, H. L. Wang, S. Hu, J. Han and Q. Li, Constructing Co-N-C Catalyst via a Double Crosslinking Hydrogel Strategy for Enhanced Oxygen Reduction Catalysis in Fuel Cells, Small, 2021, 17, e2100735 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Xiao, H. Zhang, Y. Chen, J. Zhu, L. Gao, Z. Jin, J. Ge, Z. Jiang, S. Chen, C. Liu and W. Xing, Identification of binuclear Co2N5 active sites for oxygen reduction reaction with more than one magnitude higher activity than single atom CoN4 site, Nano Energy, 2018, 46, 396–403 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhou, P. Zhou, Y. Zhang, B. Liu, P. Gao and S. Guo, 3D star-like atypical hybrid MOF derived single-atom catalyst boosts oxygen reduction catalysis, J. Energy Chem., 2021, 55, 355–360 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Iqbal, S. Ali, G. Yasin, S. Ibraheem, M. Tabish, M. Hamza, H. Chen, H. Xu, J. Zeng and W. Zhao, A novel 2D Co3(HADQ)2 metal-organic framework as a highly active and stable electrocatalyst for acidic oxygen reduction, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 430, 132642–132649 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, Z. Zhou, F. Wang, Y. Li and Y. Jing, Two-Dimensional Metal Hexahydroxybenzene Frameworks as Promising Electrocatalysts for an Oxygen Reduction Reaction, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 8, 7472–7479 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Iqbal, M. Q. Sultan, S. Hussain, M. Hamza, A. Tariq, M. B. Akbar, Y. Ma and L. Zhi, The Different Roles of Cobalt and Manganese in Metal-Organic Frameworks for Supercapacitors, Adv. Mater. Technol., 2021, 6, 2000941–2000949 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Sheberla, L. Sun, M. A. Blood-Forsythe, S. Er, C. R. Wade, C. K. Brozek, A. Aspuru-Guzik and M. Dinca, High Electrical Conductivity in Ni-3(2,3,6,7,10,11-hexaiminotriphenylene)(2), a Semiconducting Metal-Organic Graphene Analogue, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 8859–8862 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wang, Y. Liang, Y. Li and H. Dai, Co(1-x)S-graphene hybrid: a high-performance metal chalcogenide electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 10969–10972 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Wang, C. Yang, Y. Liu, M. Yang, X. Li, Y. He, H. Li, H. Chen and Z. Lin, Dual-Shelled Multidoped Hollow Carbon Nanocages with Hierarchical Porosity for High-Performance Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Both Alkaline and Acidic Media, Nano Lett., 2020, 20, 5639–5645 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Zhang, P. Li, H. Zhao, L. Zong and L. Wang, Metal-free honeycomb-like electrocatalyst with high specific mass activity for accelerated oxygen reduction reaction in both alkaline and acidic media, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2022, 579, 152149–152156 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Yang, H. Jin, C. Cui, J. Li, J. Wang, K. Amine, J. Lu and S. Wang, Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped porous carbon sheets for energy storage and pH-universal oxygen reduction reaction, Nano Energy, 2018, 54, 192–199 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Chen, K. Liu, P. An, H. Li, Y. Lin, J. Hu, C. Jia, J. Fu, H. Li, H. Liu, Z. Lin, W. Li, J. Li, Y.-R. Lu, T.-S. Chan, N. Zhang and M. Liu, Iron phthalocyanine with coordination induced electronic localization to boost oxygen reduction reaction, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 4173–4180 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Cao, R. Thapa, H. Kim, X. Xu, M. G. Kim, Q. Li, N. Park, M. Liu and J. Cho, Promotion of oxygen reduction by a bio-inspired tethered iron phthalocyanine carbon nanotube-based catalyst, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 2076–2082 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Chen, R. Gao, S. Ji, H. Li, K. Tang, P. Jiang, H. Hu, Z. Zhang, H. Hao, Q. Qu, X. Liang, W. Chen, J. Dong, D. Wang and Y. Li, Atomic-Level Modulation of Electronic Density at Cobalt Single-Atom Sites Derived from Metal-Organic Frameworks: Enhanced Oxygen Reduction Performance, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 3212–3221 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. S. Olson, S. Pylypenko, J. E. Fulghum and P. Atanassov, Bifunctional Oxygen Reduction Reaction Mechanism on Non-Platinum Catalysts Derived from Pyrolyzed Porphyrins, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2010, 157, B54–B63 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, M. Chen, D. A. Cullen, S. Hwang, M. Wang, B. Li, K. Liu, S. Karakalos, M. Lucero, H. Zhang, C. Lei, H. Xu, G. E. Sterbinsky, Z. Feng, D. Su, K. L. More, G. Wang, Z. Wang and G. Wu, Atomically dispersed manganese catalysts for oxygen reduction in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells, Nat. Catal., 2018, 1, 935–945 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Luo, H. Zhang, X. Wang, L. Gao, L. Gong, T. Zhao, Z. Jin, J. Ge, Z. Jiang, C. Liu and W. Xing, Single-Atom Cr-N4 Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Catalysis in Acid Media, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 12469–12475 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Luo, A. Roy, L. Silvioli, D. A. Cullen, A. Zitolo, M. T. Sougrati, I. C. Oguz, T. Mineva, D. Teschner, S. Wagner, J. Wen, F. Dionigi, U. I. Kramm, J. Rossmeisl, F. Jaouen and P. Strasser, P-block single-metal-site tin/nitrogen-doped carbon fuel cell cathode catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction, Nat. Mater., 2020, 19, 1215–1223 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Y. Ma, J. Ran, S. Dai, M. Jaroniec and S. Z. Qiao, Phosphorus-Doped Graphitic Carbon Nitrides Grown In Situ on Carbon-Fiber Paper: Flexible and Reversible Oxygen Electrodes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 4646–4650 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Singh, F. Razmjooei and J.-S. Yu, Active sites and factors influencing them for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in metal-N coordinated pyrolyzed and non-pyrolyzed catalysts: a review, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 20095–20119 RSC.
