Reactions of organic peroxy radicals, RO2, with substituted and biogenic alkenes at room temperature: unsuspected sinks for some RO2 in the atmosphere?†
Abstract
Until now the reactions of organic peroxy radicals (RO2) with alkenes in the gas phase have been essentially studied at high temperature (T ≥ 360 K) and in the context of combustion processes, while considered negligible in the Earth's atmosphere. In this work, the reactions of methyl-, 1-pentyl- and acetylperoxy radicals (CH3O2, C5H11O2, and CH3C(O)O2, respectively) with 2-methyl-2-butene, 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene and for the first time the atmospherically relevant isoprene, α-pinene, and limonene were studied at room temperature (298 ± 5 K). Monitoring directly the radicals with chemical ionization mass spectrometry led to rate coefficients larger than expected from previous combustion studies but following similar trends in terms of alkenes, with (in molecule−1 cm3 s−1) 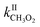 = 10−18 to 10−17 × 2/2 and
= 10−18 to 10−17 × 2/2 and 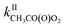 = 10−14 to 10−13 × 5/5. While these reactions would be negligible for CH3O2 and aliphatic RO2 at room temperature, this might not be the case for acyl-, and perhaps hydroxy-, allyl- and other substituted RO2. Combining our results with the Structure–Activity Relationship (SAR) predicts kII(298 K) ∼10−14 molecule−1 cm3 s−1 for hydroxy- and allyl-RO2 from isoprene oxidation, potentially accounting for up to 14% of their sinks in biogenic-rich regions of the atmosphere and much more in laboratory studies.
= 10−14 to 10−13 × 5/5. While these reactions would be negligible for CH3O2 and aliphatic RO2 at room temperature, this might not be the case for acyl-, and perhaps hydroxy-, allyl- and other substituted RO2. Combining our results with the Structure–Activity Relationship (SAR) predicts kII(298 K) ∼10−14 molecule−1 cm3 s−1 for hydroxy- and allyl-RO2 from isoprene oxidation, potentially accounting for up to 14% of their sinks in biogenic-rich regions of the atmosphere and much more in laboratory studies.

- This article is part of the themed collections: 2021 ChemSci Pick of the Week Collection and 2021 Chemical Science HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...