Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleFrom reactive carbenes to chiral polyether macrocycles in two steps – synthesis and applications made easy?
Alexandre
Homberg
 and
Jérôme
Lacour
and
Jérôme
Lacour
 *
*
Department of Organic Chemistry, University of Geneva, Quai Ernest Ansermet 30, 1211 Geneva 4, Switzerland. E-mail: Jerome.lacour@unige.ch
First published on 12th March 2020
Abstract
Chiral polyether macrocycles are versatile molecules. For their preparation, original two-step procedures were recently developed and present the advantages of high concentration conditions and simple starting reagents (stable diazo reagents, small cyclic ethers, aliphatic or aromatic amines). Enantiopure materials are readily afforded by CSP-HPLC on a semi-preparative scale. Flexibility and adaptability in the macrocyclic design are provided by a large selection of amines to choose from while the ring size and chemical nature are controlled by the choice of 5 to 7-membered cyclic ether precursors. Such macrocycles have already been used as asymmetric catalysts, mono and ditopic receptors, fluorescent sensors and probes, and chiroptical reversible switches.
Introduction
Decomposition of diazo compounds in the presence of oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur or phosphorus Lewis bases is a recognized strategy to generate the corresponding ylides efficiently.1 In the case of oxonium ylides, diazo reagents decomposed under photochemical or metal-catalyzed conditions2 are known to react with cyclic ethers such as epoxides,3 oxetane,4 THF,5 THP,6 1,3- and 1,4-dioxane,7 or oxepane,8 and the subsequent intermediates are used in a large panel of reactions including macrocyclization.7e,9 Macrocyclic molecules are an important class of compounds in nature. About 20% of the known natural products are made of a cyclic core with at least 11 atoms.10 Many of them exhibit a variety of biological11 or medicinal properties.12 Polyether macrocycles are a particular subclass of this family that act as efficient binding receptors for cations or small molecules.13 Attaching a suitable functional group or a probe to the core of the molecule leads to various and versatile uses and applications such as catalysis14 or sensing for either recognition or quantification of analytes.15However, synthesis of such large and highly functionalized molecules requires several synthetic steps and usually high dilution conditions for the key ring-closure.16 To circumvent this major drawback, a new type of macrocyclic [3 + X + 3 + X] condensation (X = 5, 6 or 7) was developed by Lacour and co-workers based on new diazo decomposition reactivity in the presence of common and simple cyclic ethers. Coupled with an unprecedented tandem [amidation + olefin transposition] sequence, the ylide reactivity then leads to the new and original family of chiral polyether macrocycles 1 (Fig. 1). This mini review will focus on the unique synthesis of compounds 1 and the various derived applications. First, the key macrocyclization step and subsequent optimizations, which lead to routine synthetic procedures on a large scale (up to 20 gram batches), will be presented. Second, the highly diastereoselective amidation plus transposition process will be detailed. Finally, different applications of such types of macrocycles ranging from catalysis to reversible chiroptical switching will be detailed.
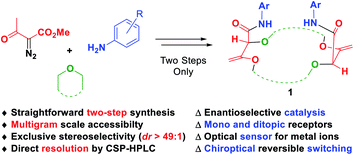 | ||
| Fig. 1 Straightforward multicomponent synthesis and applications of highly functionalized chiral polyether macrocycles 1. | ||
Chiral polyether macrocycles: synthesis
Step 1: diazo decomposition towards reactive ylide intermediates and unsaturated macrocycles
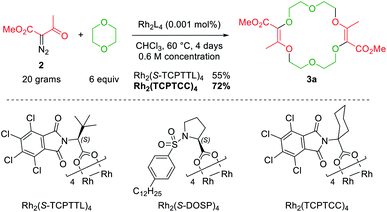
Decomposition of diazo compounds by transition metal catalysts is an effective way to generate electrophilic metal carbenes.1a These reactive species undergo further transformations such as dimerization, insertion, cyclopropanation, dipolar addition, ylide formation and subsequent rearrangement depending on conditions. Ylides, in particular, oxonium ylides, are formed by reaction of metal carbenes with ether moieties.3,4,7a,17 In this context, 16- to 20-membered ring polyether macrocycles can be synthesized by [3 + X + 3 + X] multicomponent condensation of methyl α-diazo-β-ketoester 2 with cyclic ethers (X = 5 to 7) under dirhodium(II) catalysis (Fig. 2, top).7b Contrary to conventional macrocycle