- R. Hu, Y. Li, Q. Zeng and J. Shang, Role of active sites in N-coordinated Fe-Co dual-metal doped graphene for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions: A theoretical insight, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 525, 146588–146596 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Wang, X. Jin, C. Zhu, Y. Liu, H. Tan, R. Ku, Y. Zhang, L. Zhou, Z. Liu, S. J. Hwang and H. J. Fan, Atomically Dispersed Co2-N6 and Fe-N4 Costructures Boost Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Both Alkaline and Acidic Media, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, e2104718 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. H. Yin, J. Yang, Y. Han, G. Li, L. Y. Wan, Y. H. Chen, C. Chen, X. M. Qu, Y. X. Jiang and S. G. Sun, Construction of Highly Active Metal-Containing Nanoparticles and FeCo-N4 Composite Sites for the Acidic Oxygen Reduction Reaction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 21976–21979 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Jiang, F. Wang, F. Yang, H. He, J. Yang, W. Zhang, J. Luo, J. Zhang and C. Fu, Rationalization on high-loading iron and cobalt dual metal single atoms and mechanistic insight into the oxygen reduction reaction, Nano Energy, 2022, 93, 106793–106802 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, W. Liu, G. Luo, Z. Li, C. Zhao, H. Zhang, M. Zhu, Q. Xu, X. Wang, C. Zhao, Y. Qu, Z. Yang, T. Yao, Y. Li, Y. Lin, Y. Wu and Y. Li, Synergistic effect of well-defined dual sites boosting the oxygen reduction reaction, Energy Environ. Sci., 2018, 11, 3375–3379 RSC.
- Y.-b. Chen, J.-j. Li, Y.-p. Zhu, J. Zou, H. Zhao, C. Chen, Q.-q. Cheng, B. Yang, L.-l. Zou, Z.-q. Zou and H. Yang, Vicinal Co atom-coordinated Fe–N–C catalysts to boost the oxygen reduction reaction, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 9886–9891 RSC.
- N. Yang, L. Peng, L. Li, J. Li, Q. Liao, M. Shao and Z. Wei, Theoretically probing the possible degradation mechanisms of an FeNC catalyst during the oxygen reduction reaction, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 12476–12484 RSC.
- G. Yang, J. Zhu, P. Yuan, Y. Hu, G. Qu, B. A. Lu, X. Xue, H. Yin, W. Cheng, J. Cheng, W. Xu, J. Li, J. Hu, S. Mu and J. N. Zhang, Regulating Fe-spin state by atomically dispersed Mn-N in Fe-N-C catalysts with high oxygen reduction activity, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 1734 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Cai, G. Zhang, X. Zhang, B. Chen, Z. Lu, H. Xu, R. Gao and C. Shi, Engineering the Local Coordination Environment and Density of FeN4 Sites by Mn Cooperation for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction, Small, 2022, 18, e2200911 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. He, Y. Chen, Q. Liu, B. Lu, X. Song, H. Liu, M. Liu, Y. N. Liu, Y. Zhang, X. Ouyang and S. Chen, Theory-Guided Regulation of FeN4 Spin State by Neighboring Cu Atoms for Enhanced Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysis in Flexible Metal-Air Batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, e202201007, DOI:10.1002/anie.202201007.
