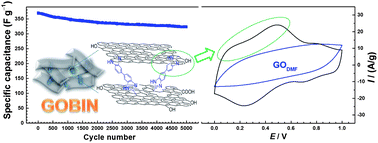
The synthesis of graphene oxide (GO)-based benzimidazole-crosslinked network (GOBIN) materials is presented. These materials are prepared by the covalent crosslinking of GO sheets using a condensation reaction between the carboxylic acid moieties on the GO surface and the o-aminophenyl end groups of 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (or 1,2,4,5-benzenetetraamine tetrahydrochloride). An efficient one-pot catalyst- and template-free synthesis was performed. The obtained porous GO-based materials possess a Brunauer–Emmett–Teller specific surface area ranging from 260 to 920 m2 g−1. Electrochemical testing indicates that the GOBIN materials display a specific capacitance up to 370 F g−1 at a current density of 0.1 A g−1 and about 90% of the original capacitance is retained after 5000 cycles at a current density of 3 A g−1. Therefore, GOBIN materials can be employed as promising electrode materials for high-performance supercapacitors with outstanding cycling stability. Furthermore, owing to their significantly high specific surface area, these materials also show hydrogen uptake (up to 1.24 wt%, at 77 K and 1.0 bar) and carbon dioxide capture (up to 14.2 wt%, at 273 K and 1.0 bar) properties. As a result, these GO-based porous materials improve both the supercapacitor performance and gas sorption property, which demonstrate an excellent performance in the practical application of energy storage.