synthesis, this transformation occurs at a high concentration of reagent 2 (c 1 M) and under strictly non-templated conditions. Mechanistically, diazo 2 is decomposed by the dirhodium catalyst to form an electrophilic metal carbene A (Fig. 2, bottom). The cyclic ether then acts as a nucleophile and generates metal-bond oxonium ylide B. After release of the catalyst, (metal-free) oxonium ylide C dimerizes in a non-concerted process to form macrocycle 3.18 The need for high concentration is explained by this last step which is rate determining and second-order in ylide C kinetically. In addition, the reaction tolerates various α-diazo-β-ketoester reagents to afford the corresponding macrocycles in moderate to good yields (up to 80% generally).7b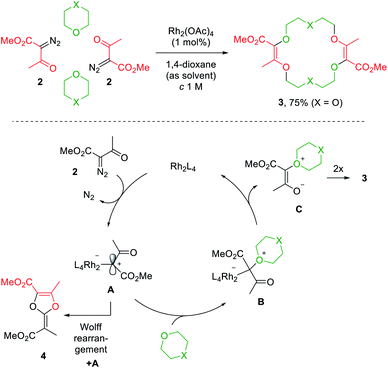 | ||
| Fig. 2 One pot [3 + X + 3 + X] condensation of diazo 2 with a cyclic ether under Rh(II) catalysis (top) and the proposed mechanism (bottom). | ||
Also, 1,4-dioxane can be replaced by other 5-, 6- or 7-membered cyclic ethers such as THF (tetrahydrofuran), THP (tetrahydropyran) or oxepane to generate products 3a–3d (Fig. 3).6 Functionalized THF and THP reagents can also be used to yield densely functionalized 16- and 18-membered ring macrocycles in moderate to good yields (35–67%). The kinetics of the diazo decomposition of 2 was studied with different rhodium catalysts by means of in situ infrared (reactIR) monitoring. The Rh2(OAc)4 catalyst used originally was shown to induce the slowest reaction rates for the diazo decomposition (0.24 h−1). Changing the catalytic complex to Rh2(Oct)4 or Rh2(R-DOSP)4 increased the reaction rate by a factor of two (0.54 h−1 and 0.55 h−1). But Hashimoto–Ikegami catalysts, Rh2(S-TCPTTL)4 and Rh2(S-PTTL)4, showed the highest activity in the decomposition of diazo 2 with first-order kinetic constants of 2.63 h−1 and 3.39 h−1 respectively. Thanks to this higher reactivity and additional speciation studies, it was possible to decrease the amount of catalyst down to 10−3 mol% and perform the macrocyclization on a multigram scale.19 Consequently, by using achiral phthalimido-based cyclohexyl-derived Rh2(TCPTCC)4 (10−3 mol%), the polyether macrocycle 3a was satisfactorily synthesized in 72% yield (Fig. 4). These optimizations lead to the routine synthesis of 3a on a large scale, up to 20 grams per batch.19
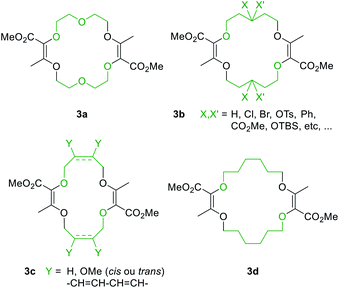 | ||
| Fig. 3 Macrocycles accessible from regular or functionalized 1,4-dioxane (3a), THP (3b), THF (3c) or oxepane (3d). | ||
Alternatively, protected morpholines were also considered. Such N-containing cyclic ethers react slower with metal carbenes than 1,4-dioxane, THP or THF derivatives (regular path A→ B). A competitive Wolff rearrangement of the metal carbene A can occur instead (pathway A→ 4, Fig. 2). A ketene intermediate is generated that reacts with a “second” metal carbene A to form compound 4, which is composed of a dioxolene ring fused with an α,β-unsaturated ester moiety. This process is detrimental to macrocycle formation. It was found that an intermediate catalyst loading (0.1 mol%) favors the O-ylide formation (A→ B, Fig. 2) and hence, following the same dimerization mechanism, diaza-macrocycles were satisfactorily afforded in moderate to good yields.20
Step 2: tandem [amidations + olefin transpositions] towards chiral polyether macrocycles
Despite the structural resemblance of compounds 3 to crown ethers, these unsaturated macrocycles do not bind cations. In 3a for instance, the lone pairs of oxygen atoms are not favorably oriented for cation binding.7b The twofold conjugated enol ester systems enforce strong molecular constraints and prevent any efficient structural rearrangement. A protocol was then developed to transform derivatives 3 into chiral frameworks by treatment with an excess of aromatic amines under strongly basic conditions (Fig. 5).21 In this single one-pot process two transformations occur: (i) the amidation of the ester functions and (ii) the transposition of the olefins from endocyclic to exocyclic positions. This double and tandem [amidation + olefin transposition] process is a highly diastereoselective reaction (diastereomeric ratio dr > 49![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) as only the chiral (racemic) isomers 1 are formed; achiral (meso) diastereoisomers are never observed.
1) as only the chiral (racemic) isomers 1 are formed; achiral (meso) diastereoisomers are never observed.
