Fluorine-containing nano-objects with the same compositions but different segment distributions: synthesis, characterization and comparison
Abstract
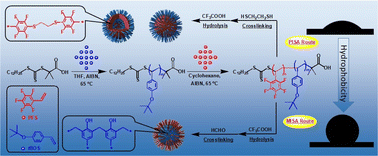
Fluorine-containing nano-objects with the same compositions but different segment distributions were investigated. Using a polymerization-induced self-assembly (PISA) process, nano-objects with a poly(pentafluorostyrene) (PPFS) core and a poly(4-hydroxystyrene) (PHOS) shell were prepared and in situ stabilized by reaction between 1,2-ethanedithiol and the pentafluorobenzene groups on the PPFS. Alternatively, using a modification-induced self-assembly (MISA) process, nano-objects with a PPFS shell and a PHOS core were prepared and in situ stabilized by reaction between formaldehyde and the phenol groups on the PHOS. The generated copolymers and nano-objects were comprehensively characterized by SEC, 1H NMR, TEM and DLS measurements. The contact angles of the fluorine-containing nano-objects were examined to evaluate the hydrophilic/hydrophobic properties. As expected, the nano-objects with PPFS as a shell showed the highest contact angle of 130.3°, while those with PHOS as a shell have the lowest contact angle of 42.5°. When the composition remained the same, the segment distribution showed a significant effect on the hydrophilic/hydrophobic properties of the fluorine-containing nano-objects. According to this strategy, the properties and applications of fluorine-containing nano-objects can be effectively modulated by altering the segment distribution, even with a defined content of fluorine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...