Assembly and relaxation behaviours of phosphatidylethanolamine monolayers investigated by polarization and frequency resolved SFG-VS†
Abstract
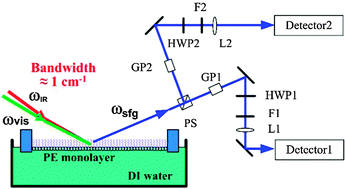
The assembly conformation and kinetics of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) lipids are the key to their membrane curvatures and activities, such as exocytosis, endocytosis and Golgi membrane fusion. In the current study, a polarization and frequency resolved (bandwidth ≈ 1 cm−1) picosecond sum frequency generation (SFG) system was developed to characterize phosphatidylethanolamine monolayers. In addition to obtaining π–A isotherms and Brewster angle microscopy (BAM) images, the conformational changes and assembly behaviors of phosphatidylethanolamine molecules are investigated by analyzing the SFG spectra collected at various surface pressures (SPs). The compression kinetics and relaxation kinetics of phosphatidylethanolamine monolayers are also reported. The conformational changes of PE molecules during the monolayer compression are separated into several stages: reorientation of the head group PO2− in the beginning of the liquid-expanded (LE) phase, conformational changes of head group alkyl chains in the LE phase, and conformational changes of tail group alkyl chains in the LE–liquid condensed (LE–LC) phase. Such an understanding may help researchers to effectively control the lipid molecular conformation and membrane curvatures during the exocytosis/endocytosis processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...