Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleEnhancing the photodynamic therapy efficacy of black phosphorus nanosheets by covalently grafting fullerene C60†
Yajuan
Liu‡
a,
Daoming
Zhu‡
 b,
Xianjun
Zhu
a,
Gaoke
Cai
c,
Jianhua
Wu
a,
Muqing
Chen
b,
Xianjun
Zhu
a,
Gaoke
Cai
c,
Jianhua
Wu
a,
Muqing
Chen
 a,
Pingwu
Du
a,
Pingwu
Du
 a,
Yongshun
Chen
*c,
Wei
Liu
a,
Yongshun
Chen
*c,
Wei
Liu
 *b and
Shangfeng
Yang
*b and
Shangfeng
Yang
 *a
*a
aHefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Materials for Energy Conversion, Anhui Laboratory of Advanced Photon Science and Technology, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China. E-mail: sfyang@ustc.edu.cn
bKey Laboratory of Artificial Micro- and Nano-Structures of Ministry of Education, School of Physics and Technology, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China. E-mail: wliu@whu.edu.cn
cDepartment of Clinical Oncology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China. E-mail: yongshun2007@163.com
First published on 9th September 2020
Abstract
Few-layer black phosphorus (BP) nanosheets show potential application in biomedicine such as photodynamic therapy (PDT), and are therefore commonly used in anticancer therapy and nanomedicine due to being relatively less invasive. However, they suffer from low ambient stability and poor therapeutic efficacy. Herein, C60 was covalently grafted onto the edges of BP nanosheets, and the resultant BP-C60 hybrid was applied as a novel endocytosing photosensitizer, resulting in not only significantly enhanced PDT efficacy relative to that of the pristine BP nanosheets, but also drastically improved stability in a physiological environment, as confirmed by both in vitro and in vivo studies. Such improved stability was due to shielding effect of the stable hydrophobic C60 molecules. The enhanced PDT efficacy is interpreted from the photoinduced electron transfer from BP to C60, leading to the promoted generation of ˙OH radicals, acting as a reactive oxygen species (ROS) that is effective in killing tumor cells. Furthermore, the BP-C60 hybrid exhibited low systemic toxicity in the major organs of mice. The BP-C60 hybrid represents the first BP-fullerene hybrid nanomaterial fulfilling promoted ROS generation and consequently enhanced PDT efficacy.
Introduction
Developing effective tumor therapies is of considerable importance due to the increased incidence of malignant tumors over recent years.1 Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a modern technique of tumor therapy and is relatively less invasive with low systemic toxicity. PDT can induce vascular damage in the tumor and activate an immune system response, and is thus commonly used in anticancer therapy and nanomedicines.2–4 The principle of PDT is based on a series of photochemical reactions triggered by a photosensitizer upon light irradiation. Excitation of the photosensitizer results in energy transfer to surrounding oxygen molecules, which generate cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) capable of killing cancer cells.2–4 A photosensitizer essentially determines the absorption efficiency and depth of light penetration and is thus decisive for PDT efficacy.5As an emerging two-dimensional (2D) layered semiconductor, few-layer black phosphorus (BP) nanosheets have recently been utilized as a novel photosensitizer in PDT.6–15 BP exhibits a thickness-dependent band gap over the range of 0.3 eV for bulk materials to 2.0 eV for monolayers, resulting in tunable and broad optical absorption across the UV to visible range.6–9 This along with the high charge carrier mobility of ∼1000 cm2 V−1 s−1 enables BP to be used in diverse potential applications, such as transistors, biomedicines, and in energy conversion and storage.6–12 Various biomedical applications of BP, such as in photodynamic and photothermal cancer therapy and in vivo photoacoustic imaging, and a drug delivery platform and multifunctional theranostic agents for cancer treatment, have been reported in recent years.10–12 In particular, in 2015 Xie et al. first demonstrated the ability and the capability of BP nanosheets in efficient generation of singlet oxygen (1O2) radicals and consequently utilized BP nanosheets as effective photosensitizers in PDT.13 This seminal work stimulates further studies of BP nanosheets in PDT, with singlet oxygen (1O2) radicals typically proposed as the principal reactive oxygen species (ROS) responsible for killing cancer cells.14–16 However, the reported therapeutic efficacies of BP nanosheets are generally poor and BP nanosheets suffer from low ambient stability, limiting their extensive PDT applications. The low ambient stability of BP nanosheets is due to the existence of a lone pair of electrons in each phosphorus atom, able to readily react with oxygen adsorbed on the surface of BP nanosheets, leading to facile oxidation.17–19 Hence, a prerequisite for realizing PDT application of BP nanosheets is to improve their ambient stability. So far a few methods have been developed to improve the ambient stability of BP nanosheets.20–25 Among them, covalent functionalizations have been demonstrated to one of the most effective approaches in improving the ambient stability of BP nanosheets because the phosphorus atom bearing a lone electron pair can bond directly with another atom, such as carbon and can thus be passivated.20,21 For example, we recently succeeded in edge-selectively functionalizing BP nanosheets by grafting stable C60 molecules via covalent P–C bonds.26 Owing to the high stability of hydrophobic C60 against light, oxygen and water, C60 molecules within the BP-C60 hybrid can act as a shield that effectively protects BP nanosheets from oxidation, resulting in significantly improved stability of BP nanosheets in water.26 An open question is whether C60 grafting can improve the physiological stability of BP nanosheets in other electrolyte solutions also. Furthermore, given that fullerenes have also been used in PDT,27,28 it is intriguing to investigate whether C60 grafting affects the PDT efficacy of BP nanosheets.
