Heteroaggregation behavior of graphene oxide on Zr-based metal–organic frameworks in aqueous solutions: a combined experimental and theoretical study†
Abstract
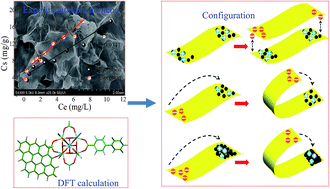
A series of zirconium-based metal–organic frameworks (Zr-based MOFs) (UiO-66, UiO-66-NH2, UiO-66-OH, UiO-66-(OH)2 and UiO-67) with different surface charge properties and geometric dimensions were tested to decrease the concentration of graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets in aqueous solutions. Based on the experimental results and density functional theory (DFT) calculations, UiO-67 showed the highest adsorption capacity of all Zr-based MOFs studied herein. The π–π interaction/stacking, hydrogen bonding and Lewis acid–base interactions were the main cause for the removal of GO by negatively charged UiO-66-OH and UiO-66-(OH)2. Electrostatic attractions governed the association between GO and positively charged Zr-based MOFs (UiO-66, UiO-66-NH2 and UiO-67) via heteroaggregation. All adsorption and desorption isotherms of GO on UiO-66, UiO-66-NH2 or UiO-67 followed the linear model, and the obvious intercept (27–51 mg g−1) between adsorption–desorption isotherms disclosed that the GO adsorption over these MOFs was irreversible. This irreversible phenomenon was associated with a type of specific sheet–particle configuration, in which the particles of Zr-based MOFs were wrapped by GO nanosheets to form multilayered GO–MOF heteroaggregates with high geometric stability. The DFT calculations showed that the most stable adsorption structures were the geometries with the para-site of the linked ligand. Given the low-cost and simple preparation of Zr-based MOFs, it is clear that Zr-based MOFs could potentially act as coagulants for the efficient elimination of GO from aqueous solutions. This experimental evidence provides valuable information for the understanding of the interaction between GO and coagulants, and the potential fate, toxicity and migration of GO under natural conditions in aquatic environments, as well as in soils and sediments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...