- C. Du, Y. Gao, H. Chen, P. Li, S. Zhu, J. Wang, Q. He and W. Chen, A Cu and Fe dual-atom nanozyme mimicking cytochrome c oxidase to boost the oxygen reduction reaction, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 16994–17001 RSC.
- S. Song, X. M. Zhang, X. L. Xu, C. C. Wu, H. Q. Li, Z. X. Xia, S. S. Yu, S. L. Wang and G. Q. Sun, Iron, Copper and Nitrogen Co-doped Carbon with Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity towards Oxygen Reduction, ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7, 3116–3122 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Li, S. Di, P. Niu, S. Wang, J. Wang and L. Li, A durable half-metallic diatomic catalyst for efficient oxygen reduction, Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15, 1601–1610 RSC.
- Z. Li, H. He, H. Cao, S. Sun, W. Diao, D. Gao, P. Lu, S. Zhang, Z. Guo, M. Li, R. Liu, D. Ren, C. Liu, Y. Zhang, Z. Yang, J. Jiang and G. Zhang, Atomic Co/Ni dual sites and Co/Ni alloy nanoparticles in N-doped porous Janus-like carbon frameworks for bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 240, 112–121 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Zhang, P. Kumar, X. Zhu, R. Daiyan, N. M. Bedford, K. H. Wu, Z. Han, T. Zhang, R. Amal and X. Lu, Electronically Modified Atomic Sites Within a Multicomponent Co/Cu Composite for Efficient Oxygen Electroreduction, Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11, 2100303–2100313 CrossRef CAS.
- S. S. A. Shah, T. Najam, M. S. Javed, M. M. Rahman and P. Tsiakaras, Novel Mn-/Co-Nx Moieties Captured in N-Doped Carbon Nanotubes for Enhanced Oxygen Reduction Activity and Stability in Acidic and Alkaline Media, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 23191–23200 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang, R. Xu, Y. Sun, Q. Liu, M. Xia, Y. Li, F. Gao, Y. Zhao and J. S. Tse, Identifying the Zn–Co binary as a robust bifunctional electrocatalyst in oxygen reduction and evolution reactions via shifting the apexes of the volcano plot, J. Energy Chem., 2021, 55, 162–168 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Cao, Y. Shao, H. Pan and Z. Lu, Designing Efficient Dual-Metal Single-Atom Electrocatalyst TMZnN6 (TM = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) for Oxygen Reduction Reaction, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2020, 124, 11301–11307 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, S. Chen, N. Yang, M. Deng, S. Ibraheem, J. Deng, J. Li, L. Li and Z. Wei, Ultrahigh-Loading Zinc Single-Atom Catalyst for Highly Efficient Oxygen Reduction in Both Acidic and Alkaline Media, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 7035–7039 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Mueller-Huelstede, D. Schonvogel, H. Schmies, P. Wagner, A. Dyck and M. Wark, Incorporation of Activated Biomasses in Fe-N-C Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction with Enhanced Stability in Acidic Media, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2021, 4, 6912–6922 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Xia, X. Yang, L. Xie, Y. Wei, W. Jiang, M. Dou, X. Li, J. Li, L. Gan and F. Kang, Direct Growth of Carbon Nanotubes Doped with Single Atomic Fe–N4 Active Sites and Neighboring Graphitic Nitrogen for Efficient and Stable Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysis, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1906174–1906183 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wan, X. Liu, Y. Li, R. Yu, L. Zheng, W. Yan, H. Wang, M. Xu and J. Shui, Fe–N–C electrocatalyst with dense active sites and efficient mass transport for high-performance proton exchange membrane fuel cells, Nat. Catal., 2019, 2, 259–268 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Wang, Y. Yang, F. Sun, G. Chen, J. Wang, L. Peng, W. T. Chen, L. Shang, J. Zhao, D. Sun-Waterhouse, T. Zhang and G. I. N. Waterhouse, Molten NaCl-Assisted Synthesis of Porous Fe-N-C Electrocatalysts with a High Density of Catalytically Accessible FeN4 Active Sites and Outstanding Oxygen Reduction Reaction Performance, Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11, 2100219–2100227 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Jiao, J. Li, L. L. Richard, Q. Sun, T. Stracensky, E. Liu, M. T. Sougrati, Z. Zhao, F. Yang, S. Zhong, H. Xu, S. Mukerjee, Y. Huang, D. A. Cullen, J. H. Park, M. Ferrandon, D. J. Myers, F. Jaouen and Q. Jia, Chemical vapour deposition of Fe–N–C oxygen reduction catalysts with full utilization of dense Fe–N4 sites, Nat. Mater., 2021, 20, 1385–1391 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © Institute of Process Engineering of CAS 2023 |