Herein, we applied a BP-C60 hybrid as a novel endocytosed photosensitizer (Fig. 1), resulting in not only significantly enhanced PDT efficacy relative to that of the pristine BP nanosheets, but also drastic improvement of its physiological stability in serum, phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and water as confirmed by both in vitro and in vivo studies. On the basis of mechanistic studies, we revealed that the enhanced PDT efficacy is due to the generation of ROS in the form of ˙OH radicals resulting from the photoinduced electron transfer from BP to C60. The cytotoxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid was further evaluated in vivo by inspecting the major organs of mice, confirming its low cytotoxicity and negligible side effects.
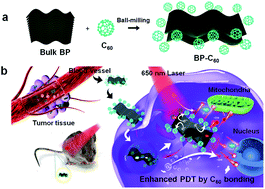 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation process of the BP-C60 hybrid. (b) Application of the BP-C60 hybrid as a novel endocytosing photosensitizer for PDT. | ||
Results and discussion
Synthesis, characterization and physiological stability of the BP-C60 hybrid
The BP-C60 hybrid was synthesized by a solid-state mechanochemical method, as reported previously.26,29,30 Briefly, bulk BP and C60 powders were mixed in a mass ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 and ball-milled within an Ar atmosphere in a planetary ball-milling machine at 250 rpm for 24 h (Fig. 1a). Unreacted C60 was removed from the resultant black product by Soxhlet-extraction with CS2 for 48 h. Grafting of C60 molecules selectively onto the edges of BP nanosheets via covalent P–C bonds was confirmed through a series of spectroscopic and morphological characterization experiments.26
2 and ball-milled within an Ar atmosphere in a planetary ball-milling machine at 250 rpm for 24 h (Fig. 1a). Unreacted C60 was removed from the resultant black product by Soxhlet-extraction with CS2 for 48 h. Grafting of C60 molecules selectively onto the edges of BP nanosheets via covalent P–C bonds was confirmed through a series of spectroscopic and morphological characterization experiments.26
The size of nanomaterials is crucial for biological applications, especially in vivo experiments. The average size and thickness of the BP-C60 hybrid are determined by using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), respectively. The TEM images indicated that the BP-C60 hybrid is 100–200 nm in diameter, smaller than that of unmodified BP nanosheets (200–300 nm), which were prepared by ball-milling bulk BP only with LiOH as the additive (abbreviated as BP-BM) (ESI Fig. S1†). The decrease in the size of the BP nanosheets is beneficial for their dispersion in aqueous solutions, as required for biomedical applications.15 AFM analysis indicated that the average thickness of the BP-C60 hybrid is ∼2.5 nm, comparable to that of BP-BM (∼2.7 nm), corresponding to a ∼4-layer nanosheet, given that the interlayer distance of BP is ∼0.52 nm (ESI Fig. S2†).26
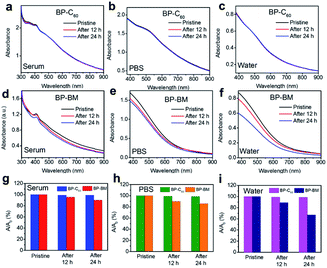
It has been revealed in our previous work that since the grafting ratio of C60 is not high (the estimated average molar content of C60 is 19 per 1000 P atoms26), C60 grafting hardly affects the dispersity of BP nanosheets, and the BP-C60 hybrid has a considerable dispersity in aqueous solutions. Besides, owing to the high stability of hydrophobic C60 when exposed to light, oxygen or water, grafting of stable C60 molecules onto the edges of BP nanosheets resulted in improvement of the stability of BP nanosheets in water by a factor of 4.6 after standing for 7 days.26 To investigate whether such improved stability of BP nanosheets was replicated in other electrolytes used in PDT applications, the stability of the BP-C60 hybrid dispersion in physiological environments was tested by using fetal bovine serum and phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) for 24 h. According to the comparison of the changes of the optical absorbances of the BP-C60 hybrid and BP-BM (Fig. 2a–f), the UV-Vis absorbances of the BP-BM dispersions in serum, PBS and water at 460 nm decrease gradually (Fig. 2g–i), with the degradation rate reaching ∼10%, 14%, and 33% after standing for 24 h, respectively (ESI Fig. S3†). The relatively lower degradation rate of BP-BM in serum is due to the presence of protein and less dissolved oxygen.5,14 These results reveal the instability of BP nanosheets in aqueous solutions, unfavorable for PDT applications.21–26 Upon grafting C60 molecules, the degradation rates of the BP-C60 hybrid dispersed in serum, PBS and water after standing for 24 h decrease dramatically to ∼1.0%, 1.4%, and 1.3%, respectively (ESI Fig. S3†). Hence, similar to the case of dispersion in water, grafting of stable C60 molecules leads to dramatic improvement of the stability of BP nanosheets in serum and PBS as well. This shows the PDT application potential of the BP-C60 hybrid.
Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation
As we have reported previously, grafting of C60 molecules onto BP nanosheets was found to result in significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity, as demonstrated using degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) dye and the apparent reaction rate constant increasing by a factor of 8.3.26 As confirmed in a time-dependent photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopic study, the BP-C60 hybrid generated ˙OH radicals during the photocatalytic process (ESI Fig. S4†), which may act as a reactive oxygen species (ROS).31 The presence of ROS at the cellular level was subsequently confirmed using 2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCF) as a probe.15 For comparison, a comparative sample of C60-BM was synthesized by ball-milling C60 alone, and an additional control sample consisting of a simple physical mixture of BP and C60 in a ratio of 70% BP-BM and 30% C60 was also synthesized, similar to their respective contents within the BP-C60 hybrid.26 As shown in Fig. 3a, for the BP-C60 hybrid, the DCF fluorescence intensity and the number of cells producing ROS are significantly higher than those observed with C60-BM, BP-BM or the BP/C60-mixture. In addition, a flow analysis of fluorescence intensity was performed for each sample, demonstrating that the BP-C60 hybrid exhibited the strongest DCF fluorescence intensity (Fig. 3a and b), with the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) value being approximately one order of magnitude higher than that of the BP/C60-mixture (Fig. 3d). This result demonstrates that grafting of C60 molecules greatly enhanced the ROS production efficiency of the BP nanosheets within cells, consistent with the results of the photocatalytic degradation of dyes reported previously. Given that excessive oxidative stress of ROS can cause mitochondrial dysfunction in tumor cells,15 we next compared the mitochondrial membrane potentials (MMPs) of different samples, as determined by the standard 1,1′,3′-tetraethyl-imidacarbocyanine (JC-1) test. Normally, red JC-1 aggregates (JC-1-A) are able to accumulate in mitochondria. However, red JC-1-A is re-dispersed in the cytoplasm, and a green JC-1 monomer (JC-1-M) is generated, which enters the mitochondria when the MMP is reduced.32 As shown in Fig. 3c, the BP-C60 hybrid shows the greatest JC-1-M ratio, indicating that the BP-C60 hybrid exhibited the greatest ability to disrupt mitochondrial function. It is worth noting that the laser power used in the in vitro experiments (0.5 W cm−2) was lower than those typically reported in the literature regarding PDT application of BP.16,33,34 Therefore, grafting of C60 molecules promoted generation of ROS at a relatively low power, benefitting in vivo PDT application of BP nanosheets. To the best of our knowledge, promoting ROS generation of BP via hybridization of fullerenes has not been widely reported; thus the BP-C60 hybrid represents the first BP-fullerene hybrid nanomaterial fulfilling promoted ROS generation.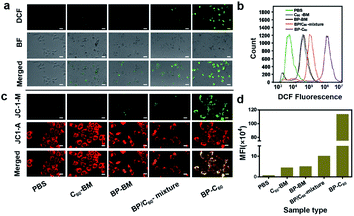 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a and c) ROS levels and MMP measured by DCF and JC-1 staining of 4T1 cells after co-incubation of the various groups with nanomaterials for 6 h: PBS+NIR, C60-BM+NIR (30 μg ml−1, 650 nm, 0.5 W cm−2, 5 min), BP-BM+NIR groups (70 μg ml−1, 650 nm, 0.5 W cm−2, 5 min), BP/C60-mixture groups (70 μg ml−1 BP and 30 μg ml−1 C60, 650 nm, 0.5 W cm−2, 5 min) and BP-C60 (70 μg ml−1 BP and 30 μg ml−1 C60, 650 nm, 0.5 W cm−2, 5 min) respectively. (b) Flow cytometric analysis and DCF fluorescence intensity of the staining displayed in Fig. 2a. (d) Corresponding main fluorescence intensity (MFI) values displayed in Fig. 2b. | ||
In vitro photodynamic therapy
The high-efficiency ROS generation stimulates us to further explore the ability of the BP-C60 hybrid to kill cancer cells in vitro. We first investigate the toxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid to 4T1 cells under light and dark conditions, using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (Fig. 4a and b). Since the content of BP in the BP-C60 hybrid is about 70% (w/w),26 the BP concentration gradients were set as 0, 70, and 140 μg ml−1 for the PDT experiments. As shown in Fig. 4a, the cell survival rate decreased with the increase of the BP-C60 hybrid concentration under near-infrared (NIR) light irradiation for all the samples, while the cell growth inhibition ratio reached approximately 90% (P < 0.001) relative to that of the control PBS sample for the BP-C60 hybrid, which is much higher than that for BP-BM (30%) and the BP/C60-mixture (∼50%). Such an in vitro cytotoxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid is also much higher than those for BP nanosheets including BP quantum dots reported in the literature.15 The superior tumor killing ability of the BP-C60 hybrid is due to its superior ability to generate ROS under light irradiation as discussed above. In the absence of light, the cell viability exceeded 90% even at a concentration of 140 μg ml−1 for all the samples, suggesting that the toxicities of these samples on tumor cells are quite low. These results are consistent with those previously reported.35,36 We further tested the toxic effect of the BP-C60 hybrid towards other tumor cells (MCF-7 and Huh-7) and normal cells (RAW 264.7 and U937), and found that, without light irradiation, all the cell types displayed viabilities of more than 90% even at a high concentration of 140 μg ml−1 (Fig. 4c). Hence, we confirmed that the intrinsic toxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid is negligible, which is beneficial for its in vivo PDT applications.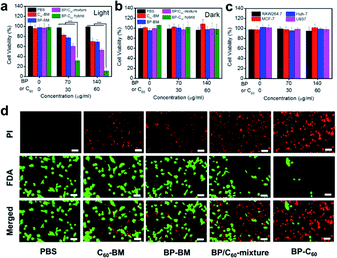 | ||
| Fig. 4 In vitro antitumor efficacy. (a) In vitro cytotoxicity of the different nanomaterials against 4T1 cells when exposed to light irradiation (650 nm, 0.5 W cm−2, 5 min). (b) In vitro cytotoxicity of the different nanomaterials against 4T1 cells in the absence of light irradiation (Dark). (c) In vitro cytotoxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid against different cells in the absence of light irradiation. For consistency, the concentration of BP within BP-BM, the BP/C60-mixture and the BP-C60 hybrid remains consistent for each group. The average weight ratio of BP within the BP-C60 hybrid is estimated to be ∼70% based on our previous study;26 accordingly the concentration of the BP-C60 hybrid injected into the mice is 0, 100, and 200 μg ml−1. (d) Fluorescence images of 4T1 cells co-stained with FDA (live cells: green) and PI (dead cells: red) following the addition of different samples with irradiation (70 μg ml−1 BP and 30 μg ml−1 C60, 650 nm, 0.5 W cm−2, 5 min). Scale bar = 50 μm. *** P < 0.001. | ||
We next evaluated the efficacy of PDT based on the staining of living and dead cells using fluorescein diacetate (FDA) and propidium iodide (PI) (Fig. 4d). For the BP-C60 hybrid, the number of viable cells decreased drastically and a large number of apoptotic cells emitting red fluorescence appeared under illumination. In contrast, a large number of living cells (green) appeared in the PBS control and, compared with those for the BP-C60 hybrid, fewer apoptotic cells appeared for other groups (BP-BM, C60-BM and BP/C60-mixture), indicating the limited therapeutic effect of these groups. These results show that grafting of C60 molecules greatly improves the in vitro photodynamic anti-tumor efficacy of BP nanosheets.
In vivo photodynamic therapy
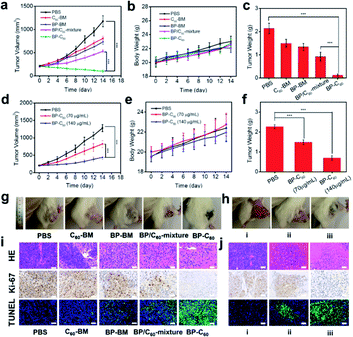
The in vivo anti-tumor effect of the BP-C60 hybrid was evaluated in a 4T1 mouse model. It has been reported that BP-based hybrid materials with a lateral size of about 200 nm and thickness of about 5.5 nm can be endocytosed into cells via micropinocytosis.33,36 Since the BP-C60 hybrid has an even smaller lateral size and thickness as discussed above, it can be endocytosed into cells (see Fig. 1b). We first injected the samples directly into the tumor for PDT measurements and studied the therapeutic effect of intravenous injection of different concentrations of the BP-C60 hybrid. The changes in tumor volume, which reflect the therapeutic effect of the BP-C60 hybrid, were monitored for 14 days (Fig. 5a and d). In addition, we monitored the whole body weight every 2 days (Fig. 5b and e). According to the changes in the tumor volume, the BP-C60 hybrid had the highest tumor inhibition rate (88.2%), which was much higher than those for C60-BM (30.7%), BP-BM (36.6%) and the BP/C60 mixture (55.2%). The BP-C60 hybrid displayed the best therapeutic effect due to its highest efficiency in generating ROS and its highest stability as discussed above. Moreover, even after injecting the BP-C60 hybrid into the tail vein, the BP-C60 hybrid still showed a considerable anti-tumor effect. At a concentration of 70 and 140 μg ml−1, the tumor inhibition rate was 35.9% and 65.6%, respectively, indicating that the anti-tumor activity of the BP-C60 hybrid was concentration dependent. There was no obvious body weight loss during treatment, suggesting a good biocompatibility of the BP-C60 hybrid. At the end of the 14 day experiment, the mice were sacrificed, the final tumor weight was obtained (Fig. 5c and f), and the tumor tissue was used for histological examination (Fig. 5i and j). According to the hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, the BP-C60 hybrid, BP-BM, C60-BM, and BP/C60-mixture all caused structural deformations to different degrees or cell death compared to the PBS control, while the tumors from the BP-C60 hybrid group exhibited the most obvious nuclear contraction or disappearance.37 In addition, following treatment with the BP-C60 hybrid, the proportion of Ki-67 positive cells was significantly lower than that for the control groups, indicating that the cell proliferation ability of tumor cells was significantly inhibited using the BP-C60 hybrid.38 In addition, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay slices were tested in the mice treated with the BP-C60 hybrid, revealing that many tumor cells were dead or apoptotic as determined by green fluorescence staining.39 In the tail vein injection experiment, the BP-C60 hybrid with the highest concentration (containing 140 μg ml−1 BP) exhibited superior anti-tumor ability to the PBS group and the group with the lower concentration (containing 70 μg ml−1 BP). With the increase of the sample concentration, more apoptosis and less proliferation of cancer cells were observed, indicating that the therapeutic effect was concentration-dependent. Together, these histological results reveal that the BP-C60 hybrid has the best anti-tumor effects compared with BP-BM or C60-BM.Assessment of systemic toxicity is another important aspect of determining biomedical material safety.40 We used histopathology to evaluate the in vivo toxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid. As shown in ESI Fig. S5,† after intravenous injection of the BP-C60 hybrid at different concentrations, the main organs of the mice showed no obvious damage, confirming the good biocompatibility and low systemic toxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid. Although it has been reported that BP is intrinsically toxic being able to kill tumor cells, at our used doses (70 or 140 μg ml−1) BP has low systemic toxicity, proving its biomedical applications.
