MXene as a non-metal charge mediator in 2D layered CdS@Ti3C2@TiO2 composites with superior Z-scheme visible light-driven photocatalytic activity†
Abstract
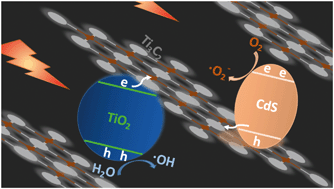
Exploitation of photocatalysts towards efficient organic pollutant degradation is highly desirable in the field of environmental remediation. Here, we report a rational synthesis of two-dimensional CdS@Ti3C2@TiO2 nanohybrids by facile calcination and a subsequent hydrothermal process. The physico-chemical properties of CdS@Ti3C2@TiO2 were investigated by a variety of characterization techniques. The effect of CdS loading on the photocatalytic performance was elucidated. When compared with Ti3C2 and Ti3C2@TiO2, the optimal ternary nanostructures exhibited significantly enhanced visible light-driven (λ ≥ 420 nm) degradation of sulfachloropyridazine, phenol and several typical dyes. The origin of improved photocatalytic performance mainly stems from the enhanced electron–hole separation efficiency. The charge carrier sinking function of Ti3C2 in this first time pre-fabricated three-phase Z-scheme catalyst was proposed based on UV-visible spectroscopy band gap calculation, photoluminescence measurement and photoelectrochemical analysis. The electron paramagnetic resonance assay verified that both superoxide ions and hydroxyl radicals played crucial roles in the removal of contaminants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...