Modeling the electrical double layer to understand the reaction environment in a CO2 electrocatalytic system†
Abstract
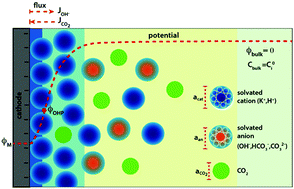
The environment of a CO2 electroreduction (CO2ER) catalyst is intimately coupled with the surface reaction energetics and is therefore a critical aspect of the overall system performance. The immediate reaction environment of the electrocatalyst constitutes the electrical double layer (EDL) which extends a few nanometers into the electrolyte and screens the surface charge density. In this study, we resolve the species concentrations and potential profiles in the EDL of a CO2ER system by self-consistently solving the migration, diffusion and reaction phenomena using the generalized modified Poisson–Nernst–Planck (GMPNP) equations which include the effect of volume exclusion due to the solvated size of solution species. We demonstrate that the concentration of solvated cations builds at the outer Helmholtz plane (OHP) with increasing applied potential until the steric limit is reached. The formation of the EDL is expected to have important consequences for the transport of the CO2 molecule to the catalyst surface. The electric field in the EDL diminishes the pH in the first 5 nm from the OHP, with an accumulation of protons and a concomitant depletion of hydroxide ions. This is a considerable departure from the results obtained using reaction-diffusion models where migration is ignored. Finally, we use the GMPNP model to compare the nature of the EDL for different alkali metal cations to show the effect of solvated size and polarization of water on the resultant electric field. Our results establish the significance of the EDL and electrostatic forces in defining the local reaction environment of CO2 electrocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...