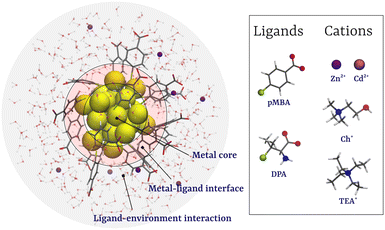
A molecular dynamics study on the ion-mediated self-assembly of monolayer-protected nanoclusters†
Vikas
Tiwari
 ,
Anushna
Bhattacharyya
and
Tarak
Karmakar
,
Anushna
Bhattacharyya
and
Tarak
Karmakar
 *
*
Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, Hauz Khas, New Delhi 110016, India. E-mail: tkarmakar@chemistry.iitd.ac.in
First published on 17th July 2024
Abstract
We studied the effects of metal and molecular cations on the aggregation of atomically precise monolayer-protected nanoclusters (MPCs) in an explicit solvent using atomistic molecular dynamics simulations. While divalent cations such as Zn2+ and Cd2+ promote aggregation by forming ligand–cation–ligand bridges between the MPCs, molecular cations such as tetraethylammonium and cholinium inhibit their aggregation by getting adsorbed into the MPC's ligand shell and reducing the ligand's motion. Here, we studied the aggregation of Au25(SR)18 nanoclusters with two types of ligands, para-mercaptobenzoic acid and D-penicillamine, as prototypical examples.
1 Introduction
Atomically precise monolayer-protected metal nanoclusters (MPCs), an emerging class of nanometer-sized (<3 nm) molecules having a metal core encircled by a layer of ligands, have redefined the realm of polydisperse nanoparticles.1,2 The well-defined metal core and the monolayer of ligands give rise to the distinctive structural features and properties of MPCs.3–6 Crucial possibilities for multiple domains arise from the substantial changes that occur to different physicochemical characteristics of MPCs when they undergo aggregation.7–10 Among the potential applications are the fabrication of nanodevices11 and nanomaterials,12 as well as the modification or enhancement of their optical13,14 or magnetic behavior.15,16The exploration of nanocluster (NC) aggregation has emerged as a focal point of interest within the nanomaterials community.17–24 This attention is primarily fueled by the recognition that aggregation induces significant alterations in the physicochemical properties of metal NCs when compared to their dispersed state.25–27 Among the myriad of properties exhibited by these NCs, photoluminescence (PL) holds particular importance and can be tuned through various strategies. Notably, aggregation-induced emission (AIE)28 has garnered attention due to its remarkable ability to enhance the photoluminescence of metal NCs, resulting in exceptionally high quantum yields.25,29–33 AIE involves the implementation of cation-mediated aggregation of MPCs protected with negatively charged ligand head groups such as carboxylates. In this approach, the aggregation of MPCs is stimulated by introducing oppositely charged species into the solution. The formation of aggregates is facilitated by strong electrostatic interactions between the negatively charged (polar) ligands of the MPCs and metal cations in the solution, leading to the facile formation of aggregates.
Bain et al. recently reported that the addition of a divalent Zn2+ ion caused the NCs to aggregate, resulting in a significant PL boost of Au NCs.34 Yao et al. employed a straightforward and versatile technique that involved carefully generating electrostatic interactions between negatively charged ligands and divalent cations (such as Zn2+ and Cd2+).35 In the presence of the counter ion Zn2+, Kuppan and his group studied the self-assembly of highly ordered, one-dimensional green emitting NCs from randomly aggregated Au NCs.36 Zn2+-induced gold cluster aggregation was also employed to develop an electro-chemiluminescence (ECL) biosensor with extraordinary sensitivity for microRNA-21 detection, using it as a high-efficiency ECL emitter.37 Qu et al. observed a noticeable increase in glutathione-AuNC emission enhancement upon the addition of Zn2+ and Cd2+ in the presence of silicon nanoparticles and thus developed a ratiometric sensor to measure the relevant ions.38 Thus, cations can be used to induce MPC aggregation, and alternatively, cation-induced aggregation may be utilized for the detection of metal ions in solution-sensing applications.
