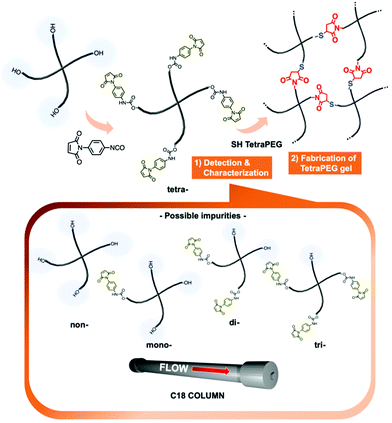
Characterization of N-phenylmaleimide-terminated poly(ethylene glycol)s and their application to a tetra-arm poly(ethylene glycol) gel†
Rikito
Takashima‡
a,
Masashi
Ohira‡
 b,
Hirogi
Yokochi
a,
Daisuke
Aoki
b,
Hirogi
Yokochi
a,
Daisuke
Aoki
 *ac,
Xiang
Li
*ac,
Xiang
Li
 *d and
Hideyuki
Otsuka
*d and
Hideyuki
Otsuka
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 2-12-1 Ookayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 152-8550, Japan. E-mail: daoki@polymer.titech.ac.jp; otsuka@mac.titech.ac.jp
bDepartment of Bioengineering, School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, Japan
cJST-PRESTO,
dInstitute for Solid State Physics, The University of Tokyo, 5-1-5 Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8581, Japan. E-mail: x.li@issp.u-tokyo.ac.jp
First published on 2nd November 2020
Abstract
Tetra-arm poly(ethylene glycol) (TetraPEG) gels are tough materials whose toughness originates from their uniform network structure. They can be formed by combining the termini of tetra-arm polymers via chemical reactions with high conversion efficiency, such as the Michael addition, condensations using an active ester group, and alkyne–azide cycloadditions. Herein, we report the synthesis of a tetra-PEG gel using a tetra-arm polymer with N-phenylmaleimide moieties at the polymer ends (tetra-N-aryl MA PEG) as a scaffold. Tetra-N-aryl MA PEG can be obtained via a simple maleimidation using the modification agent p-maleimidophenyl isocyanate (PMPI), which directly transforms the hydroxy groups at the polymer ends into reactive N-aryl maleimide groups in a one-pot reaction. The thus-obtained tetra-N-aryl MA PEG was fully characterized using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry, and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. HPLC analysis not only demonstrated the high purity of tetra-N-aryl MA PEG and the full conversion of the hydroxy groups, but also provided an effective characterization method for N-aryl maleimide-based PEG using a simple protocol, which enables us quantitative analysis of functionalized polymers with different N-aryl maleimide numbers. Furthermore, we fabricated a TetraPEG gel via Michael addition of the obtained tetra-N-aryl MA and thiol-terminated TetraPEGs. Thus, this report presents the application of tetra-N-aryl MA PEG as an effective precursor to obtain a uniform network structure and a method for its characterization; these results should provide support for the development of functional molecules, soft materials, and further functional materials based on the uniform-network-structure concept.
Introduction
Gels are macromolecular networks that are swollen with solvents and are widely used as smart materials, e.g. in drug delivery, self-healing, and molecular-recognition materials.1–7 Many researchers have synthesized gel materials by designing their molecular and macroscopic structure as well as the constituent materials from the perspective of organic chemistry, physical chemistry, and biochemistry, among others.8–22 In general, gels that consist of polymer chains and crosslinking points are fragile due to structural defects and inhomogeneities.23Recently, gels with very high mechanical strength have been developed to expand their applicability. Tetra-arm poly(ethylene glycol) (TetraPEG) gels, which are constructed from TetraPEG with a reactive site at each of its termini, have extremely low heterogeneity and can be treated as near-ideal polymer networks.24–28 TetraPEG gels exhibit high strength as well as high transparency due to their uniform mesh structure. In most cases, the network structures of TetraPEG gels are formed by combining mutually reactive TetraPEG prepolymers in solution, i.e., an AB-type coupling reaction between two TetraPEG prepolymers with reactive groups at each polymer end. For the AB-type coupling reaction, the combinations of (1) amine (NH2) and N-hydroxy-succinimide (NHS) groups or (2) N-alkyl maleimide (MA) and thiol (SH) groups have generally been used.29–32 Although the former pair is widely used, leaving groups such as ionized NHS− arise as the gelation reactions proceed and remain as byproducts in the obtained gels which prevents their use in medical applications. Additionally, their facile self-decomposition, i.e., ester hydrolysis of the NHS groups,30,33 necessitates strict handling. In contrast, the latter combination (MA and SH) affords uniform mesh structures without any byproducts.34,35 As this coupling reaction proceeds quickly under mild conditions, even in water, it can be applied to the preparation of a variety of biocompatible materials. However, the undesired dimerization of the maleimide units, i.e., the light-induced [2+2] dimerization, sometimes leads to storage instability, making prepolymers difficult to handle.36 Therefore, novel AB-type coupling reactions are still required to expand the applications of gels based on the biocompatible polymer PEG with a uniform mesh structure. Furthermore, even though the fabrication and characterization of TetraPEG gels with a uniform mesh structure have been widely studied,25,28,30,37–41 little has been reported regarding the one-pot synthesis of tetra-arm precursors from commercially available polymers.
We have recently developed one-pot post-polymerization modification reactions using p-maleimidophenyl isocyanate (PMPI) as a modification reagent to introduce maleimide moieties into polymers with hydroxy groups and studied the polymerization reactions between the introduced N-aryl MA groups and thiol groups.42 Their high reactivity was corroborated by the kinetics of the addition reactions between the alcohols and isocyanates (–OH and –NCO) and the coupling of the obtained maleimide-terminated polymers with thiol-terminated polymers (–MA and –SH). This procedure is very effective for the transformation of typical hydroxy groups in polymer chains into reactive MA groups, as the reaction is quantitative without any side reactions. Furthermore, unlike their N-alkyl MA analogues, N-aryl MA-terminated polymers are stable toward UV light, endowing the prepolymers with UV stability. Therefore, N-aryl MA-terminated PEGs represent ideal prospective functional PEG prepolymers for the fabrication of TetraPEG gels.
In the characterization of functional PEGs, accurate determination of the distribution of non-, mono-, and multifunctionalized PEGs is required for further applications, especially biomedical applications. However, conventional analytical methods such as NMR spectroscopy only provide information regarding the average functionality, not the functionality distribution. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) can be used to demonstrate the polymer structure, but it is not suitable to determine the functionality distribution since the functionality affects the ionization and detection efficiency of the polymers. Recently, liquid chromatography at critical conditions (LCCC) has been proven to be effective to analyze the functionality distribution.43–48 Jiang et al. have reported a chromatographic method for the separation of functionalized PEGs and estimated their functionality distribution based on conventional high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) measurements. Modified and unmodified PEGs can be distinguished by isocratic elution using a reversed-phase column (C18) via the changes in their polarity when functional groups are attached to the ends of the polymer chains.49,50
In this paper, we report a novel characterization method to evaluate the conversion and purity of N-aryl MA-bearing PEGs using HPLC. The establishment of this characterization method also provides a guideline for N-aryl MA-functionalized PEGs, because the “PEGylation” of drugs, peptides, proteins, and PEG-based micelles has been widely used in various fields. In addition, we report the fabrication of a TetraPEG gel from N-aryl MA-based precursors via an AB-type coupling reaction between N-aryl MA and SH groups (Fig. 1). The gelation behavior of the TetraPEG gel was also characterized using rheology and UV-vis spectroscopy.
Experimental
Materials
All reagents and solvents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (MO, USA), FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation (Tokyo, Japan), Tokyo Chemical Industry (Tokyo, Japan), or Kanto Chemical (Tokyo, Japan) and used as received unless otherwise noted. Commercially available N-alkyl maleimide- and thiol-terminated PEGs (SUNBRIGHT) were purchased from NOF Group (Tokyo, Japan). Hydroxy-terminated TetraPEGs were purchased from SINOPEG (Xiamen, China). p-Maleimidophenyl isocyanate (PMPI) was synthesized following our previous report.42Characterisation
1H NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker AVANCE III HD500 spectrometer. Analytical size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) measurements were carried out at 40 °C using a TOSOH HLC-8320 SEC system equipped with a guard column (TOSOH TSK guard column Super H–L), three columns (TOSOH TSK gel SuperH 6000, 4000, and 2500), a differential refractive index detector, and a UV-vis detector. Tetrahydrofuran (THF) was used as the eluent at a flow rate of 0.6 mL min−1. Polystyrene (PS) standards (Mn = 4430–3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 142
142![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000; Mw/Mn = 1.03–1.08) were used to calibrate the SEC system. MALDI-TOF MS spectra were obtained on a Shimadzu AXIMA-CFR mass spectrometer equipped with a nitrogen laser (λ = 337 nm) and with pulsed ion extraction. The operation was performed at an accelerating potential of 20 kV in linear-positive ion mode. The sample polymer solution (1 mg mL−1) was prepared in THF, and the matrix reagents 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHBA) or dithranol (Dith) and the cationizing agent sodium trifluoroacetate were dissolved in THF (20 and 1 mg mL−1, respectively); 50 μL of each solution was mixed prior to MALDI analysis.
000; Mw/Mn = 1.03–1.08) were used to calibrate the SEC system. MALDI-TOF MS spectra were obtained on a Shimadzu AXIMA-CFR mass spectrometer equipped with a nitrogen laser (λ = 337 nm) and with pulsed ion extraction. The operation was performed at an accelerating potential of 20 kV in linear-positive ion mode. The sample polymer solution (1 mg mL−1) was prepared in THF, and the matrix reagents 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHBA) or dithranol (Dith) and the cationizing agent sodium trifluoroacetate were dissolved in THF (20 and 1 mg mL−1, respectively); 50 μL of each solution was mixed prior to MALDI analysis.
HPLC measurements
HPLC analysis was performed at 30 °C using a Shimadzu LC-20AD pump equipped with a variable wavelength detector (SPD-20A), a refractive index detector (RID-20A), and a C18 column (YMC-Triart C18). The eluate passes through the UV detector first and then the RI detector, which causes a time difference between UV and RI peaks. The pump was operated to supply an eluent mixture containing acetonitrile and water at flow rate of 1.0 mL min−1, and the monitoring wavelength was 254 nm. Each PEG was dissolved in a solvent mixture with the same composition as the eluent for measurement (Fig. S27, ESI†).Synthesis of N-aryl MA-terminated PEGs for the characterization in the HPLC measurements and gelation experiments
For the HPLC measurements, various MA-terminated PEGs (N-aryl MA PEGs and N-aryl MA TetraPEGs) were synthesized via reactions between hydroxy-terminated PEGs and PMPI. A typical procedure is presented below.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000), PMPI (8.6 mg, 40 μmol, 0.5 equivalents relative to the –OH groups) and TetraPEG (400 mg, 20 μmol, Mn = 20
000), PMPI (8.6 mg, 40 μmol, 0.5 equivalents relative to the –OH groups) and TetraPEG (400 mg, 20 μmol, Mn = 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) were added to a round-bottom flask. Dichloromethane (DCM, 16 mL) and two drops of dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) were added to the flask under an inert atmosphere. After stirring for 24 h at 30 °C, the reaction mixture was evaporated in vacuo and poured into 120 mL of a poor solvent (diethyl ether/ethanol, 30/1 v/v) in an ice bath. The resulting precipitate was dissolved in chloroform, filtered once, and reprecipitated in 120 mL of hexane. The precipitate was dried under reduced pressure to obtain N-aryl MA TetraPEG (half conversion) as a light-yellow solid (323 mg, 81%).
000) were added to a round-bottom flask. Dichloromethane (DCM, 16 mL) and two drops of dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) were added to the flask under an inert atmosphere. After stirring for 24 h at 30 °C, the reaction mixture was evaporated in vacuo and poured into 120 mL of a poor solvent (diethyl ether/ethanol, 30/1 v/v) in an ice bath. The resulting precipitate was dissolved in chloroform, filtered once, and reprecipitated in 120 mL of hexane. The precipitate was dried under reduced pressure to obtain N-aryl MA TetraPEG (half conversion) as a light-yellow solid (323 mg, 81%).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000), PMPI (171 mg, 800 μmol, 4.0 equivalents relative to the –OH groups) and TetraPEG (1.0 g, 50 μmol, Mn = 20
000), PMPI (171 mg, 800 μmol, 4.0 equivalents relative to the –OH groups) and TetraPEG (1.0 g, 50 μmol, Mn = 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) were added to a round-bottom flask. DCM (40 mL) and 2 drops of DBTDL were added to the flask under an inert atmosphere. After stirring for 24 h at 30 °C, the reaction mixture was evaporated in vacuo and poured into 300 mL of a poor solvent (diethyl ether/ethanol, 30/1 v/v) in an ice bath. The resulting precipitate was dissolved in chloroform, filtered once, and reprecipitated in 300 mL of hexane. The precipitate was separated by filtration and dried under reduced pressure to obtain N-aryl MA TetraPEG as a yellow solid (867 mg, 87%).
000) were added to a round-bottom flask. DCM (40 mL) and 2 drops of DBTDL were added to the flask under an inert atmosphere. After stirring for 24 h at 30 °C, the reaction mixture was evaporated in vacuo and poured into 300 mL of a poor solvent (diethyl ether/ethanol, 30/1 v/v) in an ice bath. The resulting precipitate was dissolved in chloroform, filtered once, and reprecipitated in 300 mL of hexane. The precipitate was separated by filtration and dried under reduced pressure to obtain N-aryl MA TetraPEG as a yellow solid (867 mg, 87%).
Gelation measurements
To control the pH value, equal amounts of N-aryl MA TetraPEG and SH TetraPEG (Mn = 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000, 60 mg) were dissolved in 0.8 mL of a citric phosphate buffer solution (CPB; 100 mM, pH = 3.6) or mixed solutions. The two solutions were mixed in a 2 mL Falcon tube for 30 s using a vortex mixer (Delta mixer Se-08, Taitec, Japan). The resulting solution was then poured into the interstice of the double cylinder of a rheometer (MCR501, Anton Paar, Austria). The oscillatory shear rheological properties, i.e., the storage elastic modulus (G′) and the loss elastic modulus (G′′), during gelation were measured at 25 °C using a double cylinder geometry with 17 mm diameter cylinders. The strain and frequency were 5% and 2 Hz, respectively. A reference sample was prepared under similar conditions to those above using N-alkyl MA-terminated TetraPEGs (Mn = 20
000, 60 mg) were dissolved in 0.8 mL of a citric phosphate buffer solution (CPB; 100 mM, pH = 3.6) or mixed solutions. The two solutions were mixed in a 2 mL Falcon tube for 30 s using a vortex mixer (Delta mixer Se-08, Taitec, Japan). The resulting solution was then poured into the interstice of the double cylinder of a rheometer (MCR501, Anton Paar, Austria). The oscillatory shear rheological properties, i.e., the storage elastic modulus (G′) and the loss elastic modulus (G′′), during gelation were measured at 25 °C using a double cylinder geometry with 17 mm diameter cylinders. The strain and frequency were 5% and 2 Hz, respectively. A reference sample was prepared under similar conditions to those above using N-alkyl MA-terminated TetraPEGs (Mn = 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) instead of N-aryl MA.
000) instead of N-aryl MA.
Results and discussion
Synthesis and characterization of N-aryl MA TetraPEGs by HPLC
N-Aryl MA PEGs were synthesized under various conditions (Scheme 1). To synthesize N-aryl MA PEGs with different functionalities, post-polymerization modification reactions of hydroxy-terminated PEGs with different feed ratios of PMPI (Condition A: 0.5 eq. of PMPI; Condition B: 4.0 eq. of PMPI; relative to the –OH group content of the polymers) were used. Namely, N-aryl MA PEGs with different molar masses and functionalities were synthesized as shown in Table 1 (for the spectral data, see the ESI†). To facilitate the modification reaction, we added DBTDL as a catalyst. Hydroxy-terminated PEGs with different molar masses (Mn = 1000 and 2000) were treated under condition A, i.e., with half an equivalent of PMPI relative to the hydroxy groups at the termini of the PEGs. The resulting polymers were expected to exhibit a distribution of functionalities, i.e., of non-, mono-, and difunctionalized PEGs. On the other hand, the reaction of hydroxy-terminated PEGs (Mn = 1000 and 2000) under condition B with a four-fold excess of PMPI relative to the hydroxy groups was expected to afford only difunctionalized PEGs.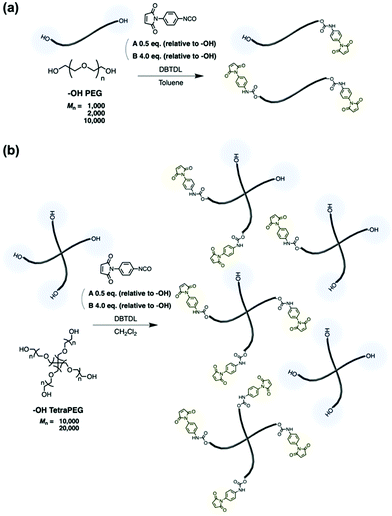 | ||
| Scheme 1 Synthesis of N-aryl MA PEGs. (a) Reaction with hydroxy-terminated PEGs. (b) Reaction with hydroxy-terminated TetraPEGs. | ||
| Run | OH number | M n [g mol−1] |
M
n![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) SEC
[g mol−1] SEC
[g mol−1] |
PMPI feedc [equiv.] (condition) | F NMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Approximated molar mass of the commercially available hydroxy-terminated PEG. b Estimated via SEC using THF as the eluent. All polymers showed narrow PDIs (1.02–1.07). c Relative to the number of hydroxy groups. d Estimated based on a 1H NMR analysis of the integral ratio of the polymer ends (for the spectral data, see the ESI). | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 1000 | 1100 | 0.5 (A) | 0.7 |
| 2 | 2 | 1000 | 1400 | 4.0 (B) | 2.0 |
| 3 | 2 | 2000 | 1900 | 0.5 (A) | 0.9 |
| 4 | 2 | 2000 | 2100 | 4.0 (B) | 2.0 |
| 5 | 2 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
0.5 (A) | 0.6 |
| 6 | 2 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
4.0 (B) | 2.0 |
| 7 | 4 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
7900 | 0.5 (A) | 1.6 |
| 8 | 4 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
7600 | 4.0 (B) | 4.0 |
| 9 | 4 | 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
0.5 (A) | 1.7 |
| 10 | 4 | 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
4.0 (B) | 4.0 |
The resulting polymers were characterized using 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopy, and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. In the 1H NMR spectra of the hydroxy-terminated PEGs, a peak corresponding to the OH end groups was observed at 2.8–3.0 ppm. In contrast, in the spectra of the modified PEGs, the OH end group peak disappeared, and a new peak originating from the methylene protons adjacent to the urethane ends appeared at 4.2–4.3 ppm (Fig. S1–S5, ESI†). The average functionality (F), the number of maleimide ends per one polymer, was calculated based on the integral ratios of these peaks in the NMR spectra and are summarized in Table 1. The average functionality estimated by NMR (FNMR) was 2.0 (OH conversion = 100%) for the fully converted PEGs synthesized using condition B (Run 2 in Table 1) and 0.74 (OH conversion = 37%) for the polymers synthesized using condition A (Run 1 in Table 1), respectively. In 13C NMR spectroscopy (Fig. S6 and S7, ESI†), a peak corresponding to the carbon adjacent to OH ends was disappeared upon the reaction and the result supported the progresses of reaction. Three sets of peaks were observed in the MALDI-TOF MS analysis of the polymers synthesized using condition A (Runs 1 and 3 in Table 1), indicating, as expected, a mixture of non-, mono-, and di-functionalized PEGs (Fig. S13 and S15, ESI†). In contrast, MALDI-TOF MS analyses of the polymers synthesized under condition B (Runs 2 and 4 in Table 1) showed one set of peaks, which was consistent with the theoretical value for disubstituted PEGs, demonstrating the successful synthesis of difunctionalized PEGs and the absence of side reactions (Fig. S14 and S16, ESI†).
Subsequently, the polymers prepared using conditions A and B were characterized via HPLC (Fig. 2, 3, and Fig. S17–S26, ESI†) using a typical C18 column at 30 °C with a mixed eluent (acetonitrile/water). In this study, the PEGs functionalized with N-aryl MA were mainly characterized using a UV detector (wavelength: 254 nm), which is a highly sensitive and common HPLC detector. A differential refractive index detector was used complementarily to detect non-functionalized PEGs, which do not absorb at 254 nm.
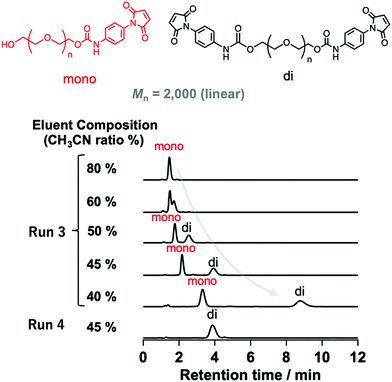 | ||
| Fig. 2 HPLC profiles of modified PEGs (Mn = 2000) with different numbers of N-aryl MA groups (Runs 3 and 4 in Table 1) using different eluent compositions (values shown are the vol% of acetonitrile in water) at a flow rate of 1.0 mL min−1 on a C18 column at 30 °C using a UV detector. | ||
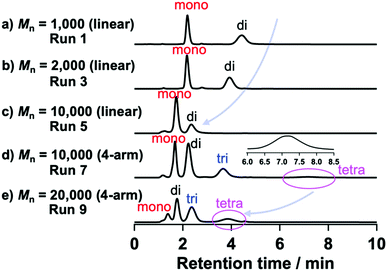 | ||
| Fig. 3 HPLC profiles of modified PEGs with different molar masses and functionalities (eluent: acetonitrile/water, 45/55, v/v; flow rate: 1.0 mL min−1 on a C18 column at 30 °C using a UV detector). | ||
The mixture (Mn = 2000) synthesized via method A was characterized by changing the eluent ratio to determine the critical condition, where the peaks originating from non-, mono-, and difunctionalized PEGs could be detected separately. As shown in Fig. 2, although only one peak was observed when acetonitrile was used as the eluent, the addition of water to the eluent mixture affected the peak position, allowing separated peaks to be observed.
Finally, we determined the appropriate eluent condition (acetonitrile/water, 45/55, v/v) where each peak could be detected separately (Fig. 3). Using this mixed eluent, we confirmed that only one peak corresponding to difunctionalized PEGs was observed for samples prepared under condition B (Fig. S18 and S20, ESI†), which was consistent with the MALDI-TOF MS results (Fig. S12 and S14, ESI†). These results also support the full conversion of the hydroxy groups and high purity of the obtained N-aryl MA PEGs. Furthermore, N-aryl MA PEGs with high molar mass and functionality (TetraPEG; Mn = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 and 20
000 and 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) were characterized using HPLC. We confirmed the effect of molar mass on the HPLC measurements by comparing several N-aryl MA terminated PEGs (Mn = 1000, 2000, and 10
000) were characterized using HPLC. We confirmed the effect of molar mass on the HPLC measurements by comparing several N-aryl MA terminated PEGs (Mn = 1000, 2000, and 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000; Fig. 3a–c), which demonstrated that the retention time decreased with increasing molar mass. This result was attributed to the polarity effect of the termini, which would diminish with increasing molar mass; i.e., the ratio of termini in the polymer clearly affected the retention time.
000; Fig. 3a–c), which demonstrated that the retention time decreased with increasing molar mass. This result was attributed to the polarity effect of the termini, which would diminish with increasing molar mass; i.e., the ratio of termini in the polymer clearly affected the retention time.
For TetraPEG (Mn = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 and 20
000 and 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000), the polymers obtained using condition A should be a mixture of non-, mono-, di-, tri-, and tetra-functionalized PEGs. In Fig. 3d and e, three peaks originating from functionalized PEGs are observed. Non-functionalized PEGs do not absorb at 254 nm, and would thus not be observed in the HPLC profiles obtained from the UV detector. On the other hand, the HPLC profile of the polymers obtained using condition B showed only one peak originating from tetrafunctionalized PEG (Fig. S24 and S26, ESI†), which is consistent with the conversion estimated based on the 1H NMR analysis.
000), the polymers obtained using condition A should be a mixture of non-, mono-, di-, tri-, and tetra-functionalized PEGs. In Fig. 3d and e, three peaks originating from functionalized PEGs are observed. Non-functionalized PEGs do not absorb at 254 nm, and would thus not be observed in the HPLC profiles obtained from the UV detector. On the other hand, the HPLC profile of the polymers obtained using condition B showed only one peak originating from tetrafunctionalized PEG (Fig. S24 and S26, ESI†), which is consistent with the conversion estimated based on the 1H NMR analysis.
To confirm the assignment of the mono-, di-, and tri-functionalized Tetra-PEG peaks, the post-polymerization modification reaction of the hydroxy-terminated TetraPEGs (Mn = 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) with PMPI (condition B) was monitored using HPLC. The peaks originating from Tetra-PEG with a higher number of N-aryl MA groups increased with reaction time, while those originating from lower-functionality Tetra-PEG decreased. The reaction was completed within 24 h (Fig. 4 and Fig. S28, ESI†). In the HPLC trace, very small unexpected peaks were appeared at about 2.8 min and 4.9 min. We presumed that those small peaks originated from urea or urethane products of PMPI.
000) with PMPI (condition B) was monitored using HPLC. The peaks originating from Tetra-PEG with a higher number of N-aryl MA groups increased with reaction time, while those originating from lower-functionality Tetra-PEG decreased. The reaction was completed within 24 h (Fig. 4 and Fig. S28, ESI†). In the HPLC trace, very small unexpected peaks were appeared at about 2.8 min and 4.9 min. We presumed that those small peaks originated from urea or urethane products of PMPI.
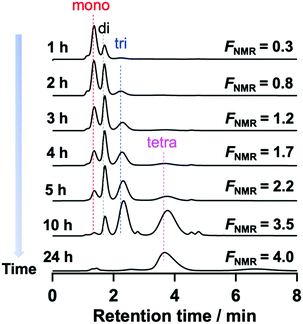 | ||
| Fig. 4 Change in the HPLC profiles during the modification reaction (eluent: acetonitrile/water, 45/55, v/v; flow rate: 1.0 mL min−1, UV detector). | ||
To summarize the HPLC characterization: we revealed that (1) peak separation of PEGs based on their functionality and molar mass can be achieved under appropriate conditions; (2) the driving force of peak separation, i.e., the interaction between the N-aryl MA groups at the termini and the C18 column, increases with increasing ratio of termini in the polymer, i.e., with smaller molar mass or higher functionality; (3) the peaks become broader with increasing number of N-aryl MA moieties at the polymer termini; (4) the peaks are too broad in eluents with more than 60% water in acetonitrile. We concluded that elution using a 45/55 (v/v) mixture of acetonitrile/water was the best conditions to separate the PEGs modified by PMPI. We also succeeded quantification of polymers with different N-aryl maleimide numbers from the area ratio of peaks at RI detector of HPLC (Fig. S17, S19, S21, S23 and S25, ESI†). Although MALDI-TOF MS allowed the functionality of the polymers to be analyzed, it was not applicable to polymers with high molecular weight (>∼10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) due to difficulties associated with ionization. Therefore, characterization of tetrafunctionalized PEG using this HPLC method represents an effective way to accurately characterize their functionality distribution. This result also demonstrated unambiguously the full conversion and high purity of the N-aryl MA TetraPEG synthesized from hydroxy-terminated TetraPEG using the one-pot reaction.
000) due to difficulties associated with ionization. Therefore, characterization of tetrafunctionalized PEG using this HPLC method represents an effective way to accurately characterize their functionality distribution. This result also demonstrated unambiguously the full conversion and high purity of the N-aryl MA TetraPEG synthesized from hydroxy-terminated TetraPEG using the one-pot reaction.
Fabrication of TetraPEG gels from N-aryl MA-based precursors
We fabricated several TetraPEG gels via Michael reaction between the obtained N-aryl MA TetraPEGs (Mn = 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000) and SH TetraPEGs in water. The reaction was also conducted using commercially available N-alkyl MA TetraPEGs instead of N-aryl MA TetraPEG as a control. We used the evolution of the shear moduli to monitor the viscoelastic properties of the samples during the gelation process. The gelation point (tgel) was determined from the crossover time of the storage modulus G′ and the loss modulus G′′ in the rheological curves (Fig. 5). The G′ value after gelation using N-aryl MA TetraPEG roughly matched that of N-alkyl MA TetraPEG, indicating high conversion of the MA terminals of the modified TetraPEG and the near-ideal network structure of the obtained gel. Surprisingly, when N-aryl MA was used, the tgel occurred much earlier than when N-alkyl MA was used, indicating a higher reactivity of N-aryl MA PEG compared to that of N-alkyl MA PEG. In our previous work,42 we found the reactivity of phenyl maleimide terminated PEG toward thiol molecule was as same as that of alkyl maleimide terminated PEG in chloroform with triethylamine as a base catalyst. To our best knowledges, this is first case that a difference in the reactivity of phenyl and alkyl N-substituted maleimide in water has been observed. As shown in Table S1 (ESI†), the pH dependence of the gelation process was also examined for the range pH = 3.0–3.6. We succeeded in changing the gelation time, i.e., the gelation time could be controlled by adjusting the pH value of the reaction system. These features of N-aryl MA TetraPEGs are expected to be useful in various fields.
000) and SH TetraPEGs in water. The reaction was also conducted using commercially available N-alkyl MA TetraPEGs instead of N-aryl MA TetraPEG as a control. We used the evolution of the shear moduli to monitor the viscoelastic properties of the samples during the gelation process. The gelation point (tgel) was determined from the crossover time of the storage modulus G′ and the loss modulus G′′ in the rheological curves (Fig. 5). The G′ value after gelation using N-aryl MA TetraPEG roughly matched that of N-alkyl MA TetraPEG, indicating high conversion of the MA terminals of the modified TetraPEG and the near-ideal network structure of the obtained gel. Surprisingly, when N-aryl MA was used, the tgel occurred much earlier than when N-alkyl MA was used, indicating a higher reactivity of N-aryl MA PEG compared to that of N-alkyl MA PEG. In our previous work,42 we found the reactivity of phenyl maleimide terminated PEG toward thiol molecule was as same as that of alkyl maleimide terminated PEG in chloroform with triethylamine as a base catalyst. To our best knowledges, this is first case that a difference in the reactivity of phenyl and alkyl N-substituted maleimide in water has been observed. As shown in Table S1 (ESI†), the pH dependence of the gelation process was also examined for the range pH = 3.0–3.6. We succeeded in changing the gelation time, i.e., the gelation time could be controlled by adjusting the pH value of the reaction system. These features of N-aryl MA TetraPEGs are expected to be useful in various fields.
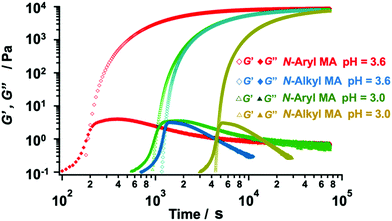 | ||
| Fig. 5 Viscoelastic properties of the gel samples (red and green: N-aryl MA; blue and yellow: N-alkyl MA) during the gelation process (6 wt% in a buffer; pH = 3.0 and pH = 3.6). | ||
The gelation behavior was also monitored using UV-vis spectroscopy. Unlike N-alkyl MA, N-aryl MA exhibits absorption in the visible light range, which originates from its fused benzene ring (Fig. S29, ESI†). When thiol compounds were added to the N-aryl MA structure, it changed from light yellow to colorless. This enabled us to check the reaction progress with the naked eye. Furthermore, we monitored the gelation using the UV absorption at λ = 340 nm. As shown in Fig. 6, the UV absorbance decreased as the gelation proceeded. This result was also in agreement with the results shown in Table S1 (ESI†).
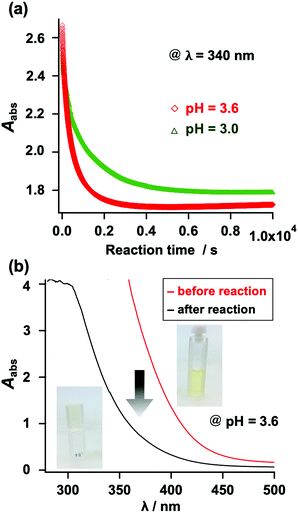 | ||
| Fig. 6 (a) Change in the UV-vis absorption at 340 nm during the gelation reaction (red: pH = 3.6; green: pH = 3.0). (b) UV-vis spectra before and after the gelation experiment. | ||
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have demonstrated the synthesis of tetra-arm polymers with N-phenylmaleimide moieties at the polymer ends (Tetra-N-aryl MA PEG) via maleimidation with p-maleimidophenyl isocyanate (PMPI), and the easy characterization of their functionality independent of their molar mass using HPLC. The characterization of maleimide-functionalized PEGs with HPLC should be useful not only to determine their conversion and purity, but also to quantify the ratio of functionalized PEGs. These characteristics make guideline for N-aryl MA-functionalized PEGs, since ‘PEGylation’ has been widely used in various fields. Preparative columns with C18 are widely used for mass production in organic chemistry; thus, the present research could be applied to obtain functionalized PEGs with the desired functionality in large scale. The successful fabrication of TetraPEG gels using the N-aryl MA-based precursor proved the usefulness of the AB-type coupling reactions for the further development of functional molecules, soft materials, and other functional materials based on the uniform network structure concept. We believe that the present report will help researchers in various fields to develop functional soft materials, considering that this maleimidation process is very simple and the maleimidation reagent PMPI can be synthesized without tedious purification procedures. Thus, the AB-type coupling reaction of N-aryl MA and SH groups should facilitate the industrial production of tough materials based on the uniform network structure concept.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by JST PRESTO grant JPMJPR18L1 (to D. A.), by JSPS KAKENHI grant JP19K15628 (to X. L.), and by JSPS KAKENHI grant JP20J22044 (to M. O.).Notes and references
- T. Miyata, T. Uragami and K. Nakamae, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2002, 54, 79–98 CrossRef CAS.
- T. R. Hoare and D. S. Kohane, Polymer, 2008, 49, 1993–2007 CrossRef CAS.
- B.-V. Slaughter, S. S. Khurshid, O.-Z. Fisher, A. Khademhosseini and N. A. Peppas, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 3307–3329 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Li, D. J. Young and X. J. Loh, Mater. Chem. Front., 2019, 3, 1489–1502 RSC.
- G.-J. Owens, R.-K. Singh, F. Foroutan, M. Alqaysi, C.-M. Han, C. Mahapatra, H.-W. Kim and J.-C. Knowles, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2016, 77, 1–79 CrossRef CAS.
- K.-Y. Lee and D.-J. Mooney, Chem. Rev., 2001, 101, 1869–1879 CrossRef CAS.
- X. J. Loh, Mater. Horiz., 2014, 1, 185–195 RSC.
- D. Nakayama, Y. Takeoka, M. Watanabe and K. Kataoka, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 4197–4200 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Okuzaki, T. Kuwabara and T. Kunugi, J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys., 1998, 36, 2237–2246 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kyriakos, M. Philipp, L. Silvi, W. Lohstroh, W. Petry, P. Müller-Buschbaum and C. M. Papadakis, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2016, 120, 4679–4688 CrossRef CAS.
- T.-C. Krasia and C.-S. Patrickios, Macromolecules, 2006, 39, 2467–2473 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Kureha, D. Aoki, S. Hiroshige, K. Iijima, D. Aoki, T. Takata and D. Suzuki, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 15393–15396 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Bin Imran, K. Esaki, H. Gotoh, T. Seki, K. Ito, Y. Sakai and Y. Takeoka, Nat. Commun., 2014, 5, 1–8 Search PubMed.
- Y. Okaya, Y. Jochi, T. Seki, K. Satoh, M. Kamigaito, T. Hoshino, T. Nakatani, S. Fujinami, M. Takata and Y. Takeoka, Macromolecules, 2020, 53, 374–386 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Kuroda, Y. Tounoue, K. Noguchi, Y. Shimasaki and H. Inokawa, Polym. J., 2020, 8, 936–946 Search PubMed.
- H. Shigemitsu and I. Hamachi, Acc. Chem. Res., 2017, 50, 740–750 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Gong, Y. Katsuyama, T. Kurokawa and Y. Osada, Adv. Mater., 2003, 15, 1155–1158 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Haraguchi and T. Takehisa, Adv. Mater., 2002, 14, 1120–1124 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Okumura and K. Ito, Adv. Mater., 2001, 13, 485–487 CrossRef CAS.
- S. M. Mithieux, J. E. J. Rasko and A. S. Weiss, Biomaterials, 2004, 25, 4921–4927 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Storm, J. J. Pastore, F. C. MacKintosh, T. C. Lubensky and P. A. Janmey, Nature, 2005, 435, 191–194 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Nakajima, Polym. J., 2017, 49, 477–485 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Shibayama, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 1998, 199, 1–30 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Sakai, T. Matsunaga, Y. Yamamoto, C. Ito, R. Yoshida, S. Suzuki, N. Sasaki, M. Shibayama and U.-I. Chung, Macromolecules, 2008, 41, 5379–5384 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Matsunaga, T. Sakai, Y. Akagi, U.-I. Chung and M. Shibayama, Macromolecules, 2009, 42, 6245–6252 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, S. Nakagawa, Y. Tsuji, N. Watanabe and M. Shibayama, Sci. Adv., 2019, 5, eaax8647 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Huang, S. Nakagawa, X. Li, M. Shibayama and N. Yoshie, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 9646–9652 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Tsuji, S. Nakagawa, C. I. Gupit, M. Ohira, M. Shibayama and X. Li, Macromolecules, 2014, 343, 873–875 Search PubMed.
- K. Fujii, H. Asai, T. Ueki, T. Sakai, S. Imaizumi, U.-I. Chung, M. Watanabe and M. Shibayama, Soft Matter, 2012, 8, 1756–1759 RSC.
- K. Nishi, K. Fujii, M. Chijiishi, Y. Katsumoto, U.-I. Chung, T. Sakai and M. Shibayama, Macromolecules, 2012, 45, 1031–1036 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Nishi, K. Fujii, Y. Katsumoto, T. Sakai and M. Shibayama, Macromolecules, 2014, 47, 3274–3281 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Kamata, Y. Akagi, Y. Kayasuga-Kariya, U.-I. Chung and T. Sakai, Science, 2014, 343, 873–875 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, Y. Tsutsui, T. Matsunaga, M. Shibayama, U.-I. Chung and T. Sakai, Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 3567–3571 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Hayashi, F. Okamoto, S. Hoshi, T. Katashima, D. C. Zujur, X. Li, M. Shiubayama, E. P. Gilbert, U.-I. Chung, S. Ohba, T. Oshika and T. Sakai, Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2017, 44 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yoshitake, Y. Kamiyama, K. Nishi, N. Yoshimoto, M. Morita, T. Sakai and K. Fujii, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017, 19, 29984–29990 RSC.
- J. Put and F. C. D. Schryver, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1973, 95, 137–145 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Akagi, T. Katashima, Y. Katsumoto, K. Fujii, T. Matsunaga, U.-I. Chung, M. Shibayama and T. Sakai, Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 5817–5821 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, K. Khairulina, U.-I. Chung and T. Sakai, Macromolecules, 2013, 46, 8657–8663 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Akagi, J. P. Gong, U.-I. Chung and T. Sakai, Macromolecules, 2013, 46, 1035–1040 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Fujiyabu, X. Li, M. Shibayama, U.-I. Chung and T. Sakai, Macromolecules, 2017, 50, 9411–9416 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, K. Khairulina, U.-I. Chung and T. Sakai, Macromolecules, 2014, 47, 3582–3586 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Takashima, J. Kida, D. Aoki and H. Otsuka, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., 2019, 57, 2396–2406 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-H. Leister, L.-E. Weaner and D.-G. Walker, J. Chromatogr. A, 1995, 704, 369–376 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Tang, F. Jariwala, M. Bolgar and D. K. Lloyd, J. Chromatogr. A, 2012, 1246, 117–122 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Liu, C. Xie, W. Xu and W. Lu, J. Chromatogr. A, 2004, 1046, 121–126 CrossRef CAS.
- B. N. Barman, D. H. Champion and S. L. Sjoberg, J. Chromatogr. A, 2009, 1216, 6816–6823 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Chang, ACS Symp. Ser., 2018, 1281, 1–17 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Radke, J. Chromatogr. A, 2014, 1335, 62–79 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-Z. Wei, Y.-F. Chu, E. Uliyanchenko, P. J. Schoenmakers, R. X. Zhuo and X. L. Jiang, Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 7506–7513 RSC.
- Y.-Z. Wei, R.-X. Zhuo and X.-L. Jiang, J. Chromatogr. A, 2016, 1447, 122–128 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d0sm01658f |
| ‡ R. T. and M. O. contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |