New insights into H2 activation by intramolecular frustrated Lewis pairs based on aminoboranes: the local electrophilicity index of boron as a suitable indicator to tune the reversibility of the process†
Abstract
A large set of intramolecular aminoborane-based FLPs was studied employing density functional theory in the H2 activation process to analyze how the acidity and basicity of boron and nitrogen atoms, respectively, affect the reversibility of the process. Three different linkers were employed, keeping the C–C nature in the connection between both Lewis centers: –CH2–CH2–, –CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH–, and –C6H4–. The results show that significant differences in the Gibbs free energy of the process are found by considering all the combinations of substituents. Of the 75 systems studied, only 9 showed the ability to carry out the process reversibly (ΔGH2 in the range of −3.5 to 2.0 kcal mol−1), where combinations of alkyl/aryl or aryl/alkyl in boron/nitrogen generate systems capable of reaching reversibility. If the alkyl/alkyl or aryl/aryl combination is employed, highly exergonic (non-reversible H2 activation) and endergonic (unfeasible H2 activation) reactions are found, respectively. No appreciable differences in the linker were found, allowing us to continue the analysis with the most entropically favorable linker, the –C6H4– linker. From this, 25 different FLP systems of type 2-[bis(X)boryl]-(Y)aniline (X: H, CF3, C6F5, PFtB, FMes and Y: H, CH3, t-but, Ph, Mes) can be formed. By analyzing the electronic properties of each system, we have found that the condensed-to-boron electrophilicity index ωB+ is inversely related to the ΔGH2. Interestingly, two relationships were found; the first is for alkyl groups (Y: CH3 and t-but) and the second for aryl groups (Y: H, Ph, and Mes), which is intimately related to the proton affinity of each aniline. In addition, it is quite interesting when the frustration degree, given by B⋯N distance dB–N, is brought together with ωB+, since the
CH–, and –C6H4–. The results show that significant differences in the Gibbs free energy of the process are found by considering all the combinations of substituents. Of the 75 systems studied, only 9 showed the ability to carry out the process reversibly (ΔGH2 in the range of −3.5 to 2.0 kcal mol−1), where combinations of alkyl/aryl or aryl/alkyl in boron/nitrogen generate systems capable of reaching reversibility. If the alkyl/alkyl or aryl/aryl combination is employed, highly exergonic (non-reversible H2 activation) and endergonic (unfeasible H2 activation) reactions are found, respectively. No appreciable differences in the linker were found, allowing us to continue the analysis with the most entropically favorable linker, the –C6H4– linker. From this, 25 different FLP systems of type 2-[bis(X)boryl]-(Y)aniline (X: H, CF3, C6F5, PFtB, FMes and Y: H, CH3, t-but, Ph, Mes) can be formed. By analyzing the electronic properties of each system, we have found that the condensed-to-boron electrophilicity index ωB+ is inversely related to the ΔGH2. Interestingly, two relationships were found; the first is for alkyl groups (Y: CH3 and t-but) and the second for aryl groups (Y: H, Ph, and Mes), which is intimately related to the proton affinity of each aniline. In addition, it is quite interesting when the frustration degree, given by B⋯N distance dB–N, is brought together with ωB+, since the 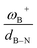 quotient has unit energy/length corresponding to unit force; concomitantly, a measure of the FLP strength in H–H bond activation can be defined. With this finding, a rational design of this kind of FLP can be performed by analyzing the acidity of boron through condensed-to-boron electrophilicity and knowing the nature of the substituent of nitrogen according to whether the Y is alkyl or aryl, optimizing the H2 reversible activation in a rational way, which is crucial to improve the catalytic performance.
quotient has unit energy/length corresponding to unit force; concomitantly, a measure of the FLP strength in H–H bond activation can be defined. With this finding, a rational design of this kind of FLP can be performed by analyzing the acidity of boron through condensed-to-boron electrophilicity and knowing the nature of the substituent of nitrogen according to whether the Y is alkyl or aryl, optimizing the H2 reversible activation in a rational way, which is crucial to improve the catalytic performance.

- This article is part of the themed collection: #MyFirstChemSci 2023


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...