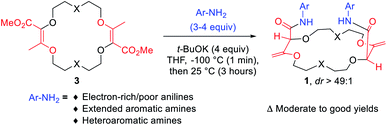
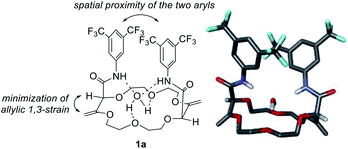
Polyether macrocycles of type 1 possess a peculiar conformation. The crown ether core is almost planar and acts as a platform while the systems formed by the olefins and C–H groups at the stereogenic center forced the two amide substituents to orient orthogonally to the plane of the skeleton to minimize allylic 1,3-strain (Fig. 6). Consequently, the two aromatic moieties are favorably and closely located facing each other. In the case of macrocycles made from 1,4-dioxane like 1a, a water molecule is also complexed within the polyether macrocyclic core and the amide functions are linked by hydrogen bonding interactions. This transformation is quite general (moderate to good yields) in terms of aromatic amine reagents as electron-rich or -poor anilines, extended aromatic amines and heteroaromatic amines are tolerated in this transformation. Additionally, unsaturated macrocycles made of different skeletons (from THF or THP) also yield the same type of chiral macrocycle after the double tandem [amidation + olefin transposition] process.22
With these new chiral macrocycles in hand, a general and practical protocol was developed to resolve derivatives 1 into single enantiomers efficiently by chiral stationary phase (CSP) HPLC. It was found that CHIRALPAK® IG is a particularly effective CSP. Its use, together with eluents in which the macrocyclic derivatives are (highly) soluble such as CH3CN and CH2Cl2, renders the enantiomeric separation operational routinely on a semi-preparative scale. Good selectivity factors (α) and pure samples of both enantiomers have always been obtained so far.23
Alternatively, to obtain macrocycles of type 1 bearing aliphatic amides, a two-step (consecutive) process is required from 3. In this case, it is necessary to decouple (i) the amidation realized by addition of aliphatic amines in the presence of TBD (1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene) from (ii) the olefin transposition step that is still performed under strongly basic conditions.24 Various linear and α-branched primary amines can be introduced and afford chiral aliphatic macrocycles in moderate to good yields. Of interest, it is possible to introduce enantiopure amines that lead to mixtures of diastereoisomers separable by simple flash chromatography and then obtain diastereomerically (and enantiomerically) pure compounds.
The functionalization of the enol ether termini of derivatives 1 was also achieved recently under radical conditions. Double thiol–ene reactions were performed under photo-irradiation. The fully regioselective anti-Markovnikov procedure yields saturated chiral macrocycles with protected or free dithiol arms, with moderate to excellent diastereoselectivity.25
Chiral polyether macrocycles: applications
Cation binding: catalysis and cooperativity
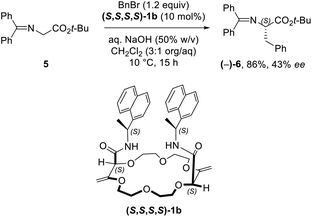
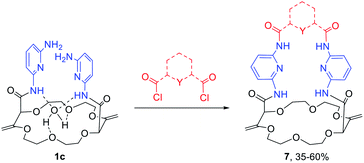
While solid state structures of macrocycles 1a (Fig. 6) indicated that the binding of a neutral molecule was possible (e.g. water),21a the coordination of cations like Na+ within the cavity of the polyether macrocycles was evidenced by X-ray crystallography during the preparation of the compounds.24 This ability to complex alkali metal salts and render them soluble in non-polar solvents can be put to use in efficient phase transfer catalysis (PTC) protocols. In fact, using non-racemic crown ether macrocycles, it is possible to achieve enantioselective alkylation, 1,4-addition or oxidation.14a–e Compounds of type 1 bearing enantiopure amide substituents were thus tested as catalysts for asymmetric PTC. The alkylation of protected glycine 5 with benzyl bromide, which affords chiral phenylalanine derivatives 6 as products, was selected as the benchmark.14d,e After optimization of the reaction conditions (catalyst, solvent, metal salt, concentration, …), macrocycle (S,S,S,S)-1b was found to be the best catalyst for this transformation. Optically active protected phenylalanine (−)-6 was afforded in 86% yield and 43% ee (Fig. 7).24Knowing that macrocycles of type 1 can bind cations, the addition of complementary anion binding sites was further considered. The ditopic receptor formation was realized in a single synthetic step using amino-substituted derivative 1c. In fact, treatment of precursors 1c with dicarbonyl dichloride reagents afforded macrocycles 7 in moderate to good yields (35–60%, Scheme 1).26 Binding properties of this new class of cryptands towards monovalent alkali cations, common anions and combined salts were studied in solution by 1H NMR spectroscopy and by X-ray diffraction analysis for solid state structures. Compounds 7 were found to be cooperative heteroditopic receptors for salts as the presence of both cations and anions is needed for favorable interactions. The cryptands present a general ion pair binding capacity towards salts made of monovalent cations (Na+, K+) and linear triatomic anions (N3−, NCO−, SCN−) or a trigonal oxyanion (NO3−) in particular. The salts are cooperatively bound within the polyamide-crown ether conjugates as contact ion pairs. The anions are generally complexed within the cavity through the NH bonding interactions while the cations lie encapsulated inside the polyether ring (Fig. 8).
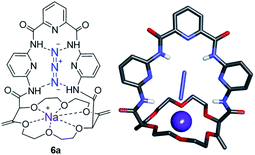 | ||
| Fig. 8 Stick view of the crystal structure of [NaN3·7a]. Reproduced from ref. 26 with permission from John Wiley and Sons. | ||
Luminescence quenching monitoring
Detection and sensing of metal ions are essential for the analysis of biological, chemical and environmental processes.15d,27 In the previous section, we used NMR spectroscopy and solid state structural analysis to monitor the interactions with salts. An alternative method was to use absorbance and fluorescence techniques28 which present the advantage of being highly sensitive (micro to nanomolar detection).29 These methods require the presence of an efficient reporting unit (e.g. fluorophore). One popular fluorophore is the pyrene moiety which exhibits a characteristic emission band at ca. 380–400 nm. In the case of spatial proximity between two (or more) pyrene units, a tell-tale excimer fluorescence (EF) centered at 500 nm is observed. The intensity of this transition strongly depends on the distance and the orientation between the two aromatic moieties.30 In fact, macrocycles of type 1 (bearing fluorophores like pyrene, perylene, fluorene, etc.) exhibit intense EF (Fig. 9).23,31 It was observed that the fluorescence of 1 can be quenched by addition of a metal ion. It was proposed that the amide C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds turn inwards in the presence of such cations to favor the complexation. The environment of the aromatic units is thus modified with the two chromophores parting from each other and elongating the distance between them. Hence, the EF is (partially) quenched and only the characteristic emission of (monomeric) the fluorophore is observed.
O bonds turn inwards in the presence of such cations to favor the complexation. The environment of the aromatic units is thus modified with the two chromophores parting from each other and elongating the distance between them. Hence, the EF is (partially) quenched and only the characteristic emission of (monomeric) the fluorophore is observed.
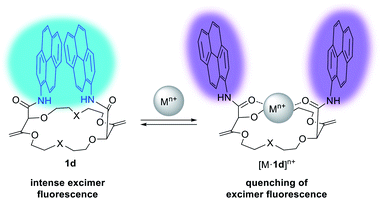 | ||
| Fig. 9 Fluorescence tuning and proposed conformational changes upon cation binding for 1d. Reproduced from ref. 31 with permission from John Wiley and Sons. | ||
Using polyether macrocycles 1d, a systematic analysis of the binding properties of a large range of mono-, di- and trivalent cations (alkaline, alkaline earth, p-, d-, and f-block metals) was performed by means of UV-Vis spectrophotometric titrations, cyclic voltammetry, excimer fluorescence quenching and transient absorption spectroscopy experiments.31 This study demonstrated that the best binding constants and most efficient quenching of EF are obtained with divalent cations (Ba2+ and Ca2+ specifically) in acetonitrile, while monovalent cations (Na+ and K+ specifically) afford similar results in CH2Cl2.23 Interestingly, the EF properties could also be used for the direct sensing of cations in competitive aqueous media. Reverse micelles composed of bis(2-ethylhexyl)sebacate (DOS), PEG, NaBArF and the pyrene derivative 1d were designed and prepared (Fig. 10A). Using excimer fluorescence quenching, these pH independent nanosensors allowed the sensing of potassium ions after exchange with the sodium contained within the micelle. An acute selectivity for the potassium ion over other metal ions (e.g. Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+) was demonstrated with the 1,4-dioxane-based 1d (X = O) macrocycle in particular (Fig. 10).8
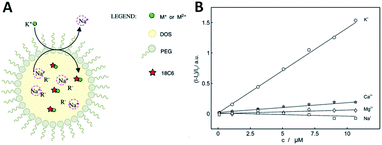 | ||
| Fig. 10 (A) Ion-selective reverse micelles; (B) normalized fluorescence (406 nm) as a function of concentrations of different cations for 1d. Reproduced from ref. 8 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
It is worth mentioning that cyclometalated dinuclear platinum(II) complexes 1e (Fig. 11) also present interesting phosphorescence properties. Derivatives 1e display 3MMLCT-based emission originating from an intramolecular Pt–Pt interaction centered around 595 nm. Upon addition of potassium ions and conformation rearrangement (Fig. 9), the dominant emission decreases in intensity while the blue shifted 3LC emission increases. The cation can be removed from the macrocycle by addition of regular 18-crown-6, making this system a reversible ratiometric luminescent switch.32
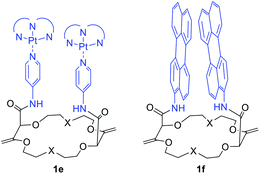 | ||
| Fig. 11 Macrocycles 1e and 1f used as reversible ratiometric luminescent switches and scaffolds to study targeted photophysical properties, respectively.32,33 | ||
Perylene substituted macrocycles 1f were also used as convenient scaffolds to study targeted photophysical properties, such as symmetry breaking charge separation. The study was performed using stationary and ultrafast electronic spectroscopies combined with molecular dynamics simulations. It was demonstrated that the nature of the excited state varies greatly from an excimer to a symmetry-broken charge separated state depending on the conformational restrictions (cation binding) and the local environment.33
Effective chiroptical properties
In the previous section, as applications did not require any asymmetric purposes, macrocycles 1a to 1f were utilized in the racemic form only. For the following uses, in contrast, care was taken to separate the chiral derivatives into single enantiomers by CSP-HPLC. In fact, a series of fluorescent macrocycles of type 1 substituted with pyrene (1d), perylene (1f), fluorene or naphthalene monoimide moieties (exhibiting intense excimer fluorescence in different spectral regions) were synthesized and resolved. Their chiroptical properties were then studied using electronic circular dichroism (ECD) and circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) in the absence and in the presence of metal ions.23 A sign inversion and enhancement of the ECD signal(s) were demonstrated for all derivatives upon addition of cations like Na+ or Ba2+. Time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) calculations were performed to determine the absolute configurations of the derivatives. The simulations also explained the origin of the signal inversions and enhancements. In compounds 1, the coexistence of multiple conformations with reciprocal arrangements of the amide moieties led to ECD transitions cancelling each other. However, upon cation addition and binding, the overall number of conformations decreased and the novel conformationally-constrained geometries favored the inverted ECD signal(s) leading to the observed enhancement (Fig. 12B). In emission, strong CPL signals (glum up to 10−2) were recorded for the macrocycles associated with excimer fluorescence (Fig. 12C). They are among the highest reported CPL values for single (non-aggregated) and purely organic molecules. Upon cation addition, as in luminescence, the CPL signal was completely quenched because of the conformational rearrangement that disfavored the EF. To induce reversibility, regular 18-crown-6 can be added as a cation scavenger (Fig. 12A),32 and this led to complete recovery of the original ECD or CPL signals of the “naked” derivatives 1. The sequence of cation addition and removal can be repeated over several cycles making the reversible system an effective and rare example of allied +/− ECD and on/off CPL switches (Fig. 12).23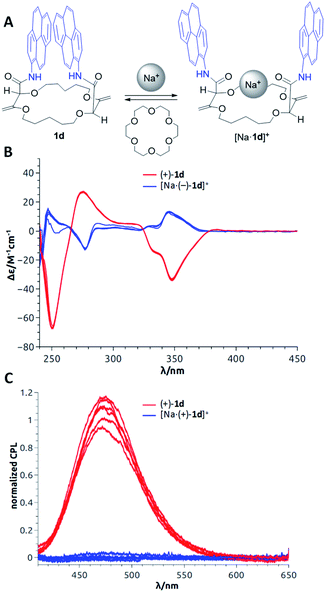 | ||
| Fig. 12 (A) Model for reversible switching; (B) reversible ECD of (+)-1d and [Na·(+)-1d]+ over 6 cycles; (C) reversible CPL of (−)-1d and [Na·(−)-1d]+ over 6 cycles. Reproduced from ref. 23 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
Recently, the ability of enantiopure macrocycle 1d to display intense circularly polarized (CP) luminescence was used in the field of electrochemiluminescence (ECL). Upon electrochemical excitation, enantiomers of 1d emitted intense CP-ECL with a dissymmetry factor of |8 × 10−3| (Fig. 13).34 This is, in fact, the first example of circularly polarized electrochemiluminescence from a purely organic molecule.