Ion-mediated AIE in MPCs has shown promising applications39–41 in various fields, which in turn needs a proper detailed understanding of the aggregation mechanism. An atomistic understanding of the interactions of various types of cations (metal and molecular) with MPC ligands and the mechanism of cation-induced aggregation is crucial for the rational design of ligands for MPC preparation and choosing the MPC–cation combinations.
In this work, we have studied the cation-induced aggregation of Au25(SR)18 NCs with two types of ligands, para-mercaptobenzoic acid (pMBA), a simple aromatic carboxylate, and D-penicillamine (DPA),34 a peptide-based ligand, as prototypical ligands (Fig. 1). Using molecular dynamics (MD) and enhanced sampling simulations, we studied the effects of metal cations Zn2+ and Cd2+ and molecular cations cholinium (Ch+) and tetraethylammonium (TEA+) on the aggregation of MPCs (Fig. 1). Our results show that while Zn2+ and Cd2+ ions promote the aggregation of Au-NCs, the bulky molecular cations, Ch+ and TEA+, inhibit the self-assembly.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Dimerization
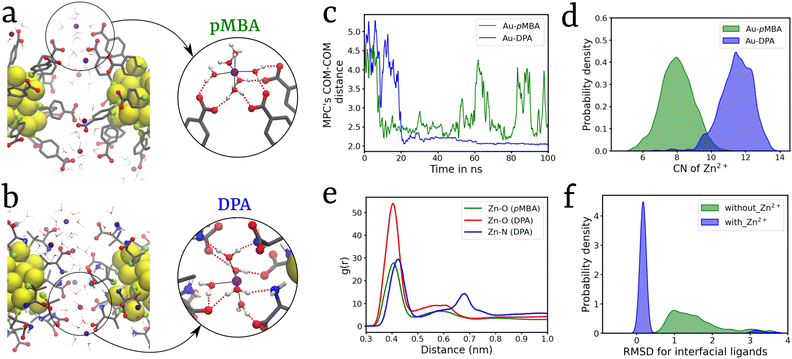
Studying dimerization serves as a crucial avenue for comprehending the self-assembly processes of MPCs as it elucidates the pivotal interactions responsible for the formation of self-assembled structures.23,24 Hence, a dimeric system was set up using pre-equilibrated monomers of Au25(SR)18 MPCs with two types of ligands: (1) pMBA and (2) DPA (Fig. 1). In both the ligands, we chose deprotonated carboxylic acid groups based on experimental results indicating that increased photoluminescence of the nanocluster is observed at a high pH value (8).34 At this pH, all pMBA ligands are found to be deprotonated.42 Equilibrium MD simulations of these two dimeric systems were performed for 100 ns in the presence of Zn2+ ions with a Zn2+ to ligand ratio (R[Zn2+/ligand]) of 1.0, which is selected based on simulations performed at various values of R[Zn2+/ligand] (Fig. S1†). Formation of an MPC-dimer was observed in both Au25(pMBA)18 and Au25(DPA)18 systems (Fig. 2a and b). The simulation trajectories were analyzed for MPC's COM–COM distance, and the Au-DPA system showed the formation of a relatively more stable dimer within ∼25 ns simulation time, which remained intact throughout the entire simulation. On the other hand, the dimer formed in the Au-pMBA system was comparatively less stable, and the back-and-forth transitions between the dimeric and monomeric states were frequently observed, which implies comparable stability between the two states (Fig. 2c). Self-assembly can be induced in the presence of cations by various driving forces such as electrostatic interactions, van der Waals interactions, dipolar interactions, and metal chelation to attain dimerization in the MPCs. After careful observation of the dimer interface, it was observed that the Zn2+ ions interact with the ligands’ carboxylate groups via a solvation shell forming hydrogen bonds (Fig. 2a) along with the electrostatic interactions. Due to the presence of an additional –NH2 group in the DPA ligand, an extended hydrogen bond network was observed in the case of the Au-DPA system (Fig. 2b and video S1†). This also led to a higher number of Zn2+ at the interface of Au-DPA than in Au-pMBA (Fig. 2d). Radial distribution function (RDF) analysis was performed and it confirmed the stronger correlation between Zn and O in Au-DPA compared to that in Au-pMBA (Fig. 2e). The main driving force behind the clustering of MPCs is the strong electrostatic attraction between Zn2+ and the COO− group of the ligand as well as the strong hydrogen bond network formed by the hydration shell of the Zn2+ ions with the ligands.The experimental reports on Zn2+-induced Au-MPC self-assembly show an increase in photoluminescence, attributed to the restricted rotation and vibration of ligands of MPCs exerted by electrostatic interactions of Zn2+ with the ligands’ carboxylate groups. The formation of self-assembly further suppresses the rotation and vibration of ligands, causing an increase in the radiative rate of Zn–Au MPCs while suppressing the nonradiative decay.34,35 Hence, to comprehend the effects of Zn2+ on the rotation and vibration of ligands, we calculated the root mean square deviations (RMSD) of the ligands present at the dimer interface. A kernel density estimation (KDE) was plotted for the dimeric system with (blue) and without (green) Zn2+ ions (Fig. 2f). In the presence of Zn2+ ions, a sharp peak centered at around RMSD = 0.1 nm was obtained, whereas in the absence of Zn2+ ions, ligand RMSD values spread over a range from 0.5 to 3 nm (Fig. 2f). These results explain the conjecture that Zn2+ ions suppress the ligand motions and are in line with experimental observations on the PL enhancement due to cation-mediated MPC aggregation.34,35
To further understand the energetics of Au-DPA MPC dimerization, we carried out a well-tempered metadynamics (WTMetaD) simulation using two collective variables, s1, which is the COM–COM distance between the MPCs, and s2, which is the interfacial Zn2+ coordination number (Fig. S2†). The reweighted free energy surface (FES) is plotted on the s1 and s2 variable spaces (Fig. 3). The Au-DPA dimer is stable by ∼15 kJ mol−1 with a barrier of a few kJ mol−1 for the monomer-to-dimer transition.
Similar results were obtained when Zn2+ was replaced by Cd2+, as discussed in the ESI section S5 (Fig. S3 and S4†). The effects of these two cations are comparable, which is not surprising, given that Cd is immediately below Zn in group 12 of the periodic table with a larger ionic radius (of the cation) and similar chemical properties. An interesting observation when comparing the interactions of Zn2+ and Cd2+ with ligand –COO− was on the g(r) plots (Fig. 2e and Fig. S3d†); unlike in the former, in the latter case, we observed a sharp peak at 0.2 nm in g(r)Cd–O that corresponds to the penetration of a few carboxylate oxygen atoms into the first coordination shell of the Cd2+ ions. Free energy calculations using the on-the-fly probability-based enhanced sampling (OPES) method43,44 revealed a lower energy barrier for the –COO− binding to Cd2+ than to Zn2+. Furthermore, Zn2+ has another high barrier for entering the double coordinated attachment to the carboxylate ion (see details in section S6 and Fig. S5 and S6 of the ESI†).
2.2 Effect of R[Zn2+/ligand] on the self-assembly of Au-DPA
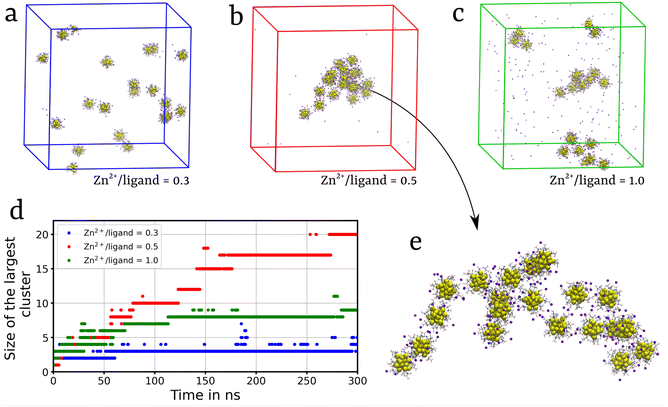
We extended our investigation on the Zn2+-mediated aggregation process and studied the effect of Zn2+ concentration on the aggregation propensity. Recently, Yao et al.35 reported that with increase in the ratio of Zn2+ ions to ligands, R[Zn2+/ligand], the aggregation propensity of Au NCs significantly increased. In particular, the size of self-assembled MPCs was observed to be maximum at a charge balance between ligands and Zn2+ ions, with R[Zn2+/ligand] at around 0.5. Beyond this point, an increase in R[Zn2+/ligand] to 1.0 resulted in a decrease in the size of the self-assembled nanoclusters.35 To further investigate this phenomenon, we conducted a series of simulations with 20 randomly dispersed Au-DPA MPCs and monitored the self-assembly process. Simulations were performed with R[Zn2+/ligand] = 0.3, 0.5, and 1.0. The evolution of the aggregation with the simulation time is shown in Fig. S7 and Video S2.† At R[Zn2+/ligand] = 0.3, small aggregates comprising no more than 3 MPCs were observed (Fig. 4a). Zn2+ ions act as bridges between the clusters, promoting aggregation. However, due to a smaller number of Zn2+ ions compared to those of ligands, the repulsion between the negatively charged ligands dominates over the bridging effect of Zn2+ ions. Whereas, at R[Zn2+/ligand] = 0.5, a charge balance between Zn2+ ions and ligands leads to strong inter-cluster interactions mediated by the Zn2+ induced bridging effect. This results in the formation of multiple small aggregates containing 5–10 MPC molecules, each at the initial stage of the simulation, which, at a later stage, aggregate to form a large cluster containing 20 MPCs (Fig. 4b). Furthermore, increasing R[Zn2+/ligand] to 1.0 resulted in the formation of faster local self-assembled structures composed of 4–5 MPCs (Fig. 4c). Interestingly, unlike in the R[Zn2+/ligand] = 0.5 system, in the R[Zn2+/ligand] = 1 system, the small clusters did not aggregate to form a large cluster. This can be due to the high salt (ZnCl2) concentration, causing electrostatic screening of the charged clusters. The Depth-First Search (DFS) clustering algorithm was employed to monitor the evolution of various clusters and calculate the size of the largest cluster (Fig. 4d). These observations complemented the experimental findings,35 further elucidating the role of Zn2+ ions in MPC's self-assembly. Similar results were obtained when the simulation was carried out in the presence of Cd2+ ions at R[Zn2+/ligand] = 0.5 (Fig. S7d and S8†).2.3 Self-assembly inhibition of Au-MPCs in the presence of Ch+ and TEA+ ions
In contrast to our findings with divalent cations Zn2+ and Cd2+ as mediators in the self-assembly process, the quaternary ammonium cations, namely Ch+ and TEA+, inhibit MPC aggregation. The ion-mediated inhibition strategy has multiple applications such as in biomedical imaging and chemosensing.45 While simulating a system with two Au-pMBA MPCs and Ch+ ions in water, we discovered that the Ch+ cations eventually begin to consolidate or freeze on the MPCs’ surfaces (Fig. 5a). Apart from the electrostatic interactions, due to the planar nature of pMBA ligands, it shows CH–π interactions between the CH bonds of the Ch+ cation and the benzene ring of pMBA ligands (Fig. 5a).46 Whereas, in the case of Au-DPA, because of the bulky DPA ligands, which sterically prevent the cations from approaching closer to MPCs, the ions are restrained from gliding around the MPC's periphery. Hence, Ch+ ions mainly interact via an H-bond with the DPA ligands along with electrostatic attraction (Fig. 5b). The coordination number analysis also shows a higher number of Ch+ ions present around Au-pMBA as compared to Au-DPA (Fig. 5e). Furthermore, the COM–COM distance analysis reveals the presence of only monomers of MPCs in both pMBA and DPA (Fig. 5c). The radial distribution function (g(r)) analysis indicates a stronger correlation between the nitrogen of Ch+ and the oxygen atoms of COO− in pMBA compared to the COO− of DPA (Fig. 5d). In the case of DPA ligands, the g(r) analysis reveals two distinct humps near 0.5 nm, attributed to H-bonding interactions with one of the oxygen atoms of –COO−. Specifically, the first hump corresponds to the distance between the nitrogen and the oxygen atoms involved in H-bonding (N–O1). In contrast, the second hump corresponds to the distance between the nitrogen atom and the other oxygen atoms of COO− (N–O2) (Fig. 5d).Subsequent simulations utilizing TEA+ cations yielded similar results with Au-pMBA. However, with Au-DPA, the bulky nature of TEA+ ions resulted in very weak interactions with the ligands due to steric hindrance. In contrast to Ch+, TEA+ is unable to form hydrogen bonds with the DPA ligands (Fig. S9†). Also, it shows a negligible correlation in RDF analysis and approximately zero probability for coordination with the nanocluster, which suggests that it exists mostly as non-interacting ions in solution (Fig. S9d and e†). Furthermore, a multimeric system consisting of 20 randomly dispersed Au-DPA MPCs was simulated for 100 ns in the presence of TEA+ and Ch+, and the results observed are consistent with our findings in the case of the dimeric system depicting a strong inhibition of the self-assembly. Cluster analysis further confirms the monomeric dispersion (Fig. S10†). Further discussion of these findings can be found in ESI section S8.†
3 Conclusions
In summary, our investigation reveals distinct impacts of divalent metal cations and monovalent molecular cations on the behavior of MPCs. While M2+ ions (where M = Zn, Cd) facilitate the aggregation of MPCs, Ch+ and TEA+ ions hinder the self-assembly process. In the dimerization process, M2+ ions engage in electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged ligands of MPCs, effectively pulling them together to form dimers. Moreover, the water molecules coordinated around the M2+ ions contribute to a robust H-bond network with the ligands, further stabilizing the dimeric structures. Notably, our analysis of R[Zn2+/ligand] aligns well with experimental observations, indicating the formation of the largest clusters occurring at R[Zn2+/ligand] = 0.5, representing the point of charge balance where the total charge on Zn equals the total charge on the ligands. Furthermore, we observed contrasting interactions between Ch+ and TEA+ ions with Au-pMBA and Au-DPA. In the case of Au-pMBA, Ch+ and TEA+ ions exhibit strong interactions, attributed to both electrostatic forces and CH–π interactions. Conversely, with Au-DPA, Ch+ ions were found to interact primarily via H-bonding. However, the steric hindrance caused by TEA+ resulted in repulsion dominating over electrostatic attraction, leading to a weaker correlation between Au-DPA and TEA+ ions.4 Methods
4.1 Force field details
The Au25(SR)18 NC structure and topology were generated using the NanoModeler server.47,48 The gold–sulfur motifs have bonded and non-bonded terms that were developed according to the work of Pohjolainen et al.49 and Heinz et al.50 and implemented in NanoModeler.48 The General AMBER Force Field (GAFF)51 was utilized for MPC ligands and Ch+ and TEA+ ions. The TIP3P potential model was used for water molecules. Lennard-Jones (LJ) force field parameters for Cd2+ were adapted from the work of Araujo et al.524.2 System details
The details of the systems simulated in this work are provided in Table 1.4.3 Well-tempered metadynamics simulation details
The kinetics and thermodynamics of Au-DPA dimerization in the presence of Zn2+ ions were extensively investigated using well-tempered metadynamics simulations.53 Two collective variables were employed for this analysis: s1, representing the COM–COM distance between the two MPCs (with only gold atoms considered for calculating the MPCs’ COM), and s2, indicating the number of Zn2+ ions present at the dimeric interface of the MPCs. The calculation of s2 involved determining the number of coordinated Zn2+ ions around the center of COMs of the MPCs (i.e., the interface) within a radial cutoff of 1 nm.For s1, a Gaussian width (σ) of 0.1 nm was chosen, while for s2, it was set to 0.5 nm. The initial Gaussian height of 1.0 kJ mol−1 was utilized, along with a bias factor of 5, to explore the free energy landscape of the system effectively. These parameters allowed for a thorough characterization of the dimerization process and its energetics in the presence of Zn2+ ions.
Author contributions
The project was conceived and the main conceptual ideas were developed by V.T. and T.K. Computation and analyses were conducted by V.T. and A.B., who also drafted the manuscript and designed the figures. T.K. assisted in interpreting the results and contributed significantly to writing and improving the manuscript. All authors actively participated in discussions regarding the results and contributed to writing the manuscript.Data availability
All input files required to run the simulations presented in this work can be found in a public GitHub repository (https://github.com/vikast282/Ion_med_self_assembly).Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
V. T. is thankful to the Ministry of Education, Govt. of India for the PMR Fellowship. A. B. acknowledges IIT Delhi for the MTech fellowship. T. K. acknowledges the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), New Delhi, India for the Start-up Research Grant (file no. SRG/2022/000969). We also acknowledge IIT Delhi for the Seed Grant. We thank the IIT Delhi HPC facility for computational resources.References
- R. Jin, C. Zeng, M. Zhou and Y. Chen, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 10346–10413 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Chakraborty and T. Pradeep, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 8208–8271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Malola and H. Häkkinen, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 2197 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Nag and T. Pradeep, ACS Nanosci. Au, 2022, 2, 160–178 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Bini, V. Tozzini and G. Brancolini, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2023, 127, 8226–8241 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Brancolini, V. M. Rotello and S. Corni, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23, 2368 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104, 663–667 CrossRef CAS.
- A. W. Snow, M. G. Ancona, W. Kruppa, G. G. Jernigan, E. E. Foos and D. Park, J. Mater. Chem., 2002, 12, 1222–1230 RSC.
- Z. Wu, J. Liu, Y. Li, Z. Cheng, T. Li, H. Zhang, Z. Lu and B. Yang, ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 6315–6323 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. V. Rival, P. Mymoona, K. M. Lakshmi, Nonappa, T. Pradeep and E. S. Shibu, Small, 2021, 17, 2005718 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Aslam, N. Chaki, J. Sharma and K. Vijayamohanan, Curr. Appl. Phys., 2003, 3, 115–127 CrossRef.
- Z. Wu, Q. Yao, S. Zang and J. Xie, ACS Mater. Lett., 2019, 1, 237–248 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Cui, Y. Zhao and Q. Song, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2014, 57, 73–82 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Jin, Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 1549–1565 RSC.
- J. P. Wilcoxon and B. L. Abrams, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2006, 35, 1162 RSC.
- M. Tadic, S. Kralj, M. Jagodic, D. Hanzel and D. Makovec, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 322, 255–264 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Goswami, K. Zheng and J. Xie, Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 13328–13347 RSC.
- Y. Lin, P. Charchar, A. J. Christofferson, M. R. Thomas, N. Todorova, M. M. Mazo, Q. Chen, J. Doutch, R. Richardson, I. Yarovsky and M. M. Stevens, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 18217–18226 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Shen, W. Baker, H. Ye and Y. Li, Nanoscale, 2019, 11, 7371–7385 RSC.
- M. Vanzan, M. Rosa and S. Corni, Nanoscale Adv., 2020, 2, 2842–2852 RSC.
- S. Dutta, S. Corni and G. Brancolini, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22, 3624 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. A. Dar, A. Jana, K. S. Sugi, G. Paramasivam, M. Bodiuzzaman, E. Khatun, A. Som, A. Mahendranath, A. Chakraborty and T. Pradeep, Chem. Mater., 2022, 34, 4703–4711 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Tiwari and T. Karmakar, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2023, 14, 6686–6694 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Bhattacharyya, V. Tiwari and T. Karmakar, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2024, 15, 687–692 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Maity, D. Bain and A. Patra, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123, 2506–2515 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yao, Z. Wu, Z. Liu, Y. Lin, X. Yuan and J. Xie, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 99–127 RSC.
- S. Kolay, D. Bain, S. Maity, A. Devi, A. Patra and R. Antoine, Nanomaterials, 2022, 12, 544 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hong, J. W. Y. Lam and B. Z. Tang, Chem. Commun., 2009, 4332 RSC.
- X. Jia, J. Li and E. Wang, Small, 2013, 9, 3873–3879 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Goswami, Q. Yao, Z. Luo, J. Li, T. Chen and J. Xie, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2016, 7, 962–975 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wu, Q. Yao, S.-q. Zang and J. Xie, Natl. Sci. Rev., 2021, 8, nwaa208 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Bera and N. Goswami, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 9033–9046 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Sahoo and I. Chakraborty, Nanoscale, 2023, 15, 3120–3129 RSC.
- D. Bain, A. Devi, Rashi, S. Chakraborty, S. Kolay and A. Patra, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2023, 127, 18244–18251 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yao, Z. Luo, X. Yuan, Y. Yu, C. Zhang, J. Xie and J. Y. Lee, Sci. Rep., 2014, 4, 3848 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Kuppan and U. Maitra, Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 15494–15504 RSC.
- Z.-C. Shen, Y.-T. Yang, Y.-Z. Guo, Y.-Q. Chai, J.-L. Liu and R. Yuan, Anal. Chem., 2023, 95, 5568–5574 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Qu, L. Zhao, W. Han and J. You, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018, 6, 4995–5002 RSC.
- S. Chandra, Nonappa, G. Beaune, A. Som, S. Zhou, J. Lahtinen, H. Jiang, J. V. Timonen, O. Ikkala and R. H. Ras, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2019, 7, 1900620 CrossRef CAS.
- J. S. Mohanty, K. Chaudhari, C. Sudhakar and T. Pradeep, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123, 28969–28976 CrossRef CAS.
- M. H. Chua, K. L. O. Chin, X. J. Loh, Q. Zhu and J. Xu, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 1845–1878 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Koivisto, X. Chen, S. Donnini, T. Lahtinen, H. Häkkinen, G. Groenhof and M. Pettersson, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120, 10041–10050 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Invernizzi and M. Parrinello, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11, 2731–2736 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Invernizzi and M. Parrinello, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2022, 18, 3988–3996 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, X. Yang, K. Wang, X. He, Q. Wang, J. Huang and Y. Liu, ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 4973–4983 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Yao, L. Liu, S. Malola, M. Ge, H. Xu, Z. Wu, T. Chen, Y. Cao, M. F. Matus, A. Pihlajamäki, Y. Han, H. Häkkinen and J. Xie, Nat. Chem., 2023, 15, 230–239 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Franco-Ulloa, L. Riccardi, F. Rimembrana, M. Pini and M. De Vivo, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2019, 15, 2022–2032 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Franco-Ulloa, L. Riccardi, F. Rimembrana, E. Grottin, M. Pini and M. De Vivo, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2023, 19, 1582–1591 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Pohjolainen, X. Chen, S. Malola, G. Groenhof and H. Häkkinen, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2016, 12, 1342–1350 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Heinz, R. A. Vaia, B. L. Farmer and R. R. Naik, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 17281–17290 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, R. M. Wolf, J. W. Caldwell, P. A. Kollman and D. A. Case, J. Comput. Chem., 2004, 25, 1157–1174 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. S. de Araujo, M. T. Sonoda, O. E. Piro and E. E. Castellano, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2007, 111, 2219–2224 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Barducci, G. Bussi and M. Parrinello, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2008, 100, 020603 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Supplementary figures and videos. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4nr02427c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |