Low bandgap semiconducting polymers for polymeric photovoltaics
Abstract
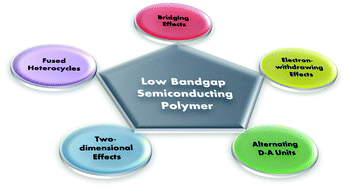
In order to develop high performance polymer solar cells (PSCs), full exploitation of the sun-irradiation from ultraviolet (UV) to near infrared (NIR) is one of the key factors to ensure high photocurrents and thus high efficiency. In this review, five of the effective design rules for approaching LBG semiconducting polymers with high molar absorptivity, suitable energy levels, high charge carrier mobility and high solubility in organic solvents are overviewed. These design stratagems include fused heterocycles for facilitating π-electron flowing along the polymer backbone, groups/atoms bridging adjacent rings for maintaining a high planarity, introduction of electron-withdrawing units for lowering the bandgap (Eg), donor–acceptor (D–A) copolymerization for narrowing Eg and 2-dimensional conjugation for broadened absorption and enhanced hole mobility. It has been demonstrated that LBG semiconducting polymers based on electron-donor units combined with strong electron-withdrawing units possess excellent electronic and optic properties, emerging as excellent candidates for efficient PSCs. While for ultrasensitive photodetectors (PDs), which have intensive applications in both scientific and industrial sectors, sensing from the UV to the NIR region is of critical importance. For polymer PDs, Eg as low as 0.8 eV has been obtained through a rational design stratagem, covering a broad wavelength range from the UV to the NIR region (1450 nm). However, the response time of the polymer PDs are severely limited by the hole mobility of LBG semiconducting polymers, which is significantly lower than those of the inorganic materials. Thus, further advancing the hole mobility of LBG semiconducting polymers is of equal importance as broadening the spectral response for approaching uncooled ultrasensitive broadband polymer PDs in the future study.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...