l-Ascorbic acid oxygen-induced micro-electronic fields over metal-free polyimide for peroxymonosulfate activation to realize efficient multi-pathway destruction of contaminants†
Abstract
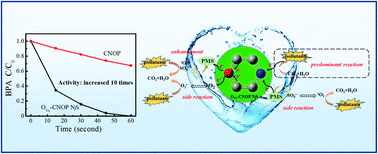
Peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation in heterogeneous processes for pollutant removal is a promising water treatment technique. However, the existing rate limiting step of the metal-containing system greatly restrains its performance and increases the consumption of PMS and energy. Herein, we describe an efficient, metal-free strategy for solving these problems. In this study, L-ascorbic acid O-doped carbon–nitrogen–oxygen polymer nano-flowers (OVc-CNOP Nfs) were fabricated via a facile thermal polymerization process. The metal-free OVc-CNOP Nfs showed excellent activity and stability in PMS activation for the degradation of various organic pollutants. Even the refractory endocrine interferon bisphenol A can be completely removed in just 1 min. Doping with O induced bidirectional transfer of electrons on aromatic rings through C–O–C bonding [C(π)→O←C(π)], which led to the formation of micro-electronic fields on the catalyst surface. During the reaction, efficient oxidation of organic pollutants by utilizing the charges of pollutants themselves around the electron-poor C(π) areas inhibited undesirable oxidation of PMS and promoted PMS reduction in the electron-rich O areas to generate hydroxyl (˙OH) and sulfate (SO4˙−) radicals. The reduction of dissolved oxygen to O2˙− around the electron-rich O areas also destroyed the pollutants, and this further drove electron donation from the pollutants and accelerated catalytic oxidation. These multi-pathway synergistic processes involving oxidation of the pollutants themselves and attack by free radicals enabled rapid degradation of contaminants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...