An effective surface modification strategy with high reproducibility for simultaneously improving efficiency and stability of inverted MA-free perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
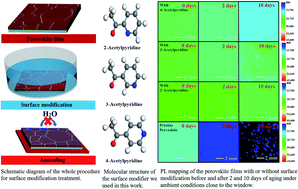
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have become the front-running photovoltaic technology and have triggered enormous research interest worldwide owing to their ultra-high solar-to-electric power conversion efficiency and low fabrication costs, but their poor intrinsic stability issues still constitute the main obstacles that hinder their rapid commercialization. Herein, we demonstrate that, by carefully designing the modifier's molecular structure, a facile, highly reproducible and scalable surface modification strategy can effectively enhance both the stability and efficiency of inverted PSCs. The most efficient modifier (2-acetylpyridine) can not only passivate the surface traps of the perovskite film but also enhance its stability against moisture by forming a hydrophobic capping layer on top. Accordingly, the efficiency of the inverted PSC has been improved from 16.75% to 20.05% for the best-performing one, which is, to our knowledge, among the highest values for inverted MA-free PSCs. More encouragingly, the stability of the modified devices can also be largely enhanced: the devices retained 95%, 90%, and 91% of their initial efficiencies after storage in the dark in ambient air for 2000 hours, 85 °C thermal aging for 500 hours in the dark, and light soaking at 45 °C for 500 hours, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...