Mechanism of enhancement of the photodynamic therapy efficacy of BP
The significantly enhanced PDT efficacy of BP nanosheets after grafting C60 molecules can be explained by considering the change in the energy band structure. The conduction band (CB) and valence band (VB) energy levels of the BP-C60 hybrid determined by synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy (SR-PES) are −3.27 eV and −4.64 eV versus vacuum level (−1.23 and 0.14 eV vs. the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE), respectively), which are both shifted negatively relative to those of pristine BP-BM.26 In particular, the negative shift of the CB level facilitates the reduction of the dissolved O2 to generate ˙O2−, which then transforms to ˙OH radicals which consequently act as ROS to kill the tumor cells (see ESI Fig. S6†). Since grafting of C60 molecules promotes generation of ROS of BP as discussed above, significantly enhanced PDT efficacy is achieved by the BP-C60 hybrid.Conclusions
In summary, the BP-C60 hybrid material, in which C60 was covalently grafted onto the edge of BP nanosheets, was applied as a novel endocytosed photosensitizer for PDT applications. Owing to the high stability of hydrophobic C60 against light, oxygen and water, grafting of stable C60 molecules onto the edges of BP nanosheets resulted in dramatic improvement of the physiological stability of BP nanosheets in serum, PBS and water. Furthermore, grafting of C60 molecules greatly promoted the ROS production efficiency of BP nanosheets within cells. Consequently the in vitro cell growth inhibition ratio reaches approximately 90% relative to that of the blank PBS sample for the BP-C60 hybrid. According to the in vivo anti-tumor measurements, the BP-C60 hybrid has the highest tumor inhibition rate of 88.2%, which is much higher than that of unmodified BP-BM (36.6%). After injection of the BP-C60 hybrid at a relatively high concentration of 70 or 140 μg ml−1 into the tail vein of mice, a tumor inhibition rate of 65.6% was achieved. The in vivo toxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid was further evaluated by using histopathology, confirming its low systemic toxicity. The significantly enhanced PDT efficacy achieved by the BP-C60 hybrid is attributed to the promoted generation of ˙OH radicals through photoinduced electron transfer from BP to C60, which act as ROS to kill tumor cells. As the first BP-fullerene hybrid nanomaterial fulfilling promoted ROS generation and consequently enhanced PDT efficacy, our strategy in enhancing the PDT efficacy of BP nanosheets paves the way for the application of BP in tumor therapies.Experimental
Materials
Black phosphorus (BP) crystals were purchased from XFNANO (Nanjing, China). C60 (99.6%) was acquired from FUNANO (Xiamen, China). Isopropanol (IPA) and absolute ethanol were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd (Shanghai, China). All the chemicals were used directly without further purification. p-Phthalic acid (PTA) was purchased from ShangHai YuanYe Biotechnology (Shanghai, China). Rhodamine B (technical grade) was obtained from INNOCHEM (Beijing, China). PBS and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were acquired from Thermo-Fisher (USA). Fluorescein diacetate (FDA), propidium iodide (PI) and cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assays were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (USA). DCFH-DA and JC-1 were obtained from Beyotime Company (China).Synthesis of the BP-C60 hybrid
The BP-C60 hybrid was prepared by a solid-state mechanochemical method, as reported previously.26 Briefly, 50 g of 3 mm diameter ZrO2 balls were placed in a ZrO2 ball-milling jar, and then 300 mg bulk BP and 600 mg C60 powders were added. The jar was sealed in an argon-filled glovebox and ball-milling was performed for 24 h, as reported previously. The rotation speed was 250 rpm, and the ball-milling procedure was also performed for 30 min milling time with a 15 min interval to cool the instrument. Finally, unreacted C60 was removed from the milled product by Soxhlet-extraction using CS2 for 48 h, followed by drying for 24 h at 40 °C in a vacuum.Cell culture
The Huh-7 human liver cancer cell line, U937 human macrophage cell line, RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cell line, MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines and 4T1 mouse breast cancer cell line cells were obtained from the Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and incubated in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37 °C.Animal models: female BALB/c mice aged 4–5 weeks were purchased from the Vital River Company (Beijing, China). A total of 1 × 106 4T1 cells suspended in 100 μl PBS were injected subcutaneously into each mouse to establish tumor models. All the protocols were approved by the Wuhan University Animal Care Facility and National Institutes of Health Guidelines.
Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation
For determination of ROS levels via fluorescence imaging, 4T1 cells were incubated for 6 h in five different groups of samples, as follows: (1) control (PBS), (2) C60-BM, (3) BP-BM, (4) BP/C60-mixture, and (5) BP-C60. BP was added at a concentration of 140 μg ml−1 in groups 3, 4 and 5. The C60 concentration was 60 μg ml−1 in groups 2, 4 and 5. The fluorescent dye DCFH-DA (10 μmol L−1) was added and co-incubated for 20 min at 37 °C. The cells in each group were then irradiated with a 650 nm laser at a power density of 0.5 W cm−2 for 5 min. ROS levels were measured using fluorescence microscopy (IX81, Olympus, Japan). The fluorescence intensity in each group was measured using a flow cytometer (FACScaliber, Becton Dickinson, USA). JC-1 assays were performed by incubating 4T1 cells for 6 h with five different groups of materials: (1) control (PBS), (2) C60-BM, (3) BP-BM, (4) BP/C60-mixture, and (5) BP-C60. The BP concentration was 140 μg ml−1 in groups 3, 4 and 5. The C60 concentration was 60 μg ml−1 in groups 2, 4 and 5. The cells in each group were then irradiated with a 650 nm laser at a power density of 0.5 W cm−2 for 5 min. The cells were stained with JC-1 for 30 min prior to washing with PBS. Mitochondrial damage or disruption was then evaluated by fluorescence microscopy (IX81, Olympus, Japan).In vitro phototoxicity
Phototoxicity was evaluated using a CCK-8 assay, performed in 96-well plates in which 4T1 cells were incubated at a density of 5 × 103 cells per well. Five different samples were compared: (1) control (PBS), (2) C60-BM, (3) BP-BM, (4) BP/C60-mixture, and (5) BP-C60. The concentration of BP was 70 μg ml−1 in groups 3, 4 and 5, and the C60 powder concentration was 30 μg ml−1 in groups 2, 4 and 5. The 4T1 cells were incubated for 6 h and then irradiated for 5 min at a power density of 0.5 W cm−2 using a 650 nm laser. CCK-8 at a concentration of 5 mg ml−1 in PBS was added to the plates and then incubated for further 4 h, after which the absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a microplate reader. Background absorption of each well was subtracted from individual measurements. The final phototoxicity of the samples was calculated using: (T/C × 100%), in which T represents the optical density value of the treatment group and C represents the optical density value of the control group. Phototoxicity of the different groups was analyzed at different concentrations, including 0 and 140 μg ml−1 BP.In addition, the phototoxicity of each sample was investigated further. 4T1 cells were seeded in the wells of 96-well plates and incubated overnight. The culture medium was refreshed and then a sample of each of the five groups was added to the cells, the groups comprising: (1) control (PBS), (2) C60-BM, (3) BP-BM, (4) BP/C60-mixture, and (5) BP-C60. The cells in contact with the different samples were then irradiated with a 650 nm laser for 5 min after incubation for 4 h at a power density of 0.5 W cm−2. After 24 h, the cells in the various groups were washed with PBS then incubated with FDA and PI. Finally, the cells were observed using a fluorescence microscope (IX81, Olympus, Japan).
In vitro dark toxicity
The toxicity of the various nanomaterials to tumor cells was evaluated in the absence of light using a CCK-8 assay. 4T1 cells were seeded in the wells of 96-well plates at a density of 5 × 103 cells per well, and then incubated for 24 h, consistent with the in vitro phototoxicity analysis described above. No laser irradiation was performed on the samples. Instead, the toxicity of the BP-C60 hybrid material was evaluated in Huh-7 human liver cancer cells, U937 human macrophages, RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages, and MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in the dark.In vivo anti-tumor study
Because C60 is hydrophobic, we initially injected the nanomaterial directly into the tumor to perform photodynamic therapy (intratumoral injection group). The therapeutic effect of the BP-C60 hybrid materials at different concentrations was assessed by injection through the tail vein of mice (tail vein injection group). Female BALB/c mice aged 4–5 weeks were purchased from the Vital River Company (Beijing, China). A total of 1 × 106 4T1 cells in suspension in 100 μl PBS were subcutaneously injected into each mouse in order to establish the tumor model. The mice were randomly divided into 5 groups, each group comprising 5 mice in order to increase the statistical power of the study. Control PBS and the different nanomaterials as described above, were injected intratumorally, as appropriate for each group. The concentration of BP in groups 3, 4 and 5 was 140 μg ml−1, with a concentration of C60 of 60 μg ml−1. The tumors in the mice were irradiated using a 650 nm laser for 30 min following injection (0.5 W cm−2, 10 min). This step was performed every 2 days for 14 days. When the tumors had increased to a volume of 200 mm3, the mice were randomly divided into three groups, each group comprising 5 mice, consisting of: (1) control (PBS), (2) BP-C60 containing 70 μg ml−1 BP and (3) BP-C60 containing 140 μg ml−1 BP. The tumor site of all the groups was irradiated for 10 min using a 650 nm laser 24 h post-injection at a power density of 0.5 W cm−2. This was also conducted every 2 days for 14 days, during which time the tumor volume and body weight of each mouse were also measured. All the mice were subsequently sacrificed after 14 days and the five major organs, including the heart, liver, spleen, lungs and kidneys from each group were collected and washed with PBS. The organs were then fixed with paraformaldehyde for further histological analysis. The tumor tissue was then weighed, fixed in 4% neutral buffered formalin, placed in paraffin and ultimately sectioned to a thickness of 4 μm. Finally, the tissues were stained and examined by optical microscopy.Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a post-hoc Tukey comparison test, using GraphPad Prism 5.0 software. A P-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.Measurements and characterization
UV-vis absorption spectroscopy was performed on a 3700 UV-vis spectrometer (Shimadzu, Japan). FTIR spectra were obtained on a TENSOR 27 spectrometer (Bruker, Germany) at room temperature. Raman spectra were obtained using inVia Raman Microscope equipment (Renishaw, England) with a 532 nm excitation laser. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were obtained from a JEOL JSM-6390LA instrument (Rigaku, Japan). The high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) was performed on a JEOL-2010 (Rigaku, Japan) microscope operating at a voltage of 200 kV. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) measurements were conducted on an XE7 scanning probe microscope (Park, Korea).Synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy (SR-PES) experiments were performed at the Catalysis and Surface Science endstation in the National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory (NSRL), Hefei, China, measured using synchrotron radiation light as the excitation source with a photon energy of 39.9 eV. A sample bias of −5 V was applied to observe the secondary electron cutoff. The powdery materials were fixed on the substrate with conductive adhesive and then loaded into the cavity and evacuated overnight for testing.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0402800 and 2018YFC1311300) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1932214, 51925206, and U1604175).Notes and references
- C. Minelli, S. B. Lowe and M. M. Stevens, Small, 2010, 6, 2336–2357 CrossRef CAS.
- D. E. Dolmans, D. Fukumura and R. K. Jain, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2003, 3, 380–387 CrossRef CAS.
- X. S. Li, S. Lee and J. Yoon, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 1174–1188 RSC.
- H. Abrahamse and M. R. Hamblin, Biochem. J., 2016, 473, 347–364 CrossRef CAS.
- R. C. Lv, D. Yang, P. P. Yang, J. T. Xu, F. He, S. L. Gai, C. X. Li, Y. L. Dai, G. X. Yang and J. Lin, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28, 4724–4734 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Mannix, B. Kiraly, M. C. Hersam and N. P. Guisinger, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2017, 1, 0014 CrossRef CAS.
- L. K. Li, Y. J. Yu, G. J. Ye, Q. Q. Ge, X. D. Ou, H. Wu, D. L. Feng, X. H. Chen and Y. B. Zhang, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2014, 9, 372–377 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Z. Kou, C. F. Chen and S. C. Smith, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6, 2794–2805 CrossRef CAS.
- S. H. Liu, S. H. Lin, P. You, C. Surya, S. P. Lau and F. Yan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 13717–13721 CrossRef CAS.
- J. R. Choi, K. W. Yong, J. Y. Choi, A. Nilghaz, Y. Lin, J. Xu and X. N. Lu, Theranostics, 2018, 8, 1005–1026 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Anju, J. Ashtami and P. V. Mohanan, Mater. Sci. Eng., C, 2019, 97, 978–993 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Y. Wang and X. F. Yu, Small, 2018, 14, 1702830 CrossRef.
- H. Wang, X. Z. Yang, W. Shao, S. C. Chen, J. F. Xie, X. D. Zhang, J. Wang and Y. Xie, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 11376–11382 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, S. Yu, P. Yang and B. Hu, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, 1–11 Search PubMed.
- T. Guo, Y. Wu, Y. Lin, X. Xu, H. Lian, G. M. Huang, J. Z. Liu, X. P. Wu and H. H. Yang, Small, 2018, 14, 1702815 CrossRef.
- J. T. Liu, T. R. Liu, P. Du, L. Zhang and J. P. Lei, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 7808–7812 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kuriakose, T. Ahmed, S. Balendhran, V. Bansal, S. Sriram, M. Bhaskaran and S. Walia, 2D Mater., 2018, 5, 032001 CrossRef.
- Y. Abate, D. Akinwande, S. Gamage, H. Wang, M. Snure, N. Poudel and S. B. Cronin, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1704749 CrossRef.
- Z. H. Hu, Q. Li, B. Lei, Q. H. Zhou, D. Xiang, Z. Y. Lyu, F. Hu, J. Y. Wang, Y. J. Ren, R. Guo, E. Goki, L. Wang, C. Han, J. L. Wang and W. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 9131–9135 CrossRef CAS.
- C. R. Ryder, J. D. Wood, S. A. Wells, Y. Yang, D. Jariwala, T. J. Marks, G. C. Schatz and M. C. Hersam, Nat. Chem., 2016, 8, 597–602 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. J. Liu, P. F. Gao, T. M. Zhang, X. J. Zhun, M. M. Zhang, M. Q. Chen, P. W. Du, G. W. Wang, H. X. Ji, J. L. Yang and S. F. Yang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 1479–1483 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Wu, J. H. Wang, J. Lu, D. N. Liu, N. Yang, H. Huang, P. K. Chu and X.-F. Yu, Small, 2018, 14, 1801405 CrossRef.
- Y. H. Zhao, Q. H. Zhou, Q. Li, X. J. Yao and J. L. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1603990 CrossRef.
- Q. L. Feng, H. Y. Liu, M. J. Zhu, J. Shang, D. Liu, X. Q. Cui, D. Q. Shen, L. Z. Kou, D. Mao, J. B. Zheng, C. Li, J. Zhang, H. Xu and J. L. Zhao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 9679–9687 CrossRef CAS.
- K. L. Kuntz, R. A. Wells, J. Hu, T. Yang, B. J. Dong, H. H. Guo, A. H. Woomer, D. L. Druffel, A. Alabanza, D. Tománek and S. C. Warren, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 9126–9135 CrossRef CAS.
- X. J. Zhu, T. M. Zhang, D. C. Jiang, H. L. Duan, Z. J. Sun, M. M. Zhang, H. C. Jin, R. N. Guan, Y. J. Liu, M. Q. Chen, H. X. Ji, P. W. Du, W. S. Yan, S. Q. Wei, Y. L. Lu and S. F. Yang, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 4177 CrossRef.
- P. Mroz, G. P. Tegos, H. Gali, T. Wharton, T. Sarna and M. R. Hamblin, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2007, 6, 1139–1149 RSC.
- T. S. Wang and C. R. Wang, Small, 2019, 1901522 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Y. Jeon, H. J. Choi, S. M. Jung, J. M. Seo, M. J. Kim, L. M. Dai and J. B. Baek, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 1386–1393 CrossRef CAS.
- S. E. Zhu, F. Li and G. W. Wang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 7535–7570 RSC.
- B. Chai, X. Liao, F. K. Song and H. Zhou, Dalton Trans., 2014, 43, 982–989 RSC.
- S. H. Wang, L. Shang, L. L. Li, Y. J. Yu, C. W. Chi, K. Wang, J. Zhang, R. Shi, H. Y. Shen, G. I. Waterhouse, S. J. Liu, J. Tian, T. R. Zhang and H. Y. Liu, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 8379–8387 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Y. Yang, D. Y. Wang, Y. H. Shi, J. H. Zou, Q. Zhao, Q. Zhang, W. Huang, J. J. Shao, X. J. Xie and X. C. Dong, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 12431–12440 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Jain, Y. Singh, S. Cho, S. P. Sasikala, S. H. Koo, R. Narayan, H. Jung, Y. Jung and S. O. Kim, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 2786–2794 CrossRef CAS.
- X. W. Zeng, M. M. Luo, G. Liu, X. S. Wang, W. Tao, Y. X. Lin, X. Y. Ji, L. Nie and L. Mei, Adv. Sci., 2018, 5, 1800510 CrossRef.
- W. S. Chen, J. Ouyang, H. Liu, M. Chen, K. Zeng, J. P. Sheng, Z. J. Liu, Y. J. Han, L. Q. Wang, J. Li, L. Deng, Y. N. Liu and S. J. Guo, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1603864 CrossRef.
- L. L. Bu, Z. L. Zhao, J. F. Liu, S. R. Ma, C. F. Huang, B. Liu, W. F. Zhang and Z. J. Sun, Oncotarget, 2015, 6, 41944–41958 CrossRef.
- G. T. Yu, L. L. Bu, Y. Y. Zhao, B. Liu, W. F. Zhang, Y. F. Zhao, L. Zhang and Z. J. Sun, Am. J. Cancer Res., 2014, 4, 764–775 CAS.
- M. Q. Chu, Y. X. Shao, J. L. Peng, X. Y. Dai, H. K. Li, Q. S. Wu and D. L. Shi, Biomaterials, 2013, 34, 4078–4088 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Nel, T. Xia, L. Madler and N. Li, Science, 2006, 311, 622–627 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d0sc03349a |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |