Laser cleavable probes for in situ multiplexed glycan detection by single cell mass spectrometry†
Abstract
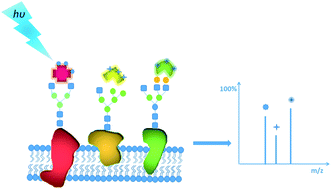
Glycans binding on the cell surface through glycosylation play a key role in controlling various cellular processes, and glycan analysis at a single-cell level is necessary to study cellular heterogeneity and diagnose diseases in the early stage. Herein, we synthesized a series of laser cleavable probes, which could sensitively detect glycans on single cells and tissues by laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (LDI-MS). This multiplexed and quantitative glycan detection was applied to evaluate the alterations of four types of glycans on breast cancer cells and drug-resistant cancer cells at a single-cell level, indicating that drug resistance may be related to the upregulation of glycan with a β-D-galactoside (Galβ) group and Neu5Aca2-6Gal(NAc)-R. Moreover, the glycan spatial distribution in cancerous and paracancerous human tissues was also demonstrated by MS imaging, showing that glycans are overexpressed in cancerous tissues. Therefore, this single-cell MS approach exhibits promise for application in studying glycan functions which are essential for clinical biomarker discovery and diagnosis of related diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...