Mixed mechanisms of bond exchange in covalent adaptable networks: monitoring the contribution of reversible exchange and reversible addition in thiol–succinic anhydride dynamic networks†
Abstract
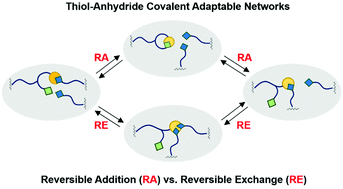
Dynamic photopolymer networks that take advantage of the thermodynamically controlled reversibility of thiol–succinic anhydride adducts were synthesized from commercial substrates and investigated as a new class of covalent adaptable networks (CANs). Through systematic studies of the catalyst and stoichiometry effects on the exchange dynamics two distinctive exchange mechanisms were found, and then demonstrated to contribute to the overall dynamic characteristics. By varying the catalyst activity, i.e. basicity and/or nucleophilicity, control over the dynamic responsiveness through changes in the type of dynamic covalent chemistry mode (reversible addition vs. reversible exchange) was achieved in otherwise compositionally analogous materials. More specifically, the participation of the associative mechanism (thiol–thioester exchange) in the otherwise dissociative networks, and its relevance on materials properties was demonstrated by dielectric analysis (DEA) and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA). The activation energies (Ea) for viscous flow obtained from DMA stress relaxation experiments and from dielectric modulus and loss crossover points were shown to match well between the two techniques. The Ea in stoichiometric systems was found to be 110–120 kJ mol−1, whereas 50% excess thiol systems were characterized by Ea ranging 95–105 kJ mol−1. The thermodynamic equilibrium conversion, estimated in the temperature controlled FTIR, for a stoichiometric 3-mercaptopropionate-succinic anhydride combination was determined at 92 ± 1% at ambient temperature, and decreased to 67 ± 1% at 120 °C within one hour of equilibration time (ΔH° = −46 ± 5 kJ mol−1). Such high potential for reversibility of the thioester anhydride linkages resembles maleimide-furan Diels–Alder networks but has many other attributes that make these CANs of unprecedented value in fundamental research on dynamic materials.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Polymer Chemistry Most Popular 2020 and Chemistry for Covalent Adaptable Polymer Networks


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...