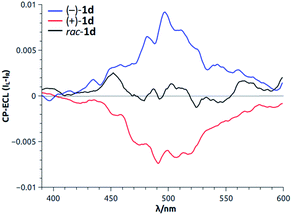 | ||
| Fig. 13 CP-ECL of 1d (both enantiomers and racemic mixture). Reproduced from ref. 34 with permission from John Wiley and Sons. | ||
Conclusion
The catalytic two-step synthesis of macrocycles 1, starting from simple building blocks (diazo, small cyclic ether and amine), has been highlighted in this mini-review. First, multicomponent [3 + X + 3 + X] condensation of diazo 2 with small cyclic ethers affords, under dirhodium(II) catalysis (down to 0.001 mol%) and high concentration conditions, unsaturated precursor 3 on a multigram scale. Second, a straightforward double tandem [amidation + olefin transposition] procedure yields chiral macrocycles 1 with excellent stereoselectivity (dr > 49![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). Applications in a multitude of fields have been found and reported. Compounds 1 have been used for asymmetric PTC and the preparation of scalemic phenylalanine 5. The cooperative recognition of salts was also achieved using novel ditopic cryptands 6 made in one step from 1c. The optical properties of derivatives 1 are also interesting as they allow the direct detection and quantification of metal ions and the development of reversible ratiometric luminescent switches. Thanks to strong chiroptical properties, reversible allied +/− ECD and on/off switches were efficiently designed. Finally, the first observation of circularly polarized electrochemiluminescence from a purely organic molecule was presented using 1d.
1). Applications in a multitude of fields have been found and reported. Compounds 1 have been used for asymmetric PTC and the preparation of scalemic phenylalanine 5. The cooperative recognition of salts was also achieved using novel ditopic cryptands 6 made in one step from 1c. The optical properties of derivatives 1 are also interesting as they allow the direct detection and quantification of metal ions and the development of reversible ratiometric luminescent switches. Thanks to strong chiroptical properties, reversible allied +/− ECD and on/off switches were efficiently designed. Finally, the first observation of circularly polarized electrochemiluminescence from a purely organic molecule was presented using 1d.
Perspectives
Finally, in the following paragraphs, we will try to draw some possible lines of future research − with all the limits that such an exercise encounters.In terms of synthesis, a direct access to macrocycles larger than 20-membered rings would be ideal for applied projects. However, so far, attempts at using medium-sized rings or traditional crown ethers as substrates, such as the regular 18-C-6, have failed. This is most probably due, in part, to the conformations of these moieties that favor intratoroidal arrangements of the ether oxygen atoms rendering their lone pairs inaccessible. Conditions will have to be found to generate reactive metal carbenes in the immediate proximity of intracyclic heteroatoms for future developments. Care should also be taken to find conditions to perform the tandem [amidation + olefin transposition] in an enantio- and diastereo-selective manner. In fact, while CSP-HPLC conditions provide a reliable and effective means to generate macrocycles 1 as single enantiomers, the process remains limited to the production of scalemic compounds on the milligram scale up to now.
In terms of applications, the distinctive geometry of compounds 1 should be further harnessed. The spatial proximity of the amide arms ought to lead to effective divalent recognition and activation phenomena, and hence to further applications related not only to supramolecular chemistry and spectroscopy but also to enantioselective catalysis. The functionalization of the enol ether groups of derivatives 1 should also remain a priority as the introduction of terminal thiols or carboxylic acid moieties opens an orthogonal chemical space that ought to be useful, for instance, in the manipulation of metal clusters and surfaces.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank the University of Geneva and the Swiss National Science Foundation for financial support (SNF 200020-172497 and 200020-184843). We thank Dr Pilar Franco and Mrs Assunta Green (Chiral Technologies, Illkirch, France) for their help and advice concerning the use of CSP. The group is indebted to the many contributions from fellow collaborators who have participated previously in the diazo decomposition chemistry study and, in this chiral macrocycle domain, we would like to specifically mention Dr Elodie Brun, Dr Radim Hrdina, Dr Sumit Kumar Ray, Mr Daniele Poggiali, Mr Mahesh Vishe, Dr Walid Zeghida and Dr Francesco Zinna.Notes and references
- (a) M. P. Doyle and M. A. McKervey, Modern Catalytic Methods for Organic Synthesis with Diazo Compounds: From Cyclopropanes to Ylides, John Wiley & Son, Ldt., New York, 1998 Search PubMed; (b) J. S. Clark, Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Sulfur Ylide Chemistry: A Practical Approach in Chemistry, 2002 Search PubMed; (c) A. Ford, H. Miel, A. Ring, C. N. Slattery, A. R. Maguire and M. A. McKervey, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 9981–10080 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) G. K. Murphy, C. Stewart and F. G. West, Tetrahedron, 2013, 69, 2667–2686 CrossRef CAS; (e) H. M. L. Davies and D. Morton, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 1857–1869 RSC; (f) M. P. Doyle, R. Duffy, M. Ratnikov and L. Zhou, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 704–724 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) A. Padwa, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 3072–3081 RSC; (h) Y. Zhang and J. Wang, Chem. Commun., 2009, 5350–5361 RSC; (i) Z. Zhang and J. Wang, Tetrahedron, 2008, 64, 6577–6605 CrossRef CAS; (j) A. Padwa, Helv. Chim. Acta, 2005, 88, 1357–1374 CrossRef CAS; (k) H. M. L. Davies and R. E. J. Beckwith, Chem. Rev., 2003, 103, 2861–2904 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (l) D. M. Hodgson, F. Y. T. M. Pierard and P. A. Stupple, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2001, 30, 50–61 RSC; (m) M. P. Doyle and D. C. Forbes, Chem. Rev., 1998, 98, 911–936 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (n) A. Padwa and M. D. Weingarten, Chem. Rev., 1996, 96, 223–270 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (o) T. Ye and M. A. McKervey, Chem. Rev., 1994, 94, 1091–1160 CrossRef CAS; (p) M. P. Doyle, Acc. Chem. Res., 1986, 19, 348–356 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Padwa and S. F. Hornbuckle, Chem. Rev., 1991, 91, 263–309 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Achard, C. Tortoreto, A. I. Poblador-Bahamonde, L. Guénée, T. Bürgi and J. Lacour, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 6140–6144 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) L. Egger, L. Guénée, T. Bürgi and J. Lacour, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2017, 359, 2918–2923 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Kitamura, M. Kisanuki, K. Kanemura and T. Okauchi, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 1554–1557 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) D. Rix, R. Ballesteros-Garrido, W. Zeghida, C. Besnard and J. Lacour, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 7308–7311 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) W. Kirmse and R. Lelgemann, Chem. Ber., 1991, 124, 1865–1866 CrossRef CAS; (e) W. Kirmse, R. Lelgemann and K. Friedrich, Chem. Ber., 1991, 124, 1853–1863 CrossRef CAS; (f) K. Friedrich, U. Jansen and W. Kirmse, Tetrahedron Lett., 1985, 26, 193–196 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) C. Tortoreto, T. Achard, W. Zeghida, M. Austeri, L. Guénée and J. Lacour, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 5847–5851 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) E. Ihara, Y. Hara, T. Itoh and K. Inoue, Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 5955–5960 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Vishe, R. Hrdina, L. Guénée, C. Besnard and J. Lacour, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2013, 355, 3161–3169 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) R. Ballesteros-Garrido, D. Rix, C. Besnard and J. Lacour, Chem.–Eur. J., 2012, 18, 6626–6631 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) W. Zeghida, C. Besnard and J. Lacour, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 7253–7256 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) E. Ihara, K. Saiki, Y. Goto, T. Itoh and K. Inoue, Macromolecules, 2010, 43, 4589–4598 CrossRef CAS; (d) W. Zhang, X. Shao, L. Yang, Z.-L. Liu and Y. L. Chow, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 2002, 1029–1032 RSC; (e) S. Cenini, G. Cravotto, G. B. Giovenzana, G. Palmisano and S. Tollari, Tetrahedron, 1999, 55, 6577–6584 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Jarolímová, M. Vishe, J. Lacour and E. Bakker, Chem. Sci., 2016, 7, 525–533 RSC.
- (a) D. M. Hodgson and D. Angrish, Chem.−Eur. J., 2007, 13, 3470–3479 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) T. M. Weathers, Y. Wang and M. P. Doyle, J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 8183–8189 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. P. Doyle, C. S. Peterson, M. N. Protopopova, A. B. Marnett, D. L. Parker, D. G. Ene and V. Lynch, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 8826–8837 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. P. Doyle, C. S. Peterson and D. L. Parker Jr, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1996, 35, 1334–1336 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Davis and S. Higson, Macrocycles: Construction, Chemistry and Nanotechnology Applications, John Wiley & Son, Ldt., Chichester, U.K., 2011 Search PubMed.
- (a) E. M. M. Abdelraheem, S. Shaabani and A. Dömling, Synlett, 2018, 29, 1136–1151 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) F. Kopp and M. A. Marahiel, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2007, 24, 735–749 RSC.
- (a) J. Mallinson and I. Collins, Future Med. Chem., 2012, 4, 1409–1438 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) E. M. Driggers, S. P. Hale, J. Lee and N. K. Terrett, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2008, 7, 608 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) L. A. Wessjohann, E. Ruijter, D. Garcia-Rivera and W. Brandt, Mol. Diversity, 2005, 9, 171–186 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) T. Walsh Christopher, ChemBioChem, 2002, 3, 124–134 CrossRef.
- L. K. S. von Krbek, C. A. Schalley and P. Thordarson, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 2622–2637 RSC.
- (a) Z. Rapi, T. Nemcsok, P. Bagi, G. Keglevich and P. Bakó, Tetrahedron, 2019, 75, 3993–4004 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. Schettini, M. Sicignano, F. De Riccardis, I. Izzo and G. Della Sala, Synthesis, 2018, 50, 4777–4795 CrossRef CAS; (c) J. Tan and N. Yasuda, Org. Process Res. Dev., 2015, 19, 1731–1746 CrossRef CAS; (d) S. Shirakawa and K. Maruoka, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 4312–4348 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) T. Ooi and K. Maruoka, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 4222–4266 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) R. Mohammadzadeh Kakhki, J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem., 2013, 75, 11–22 CrossRef; (b) A. Späth and B. König, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2010, 6, 32 Search PubMed; (c) P. Mateus, N. Bernier and R. Delgado, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2010, 254, 1726–1747 CrossRef CAS; (d) G. W. Gokel, W. M. Leevy and M. E. Weber, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 2723–2750 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S. M. Khopkar, Analytical Chemistry of Macrocyclic and Supramolecular Compounds, Springer-Veralg, Berlin, 2002 Search PubMed; (f) J. S. Bradshaw and R. M. Izatt, Acc. Chem. Res., 1997, 30, 338–345 CrossRef CAS; (g) H. An, J. S. Bradshaw and R. M. Izatt, Chem. Rev., 1992, 92, 543–572 CrossRef CAS; (h) I. M. Kolthoff, Anal. Chem., 1979, 51, 1–22 CrossRef.
- V. Martí-Centelles, M. D. Pandey, M. I. Burguete and S. V. Luis, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 8736–8834 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) C. Tortoreto, T. Achard, L. Egger, L. Guénée and J. Lacour, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 240–243 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. Austeri, D. Rix, W. Zeghida and J. Lacour, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 1394–1397 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Poggiali, A. I. Poblador-Bahamonde and J. Lacour, manuscript in preparation.
- D. Poggiali, A. Homberg, T. Lathion, C. Piguet and J. Lacour, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 4877–4881 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Homberg, D. Poggiali, M. Vishe, C. Besnard, L. Guénée and J. Lacour, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 687–691 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. Vishe, R. Hrdina, A. I. Poblador-Bahamonde, C. Besnard, L. Guénée, T. Bürgi and J. Lacour, Chem. Sci., 2015, 6, 4923–4928 RSC; (b) B. R. Kim, H.-G. Lee, S.-B. Kang, G. H. Sung, J.-J. Kim, J. K. Park, S.-G. Lee and Y.-J. Yoon, Synthesis, 2012, 44, 42–50 CrossRef CAS.
- With macrocycles not based on the 1,4-dioxane skeleton, water molecules are not complexed in the final products.
- A. Homberg, E. Brun, F. Zinna, S. Pascal, M. Górecki, L. Monnier, C. Besnard, G. Pescitelli, L. Di Bari and J. Lacour, Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 7043–7052 RSC.
- A. Homberg, R. Hrdina, M. Vishe, L. Guénée and J. Lacour, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 6905–6910 RSC.
- E. Brun, K.-F. Zhang, L. Guénée and J. Lacour, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2020, 18, 250–254 RSC.
- S. K. Ray, A. Homberg, M. Vishe, C. Besnard and J. Lacour, Chem.−Eur. J., 2018, 24, 2944–2951 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. J. Pedersen and H. K. Frensdorff, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1972, 11, 16–25 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. Yin, Y. Hu and J. Yoon, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 4619–4644 RSC; (b) J. F. Callan, A. P. de Silva and D. C. Magri, Tetrahedron, 2005, 61, 8551–8588 CrossRef CAS; (c) L. Prodi, F. Bolletta, M. Montalti and N. Zaccheroni, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2000, 205, 59–83 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. H. Keefe, K. D. Benkstein and J. T. Hupp, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2000, 205, 201–228 CrossRef CAS; (e) B. Valeur and I. Leray, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2000, 205, 3–40 CrossRef CAS; (f) C. Bargossi, M. C. Fiorini, M. Montalti, L. Prodi and N. Zaccheroni, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2000, 208, 17–32 CrossRef CAS; (g) A. J. Bryan, A. P. de Silva, S. A. De Silva, R. A. D. D. Rupasinghe and K. R. A. S. Sandanayake, Biosensors, 1989, 4, 169–179 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) B. Wang and E. V. Anslyn, Chemosensors: Principles, Strategies, and Applications, John Wiley & Sons, 2011 CrossRef; (b) P. Thordarson, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 1305–1323 RSC.
- F. M. Winnik, Chem. Rev., 1993, 93, 587–614 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Vishe, T. Lathion, S. Pascal, O. Yushchenko, A. Homberg, E. Brun, E. Vauthey, C. Piguet and J. Lacour, Helv. Chim. Acta, 2018, 101, e1700265 CrossRef.
- S. Sinn, F. Biedermann, M. Vishe, A. Aliprandi, C. Besnard, J. Lacour and L. De Cola, ChemPhysChem, 2016, 17, 1829–1834 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Aster, G. Licari, F. Zinna, E. Brun, T. Kumpulainen, E. Tajkhorshid, J. Lacour and E. Vauthey, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 10629–10639 RSC.
- F. Zinna, S. Voci, L. Arrico, E. Brun, A. Homberg, L. Bouffier, T. Funaioli, J. Lacour, N. Sojic and L. Di Bari, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 6952–6956 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |