Principles and mechanisms of photocatalytic dye degradation on TiO2 based photocatalysts: a comparative overview
Anila Ajmal
a,
Imran Majeed
b,
Riffat Naseem Malik
a,
Hicham Idriss
c and
Muhammad Amtiaz Nadeem
*ac
aDepartment of Environmental Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad 4200, Pakistan. E-mail: NadeemMI@SABIC.com
bDepartment of Chemistry, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad 4200, Pakistan
cCRI-KAUST, Saudi Basic Industries Corporation, Thuwal, Saudi Arabia
First published on 5th August 2014
Abstract
The total annual production of synthetic dye is more than 7 × 105 tons. Annually, through only textile waste effluents, around one thousand tons of non-biodegradable textile dyes are discharged into natural streams and water bodies. Therefore, with growing environmental concerns and environmental awareness there is a need for the removal of dyes from local and industrial water effluents with a cost effective technology. In general, these dyes have been found to be resistant to biological as well as physical treatment technologies. In this regard, heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), involving photo-catalyzed degradation of dyes using semiconductor nanoparticles is considered as an efficient cure for dye pollution. In the last two decades TiO2 has received considerable interest because of its high potential as a photocatalyst to degrade a wide range of organic material including dyes. This review starts with (i) a brief overview on dye pollution, dye classification and dye decolourization/degradation strategies; (ii) focuses on the mechanisms involved in comparatively well understood TiO2 photocatalysts and (iii) discusses recent advancements to enhance TiO2 photocatalytic efficiency by (a) doping with metals, non-metals, transition metals, noble metals and lanthanide ions, (b) structural modifications of TiO2 and (c) immobilization of TiO2 by using various supports to make it a flexible and cost-effective commercial dye treatment technology.
Anila Ajmal has recently completed her M.Phil in Environmental Remediation from Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan. She has recently completed her M.Phil thesis project that focuses photocatalytic treatment of dye contaminated wastewater. She obtained her BS honors (2010) in Environmental Sciences from Lahore College for Women University, Lahore, Pakistan. Her main research interests include applications of photocatalytic techniques for the remediation of environmental contaminants. |
Imran Majeed is currently doing his Ph.D at Department of Chemistry, Quaid-i-Azam University Islamabad, Paksiatan. His Ph.D project is about hydrogen production from renewables using visible light active TiO2 based photocatalysts. He completed Masters (2005) in Applied Chemistry from University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan and M.Phil (2008) in Analytical/Inorganic Chemistry from the same University. Before starting his Ph.D, he was been working as Senior Scientist in Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan. |
Riffat Naseem Malik is currently an Associate Professor as well as Chairperson of Department of Environmental Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam University Islamabad, Pakistan. Before this, she worked as Post-Doctoral Research Fellow (2001–2003) at Lancaster Environmental Centre, Lancaster University, UK. She has completed her Ph.D in Environmental Biology from The Reading University, Reading, UK. She had received Research Fellowship from Department of Geography, University of Turku, Finland after completing her M.Phil and M.Sc from Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan. She is the author and co-author of more than 90 scientific publications. |
Hicham Idriss is currently working at CRI-KAUST, Saudi Basic Industries Corporation, Thuwal, Saudi Arabia as Chief Scientist. Formerly, he worked as Aberdeen Energy Futures Chair and Professor of Chemistry at the University of Aberdeen and Robert Gordon University, UK from 2008 to 2010. He is also Adjunct Professor at the Department of Chemical Engineering, Louisiana State University in the USA. Prior to 2008 he was Associate Professor at the Department of Chemistry, the University of Auckland in New Zealand where he worked for 13 years. He served as a member of the New Zealand National Energy Panel who delivered the 2020 Energy report to the New Zealand Government in 2008. He has obtained his B.Sc (1984), M.Sc (1985), Ph.D (1987) and habilitation (1997) from the University of Strasbourg in France and has postdoctoral and research associate positions at the University of Delaware and University of Illinois, Urbana (USA). He is the author and co-author of over 140 scientific papers and has served/is serving at the editorial board of scientific journals including Applied Catalysis A, Catalysis Today and Catalysis Survey from Asia. His main interest in surface science and catalysis is on metal oxides and their interface with transition metals at the fundamental and applied levels. |
Muhammad Amtiaz Nadeem is currently an Assistant professor at Quaid-i-Azam University Islamabad. He completed Masters (2003) in Chemistry from University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan and M.Phil in Analytical/Inorganic Chemistry (2006) from Quaid-i-Azam University Islamabad, Pakistan. He joined Prof. Hicham Idriss group based at University of Auckland as a Ph.D student in 2008 and in 2009 moved with him at the Energy Future Center in Aberdeen, UK, to complete his Ph.D in 2012. His Ph.D thesis has been placed in Dean, Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Auckland theses excellence list. His thesis was also nominated for University of Auckland best thesis award for 2012. His main interest in surface science and catalysis is on metal oxides and their interface with transition metals at the fundamental and applied levels. |
Dye pollution-an overview
Dyes play a vital role in various branches of the dyeing and textile industries. Over 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 commercially available synthetic dyes are the most frequently used dyes in such industries. These dyes are usually derived from two main sources i.e. coal tar and petroleum intermediates with a total annual production of more than 7 × 105 tons.5–7 Annually, through textile waste effluents, around 15% (one thousand tons) of these non-biodegradable textile dyes are discharged into natural streams and water bodies.1–4,8,9 Typically, on an average for every kilogram of cloth, being processed in dyeing and finishing plants, about 120–280 L of water is being consumed.10
000 commercially available synthetic dyes are the most frequently used dyes in such industries. These dyes are usually derived from two main sources i.e. coal tar and petroleum intermediates with a total annual production of more than 7 × 105 tons.5–7 Annually, through textile waste effluents, around 15% (one thousand tons) of these non-biodegradable textile dyes are discharged into natural streams and water bodies.1–4,8,9 Typically, on an average for every kilogram of cloth, being processed in dyeing and finishing plants, about 120–280 L of water is being consumed.10
Konstantinou and Albanis11 reported that industrial dye stuffs and textile dyes constitute one of the largest groups of toxic organic compounds. According to an estimate made by World Bank, nearly 17–20% water pollution has the major contributors related to textile finishing and dyeing industries. According to a study by Kant, out of major identified wastewater toxic chemicals, 72 chemicals were solely released by the textile dyeing and nearly 30 of such chemicals were not treatable.12 In 1974, Ecological and Toxicological Association of the Dyestuffs Manufacturing Industry (ETAD) was formed with an aims to protect consumers by preventing and reducing environmental damages by fully cooperating with government over the concerns related to the toxicological impact of their own products.13 In an ETAD survey, of all 4000 tested dyes, 90% dyes were found to be having their LD50 values greater than 2 × 103 mg kg−1. Among all tested dyes diazo, direct and basic dyes showed the highest rates of toxicity.14
Bright coloured dyes such as reactive and acid dyes are water soluble and the most problematic dyes to remove.15 Conventional and municipal aerobic treatment systems have been proved to be ineffective on both type of dyes.16,17 Compared to other types of dyes, reactive dyes are least taken up by the fabric during dyeing process, implying that the remaining quantity of dye is directly lost into the wastewater.18 Leena and Raj19 reported that reactive dye effluent possess the ability to remain stable and unaffected in environment for several years i.e. hydrolyzed reactive blue 19 has a half-life of about 46 years. Dispersed dyes do not ionize in an aqueous medium enhancing their ability to bioaccumulate in aquatic living organisms.20 Currently concerns related to the dye effluents are arising as many dyes are synthesized by known carcinogens such as aromatic compounds and benzidine.20
Chung et al.21 have illustrated the dye reduction in the intestinal environment, that resulted into the formation of toxic amines. Moreover, azo dyes are readily reduced into the aromatic amines that are potentially hazardous as a result of anaerobic treatment conditions.22–25
In addition to dye pollution, in textile industries processing prior to dying procedure such as mercerization, scouring, sizing and bleaching results into the production of bleaching as well as scouring agents. However, amongst all of above mentioned concerns, colour removal from wastewater is the most complex and difficult task.18 Dyes are usually the first contaminant to be recognized in industrial wastewater due to their high visibility even in minute concentrations (<1 ppm).26 These coloured wastewaters are a considerable source of eutrophication as well as non-aesthetic pollution that can produce dangerous by-products by further oxidation, hydrolysis, or other chemical reactions taking place in the wastewater phase. Apart from the toxic effects of dyes in wastewater streams, presence of dyes can cause reduced light penetration resulting in reduced photosynthetic activity thus making oxygen unavailable for biodegradation of microorganism in the water.27
Apart from the textile industry, leather tanning industry,28 paper industry,29 food industry,30 hair colourings,31 photoelectrochemical cells32 and light-harvesting arrays33,34 also contribute towards the presence of dyes in wastewater. Majority of dyes used in various industries are toxic and carcinogenic thus posing a serious hazard to humans as well as to marine ecosystem.35 Therefore, the impact of dyes released into the environment have been studied extensively in last few years.36,37 This paper presents an overview of the recent research improvements targeting the degradation of various dyes by using TiO2 as a potential photocatalyst.
Dye classification
Dyes usually have many structural varieties and their complete classification with respect to one parameter is very difficult and of no use from practical understanding point of view. However, dyes are generally divided into different groups and classes depending on their source, general dye structure and the fiber type with which they are most compatible as shown in the Fig. 1.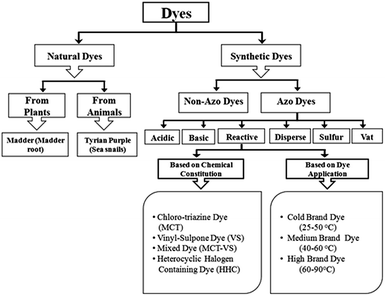 | ||
| Fig. 1 Flow chart indicating dye classification on the basis of dye chemical constitution and its application. | ||
Among major dye categories, azo dyes are the largest group of colourants and over 50% of all the dyes used in industries are azoic dyes. Azo dyes are characterized by double bond of nitrogen (–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e001.gif) N–), where at least one of the nitrogen atom is attached to an aromatic group (rings of naphthalene or benzene). Moreover, they have amphoteric properties due to the presence of additional carboxyl, hydroxyl, amino or sulfoxyl functional groups. Azo dyes can behave anionic (deprotonation at the acidic group), cationic (protonated at the amino group) or non-ionic depending upon the pH of the medium.38 Most notable azo dyes are: acid dyes, basic dyes (cationic dyes), direct dyes (substantive dyes), disperse dyes (non-ionic dyes), reactive dyes, vat dyes and sulfur dyes.39 Dyes based on general structure can also be classified as anionic, non-ionic and cationic dyes. The anionic dyes mainly include direct acidic and reactive dyes.26 Major nonionic dyes include; disperse dyes which does not ionizes in the aqueous environment and the major cationic dyes include basic and disperse dyes.38
N–), where at least one of the nitrogen atom is attached to an aromatic group (rings of naphthalene or benzene). Moreover, they have amphoteric properties due to the presence of additional carboxyl, hydroxyl, amino or sulfoxyl functional groups. Azo dyes can behave anionic (deprotonation at the acidic group), cationic (protonated at the amino group) or non-ionic depending upon the pH of the medium.38 Most notable azo dyes are: acid dyes, basic dyes (cationic dyes), direct dyes (substantive dyes), disperse dyes (non-ionic dyes), reactive dyes, vat dyes and sulfur dyes.39 Dyes based on general structure can also be classified as anionic, non-ionic and cationic dyes. The anionic dyes mainly include direct acidic and reactive dyes.26 Major nonionic dyes include; disperse dyes which does not ionizes in the aqueous environment and the major cationic dyes include basic and disperse dyes.38
Acidic dyes are named so as they are normally applied to the nitrogenous fibers or fabrics in inorganic or organic acid solutions. Basic dyes give cations in the solution which are generally applied to acrylic and modacrylic fibers. Direct dyes are applied in aqueous bath containing ionic salts and electrolytes that bond to fibers/fabrics by electrostatics forces.40,41 Disperse dyes have low solubility in water, but they can interact with the polyester chains by forming dispersed particles.42 The wash fastness with disperse dyes varies with the type of fibers being used for dyeing purpose i.e. poor on acetate, excellent on polyester.38 Reactive dyes are primarily utilized on cellulosic fibers, but occasionally on protein fibers and nylon as well forming covalent bond with the appropriate textile functionality.43 Sulfur dyes are used on cellulosic fibers to produce dull shades such as navy, black and brown. They have excellent fastness in most areas, but fades off when exposed to chlorine. Vat dyes that works with a special chemistry having excellent fastness in all areas and especially on exposure to chlorine and bleach.44–46 Further characteristics of these dyes are summarized in Table 1.
| Dye class | Characteristics | Fiber | Dye fixation (%) | Pollutant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic | Water-soluble anionic compounds | Wool, nylon, cotton blends, acrylic and protein fibers | 80–93 | Colour; organic acids; unfixed dyes |
| Basic | Water-soluble, applied in weakly acidic dye baths, very bright dyes | Acrylic, cationic, polyester, nylon, cellulosic, and protein fibers | 97 and 98 | NA |
| Direct | Water-soluble, anionic compounds, applied without mordant | Cotton, rayon and other cellulosic fibers | 70–95 | Colour; salts; unfixed dye; cationic fixing agents; surfactant; defoamer; levelling and retarding agents; finish; diluents |
| Dispersive | Insoluble in water | Polyester, acetate, modacrylic, nylon, polyester, triacetate and olefin fibers | 80–92 | Colour; organic acids; carriers; levelling agents; phosphates; defoamers; lubricants; dispersants; delustrants; diluents |
| Reactive | Water-soluble, anionic compounds, largest dye class | Cotton, cellulosic and wool fibers | 60–90 | Colour; salt; alkali; unfixed dye; surfactants; defoamer; diluents; finish |
| Sulphur | Organic compounds containing sulfur or sodium sulfide | Cotton and other cellulosic fibers | 60–70 | Colour; alkali; oxidizing agent; reducing agent; unfixed dye |
| Vat | Oldest dyes, chemically complex, water-insoluble | Cotton, wool and other cellulosic fibers | 60–70 | Colour; alkali; oxidizing agents; reducing agents |
Dye treatment strategies
Apart from their physically unpleasant nature and toxicity, ever increasing massive production rate of dyes due to increasing industrialization have led to the necessity of effective treatment.47,48 Therefore, in order to treat such obvious and challenging effluents, a wide range of technologies have been tested to reduce their potential magnified impacts on environment. Traditional physical techniques such as activated carbon, adsorption, reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration can be used for dye removal. However, these processes simply transfer the pollutants from one to another medium causing secondary pollution. This generally requires further treatment of solid-wastes and regeneration of the adsorbent, which adds more cost to the process. Chemical process such as chlorination, ozonation,49 adsorption on organic or inorganic matrices, precipitation, chemical oxidation processes,50 advanced oxidation processes such as Fenton and photo-Fenton catalytic reactions,51 H2O2/UV processes52 and photodegradation through photocatalysis are also commonly being used for the synthetic dye removal.53 However, toxic unstable metabolites as a result of most of these processes54 imparts adverse effects on animal and human health.55Biological processes involving microbiological or enzymatic decomposition56 and biodegradation have also been used for dye removal from wastewaters. Moutaouakkil et al.57 isolated Azoreductase enzyme from Enterobacter agglomerans having ability to grow fast on methyl red dye under aerobic condition by catalyzing reductive cleavage of azo bonds. Anaerobic conditions also facilitates58 the azo bond rupture leading to the colour disappearance but result in incomplete mineralization of toxic and carcinogenic by-products.59 However, it has been found that these conventional biological treatment processes are ineffective for synthetic dyes having recalcitrant nature.60,61 In recent years, a broad range of synthetic dyes have been extensively studied to develop a more promising technology based on advanced oxidation process (AOPs) that has the ability to oxidize contaminants quickly and non-selectively.50,62,63 AOPs rely on in situ production of highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (OH˙) which can virtually oxidize any compound present in the water matrix, often at a diffusion controlled reaction speed. These radicals are produced with the help of one or more primary oxidants (e.g. ozone, hydrogen peroxide, oxygen) and/or energy sources (e.g. ultraviolet light) or catalysts (e.g. titanium dioxide).64,65 This review focuses on mechanistic and practical aspects of dye degradation by TiO2 based photocatalysts.
Photocatalytic dye treatment
Heterogeneous photocatalysis has proved to be as an efficient tool for degrading both atmospheric and aquatic organic contaminants.66 It uses the sunlight in the presence of a semiconductor photocatalyst to accelerate the remediation of environmental contaminants and destruction of highly toxic molecules.67,68 The type of the radiation used depends on the type of catalyst i.e. pure TiO2 works under UV light (370–415 nm). Visible light can also be used for the excitation purpose but due to unavailability of proper catalyst and other contributing factor, it has been considered as less effective source for irradiation. Generally speaking, final products of TiO2 photocatalysis have not been reported properly, which often makes evaluation of the photocatalysis difficult. The reactions of dye molecules on TiO2 photocatalysts are often confusing, and could be classified into the following categories according to the photocatalysis products. (1) Photodecolourization69–73 involves simple photooxidation or photoreduction where dyes can return to the original form by either corresponding back reduction or back oxidation, respectively. (2) Photodegradation74–79 involves dye decomposition to some stable products. It is the most widely used name for photocatalytic dye treatment. (3) Photomineralization80–84 is regarded as complete decomposition to CO2, H2O, N2, NO3−, NO2− etc. The goal of ideal photocatalysis should be mineralization. (4) Photodecomposition76,77 could imply both photodegradation and mineralization differently, depending also on the researchers. However, it rarely involves decolourization. Hereafter in this review care will be taken to use these terminologies as precisely as possible.In order to assess the degree of dye photodegradation achieved during the treatment, generally formation of CO2 and inorganic ions is determined.81,82,85–88 However, it is impossible to measure the exact concentration of these ions in case of real wastewaters. In such cases the determination of total organic carbon (TOC) or the measurement of the chemical oxygen demand (COD) or the biological oxygen demand (BOD) is used to monitor extent of dye mineralization.82,83,86,89–92 In general, at lower dye concentration and for compounds which do not form stable intermediates, complete mineralization proceed with similar half-lives for parent dye and the intermediates but at higher concentration intermediates mineralization is slower than the degradation of the parent dye. To date most azo dyes have been found to undergo complete mineralization except triazine containing dyes.81–84,90 The later does not undergo complete mineralization due to high stability of triazine nucleus and the stable cyanuric acid intermediates.93 However, fortunately these intermediates are not toxic.80,91,92 Usually COD or TOC values decrease with irradiation time whereas the amount of NH4+, Cl−, SO42− and NO3− ions increase.81,91,94
For chlorinated dye molecules, Cl− ions are the first of the ions which appear during photocatalytic degradation.90,92,95 This could be interesting in photocatalytic biological treatment which is generally not efficient for chlorinated compounds. Nitrogen is mineralized into NH4+, NO3− and N2 depending upon initial oxidation oxidation state of nitrogen, the substrate structure and irradiation time.96,97 The total amount of nitrogen-containing ions present in the solution at the end of the experiments is usually lower than that expected from stoichiometry indicating that N-containing species remain adsorbed in the photocatalyst surface or most probably, that significant quantities of N2 and/or NH3 have been produced and transferred to the gas-phase.81,83,90
The dyes containing sulfur atoms are mainly mineralized into sulfate ions stoichiometrically.92,95 Non-stoichiometric formation of sulphate ions is usually explained by a strong SO4− adsorption on the photocatalyst surface which could partially inhibit the reaction rate.81,98,99 Generally, it is found that nitrate anions have little effect on the kinetics of reaction whereas sulfate, chloride and phosphate ions, especially at concentrations of greater than 10−3 mol dm−3, can reduce the rate by 20–70% due to the competitive adsorption at the photoactivated reaction sites.98
TiO2 as dye treatment photocatalyst
Among various types of photocatalysts, titanium dioxide (TiO2) assisted photocatalytic oxidation has received much attention the last few years due to its non-toxicity, strong oxidizing power and long-term photostability.100 Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a white powder semiconductor having a wide band gap of 3.0–3.2 eV.101–103 It can be excited by UV light with a wavelength below ca. 415 nm (in its rutile form). However, the use of TiO2 is limited as only about 3–4% of the solar spectrum falls within UV range.102,104–106 In general, there are three types of titanium dioxide i.e. anatase, rutile and brookite. In general TiO2 nanoparticles are widely available commercially or can be easily prepared using sol gel method. Typically, anatase phase is often found having particle size equal to 10 nm or less with a band gap of 3.2 eV corresponding to a UV wavelength of 385 nm.107 Comparatively, though some exceptions exists, rutile phase generally exists having particle size in the order of 50 nm or so.108 Moreover, rutile has a smaller band gap of 3.0 eV with excitation wavelengths extending to visible 410 nm range. Thermodynamics dictates that heating the anatase phase results in gradual phase transformation of anatase to rutile and therefore depending on the method of preparation mix phase anatase-rutile can be easily prepared or purchased. For example, some commercially available TiO2 that is a mixture of two phases, 80% anatase and 20% rutile, and has usually a BET area of 50 m2 g−1 has widely been studied.109Most of the studies have been carried out with anatase phase due to its high photocatalytic efficiency and adsorption affinity for the organic compounds as compared to the rutile phase.110,111 Shiga et al.112 using nanocrystalline film electrodes of TiO2 for photoelectrochemical activities showed that the anatase has a higher photoactivity than rutile phase at a longer wavelength. This is due to the fact that anatase phase due to its greater hole trapping ability (about 10-fold) exhibits lower recombination rates compared to rutile type.113,114 Therefore, anatase is generally regarded as photochemically more active phase of TiO2 due to these combined effect.107 Moreover, recently developed various forms of TiO2, such as TiO2 powders, TiO2 film,115 supported TiO2,116,117 TiO2 nanotubes118 and doped TiO2119,120 have been evaluated through degradation of dyes and phenolic compounds. Such studies demonstrated the higher efficiency of various forms of TiO2 used for removal of dyes and phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions.121
Basic principles and mechanism for photocatalyzed dye degradation
Indirect dye degradation mechanism
The indirect heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation mechanism using semiconducting materials can be summarized as follows.122,123| TiO2 + hν(UV) → TiO2(e−(CB) + h+(VB)) | (1) |
| H2O(ads) + h+(VB) → OH˙(ads) + H+(ads) | (2) |
The HO˙ radical formed on the irradiated semiconductor surface are extremely powerful oxidizing agent. It attacks adsorbed organic molecules or those that are very close to the catalyst surface non-selectively, causing them to mineralize to an extent depending upon their structure and stability level. It does not only easily attack organic pollutants but can also attack microorganisms for their enhanced decontamination.124
| O2 + e−(CB) → O2−˙(ads) | (3) |
This superoxide ion may not only take part in the further oxidation process but also prevents the electron-hole recombination, thus maintaining electron neutrality within the TiO2 molecule.
| O2−˙(ads) + H+ ⇄ HOO˙(ads) | (4) |
| 2HOO˙(ads) → H2O2(ads) + O2 | (5) |
| H2O2(ads) → 2OH˙(ads) | (6) |
| Dye + OH˙ → CO2 + H2O(dye intermediates) | (7) |
| Dye + h+(VB) → oxidation products | (8) |
| Dye + e−(CB) → reduction products | (9) |
Both oxidation and reduction processes commonly take place on the surface of the photoexcited semiconductor photocatalyst. The complete process has been represented by the Fig. 2.
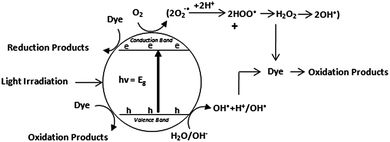 | ||
| Fig. 2 Pictorial representation of indirect dye degradation process.24 | ||
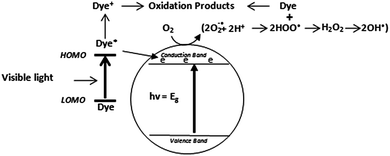
Direct mechanism for dye degradation
Owing to their ability to easily absorb some of visible light, another mechanism of photocatalytic dye degradation can also occur under visible light. This mechanism involves the dye excitation under visible light photon (λ > 400 nm) from the ground state (Dye) to the triplet excited state (Dye*). This excited state dye species is further converted into a semi-oxidized radial cation (Dye+˙) by an electron injection into the conduction band of TiO2.125 Due to reaction between these trapped electrons and dissolved oxygen in the system superoxide radical anions (O2−˙) are formed which in turn result into hydroxyl radicals (OH˙) formation. These OH˙ radicals are mainly responsible for the oxidation of the organic compounds represented by the equations and Fig. 3 below.126–128| Dye + hν → dye* | (10) |
| Dye* + TiO2 → dye+ + TiO2− | (11) |
According to many studies, indirect mechanism is generally prevalent over direct mechanism and its contribution to the dye degradation is much more pronounced than the visible light initiated mechanism. The latter is believed to be a far slower reaction compared to indirect mechanism.126,129
Factors affecting photocatalytic dye degradation
Effect of pH
The pH is one of the significant parameters for the photocatalytic dye degradation as it can influence dye reaction rates in multiple ways as explained here on. It can influence dye adsorption onto the semiconductor surface121 as catalyst surface charge depends on the pH of a given solution. Zhu et al.130 demonstrated that pH effect is related to the surface-charge properties of the photocatalysts, and could be explained on the basis of point of zero charge (PZC). The point of zero charge for TiO2 particles is pHpzc = 6.8.3 At a pH values lower than pHpzc (pH < 6.8) or at acidic solution, the surface of the catalyst gets positively charged and vice versa131,132 according to the eqn (12) and (13) given below.| TiOH(Surface) + H+ → TiOH2(surface)+ | (12) |
| TiOH(Surface) + OH− → TiO(Surface)− + H2O | (13) |
When the pH is lower than the PZC value the adsorbent surface is positively charged and the surface becomes anions attracting/cation repelling. Conversely, above PZC the surface is negatively charged and the surface becomes cation attracting/anion repelling.
Zhu et al.130 explained that highest degree of decolourization of methyl orange observed at pH 2 is attributed to the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged catalyst surface and methyl orange anions, which led to the increase in degree of adsorption and 97% photodecolourization. However, the dye treatment results based on dye adsorption strength cannot be explained as there are many other parameters operating at the same time. For example, Muruganandham et al.133 found that increasing pH from 1 to 9 increased decolourization rates for reactive orange 4 (an anionic dye) from 25.27% to 90.49% after 40 min and degradation from 15.16% to 87.24% within 80 minutes, respectively. However, the faster rate of color removal and photodegradation was observed at alkaline pH. In contrast, the degradation studies of some azo dyes showed conflicting results.134 For example, acid yellow 17 (an anionic dye) has shown to be more degraded at pH 3, whereas, orange II (anionic dye) and amido black 10B (anionic dye) showed maximum degradation at pH 9.135
The pH can also affect whole photocatalytic dye degradation mechanism and thus the degradation rate. For example positive holes generated at lower pH act as major oxidation species, however at higher or neutral pH range, hydroxyl radicals (OH˙) are largely responsible for oxidation process.136 On one hand, these radicals can be generated in an alkaline solution,137 however, on the other hand sites the semiconductor surface may not adsorb dye anions due to electrostatic repulsion thereby decreasing their degradation and vice versa.138 It is believed that hydroxyl radicals play an essential role in the fission of the –N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N– conjugated system in azo dyes in a TiO2 assisted photodegradation. The azo linkage (–N
N– conjugated system in azo dyes in a TiO2 assisted photodegradation. The azo linkage (–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–) is mainly vulnerable to electrophilic attack by hydroxyl radical. Riga et al.109 reported that dye decolourization and degradation rate increases with increasing pH. Whereas, at lower pH the concentration of H+ exceeds and these H+ ions interact with azo linkage reducing the azo group electron densities, resulting into decrease in hydroxyl reactivity of hydroxyl radicals by electrophilic mechanism.
N–) is mainly vulnerable to electrophilic attack by hydroxyl radical. Riga et al.109 reported that dye decolourization and degradation rate increases with increasing pH. Whereas, at lower pH the concentration of H+ exceeds and these H+ ions interact with azo linkage reducing the azo group electron densities, resulting into decrease in hydroxyl reactivity of hydroxyl radicals by electrophilic mechanism.
It has been reported that a dye with positive charge shows higher adsorption rate on an unmodified TiO2 than for dyes with a negative charge (anionic).139 It has been studied that titanium dioxide has a higher oxidizing activity at lower pH; however, excess of H+ at very low pH can decrease the rate of reaction too. This can be explained by the characteristic of TiO2 particles that tend to agglomerate at lower or acidic condition, which may reduce surface area of catalyst for maximum dye adsorption as well as photon absorption.121,140,141 Bizani et al.142 reported that the pH effect on dye degradation rate can be explained mainly by the modification of the electrical double layer of the solid–electrolyte interface, which consequently affects the sorption-desorption processes and the separation of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs on the surface of the semiconductor particles.142
Effect of pollutant adsorption strength
In heterogeneous photocatalysis, competitive adsorption between water molecules and the target molecules that are to be degraded plays an important role in photocatalysis.143,144 This is due to the fact that photogenerated oxidizing species may not migrate far away from their formation centres resulting into negligible or a very slow rate of degradation at few nanometer layers around the catalyst particles surface.145 However, in various studies many authors have not reported a direct relationship between adsorption and photodegradation. In some cases, adsorption of compounds or intermediates may acts as poison on the catalyst surface. Vautier et al.146 reported that an electrostatic interactions between the dye molecule and the hydroxyl groups of the photocatalyst is always required for proper dye adsorption.Bizani et al.142 reported that strong adsorption may lead to a multilayer of dye molecules around the catalyst particles surface. This may result into limited interaction between excited dye molecule and the catalyst in case of direct degradation mechanism or between incoming light and the catalyst in case of indirect mechanism. In both of above cases the photooxidation process is expected to decrease. This could be the reason due to which the initial decolourization rate of the dye is reported lower in acidic solutions. On the other hand, in alkaline solutions, decrease in the initial rate of degradation reflects the difficulty of the anionic dye molecules to approach the catalyst surface.147–149
Effect of light intensity
Band-gap sensitization mechanism does not have any influence on photocatalytic degradation rate or mechanism.101 However, various studies have revealed that with an increasing light intensity, the rate of photocatalytic degradation increases.150–152 Collazzo et al.153 compared the direct black 38 dye degradation ability of nitrogen doped TiO2 under visible light source and sunlight. It was confirmed that nitrogen doped TiO2 due to its higher absorption in visible region showed higher dye degradation (60% in 6 hours) under visible light. Under sunlight irradiation, N-doped TiO2 exhibited degradation efficiency slightly higher than non-doped TiO2 as shown in Fig. 4.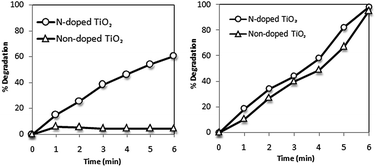 | ||
| Fig. 4 Photocatalytic degradation of direct black 38 as a function of time under visible light (left) and sunlight (right). Experimental conditions: Co = 0.055 g L−1, Ccatalyst = 1.0 g L−1, pH = 2.5, T = 25 °C.153 | ||
Effect of photocatalyst load
In order to avoid the excess use of the catalyst, it is necessary to calculate optimum dose or loading of the catalyst for efficient removal of dye. Off course the amount of catalysts required will depend on the configuration of the reactor, light intensity, type of the targeted dye and the type as well as particle morphology of the catalyst. Owing to these many contributing factors there are inconsistencies in the optimum catalyst dose used by different researchers. Several authors have investigated the function of catalyst loading on the reaction rate of photocatalytic oxidation process.133,154–156 Riga et al. reported that the amount of dye adsorbed on catalyst surface generally increases by increasing the TiO2 loading or the catalyst used. It was found that generally TiO2 loading increases rate of photodecolourization, especially up to 1000 mg L−1 with an overall 60% TOC removal rate.109Kaur et al.102 reported that in all of the optimized conditions of efficiency, the catalyst dose for maximum photocatalytic degradation of reactive red 198 is 0.3 g L−1. However, in another study, the optimized condition for TiO2 consumption was stated to be 0.5 g L−1.157 Mahvi et al.138 studied that an increase in the amount of catalyst to the level constant with the optimized level of light absorption (normally 0.4 g L−1), increases the amount of the decolourization.157–159 Also, Muruganandham et al.133 reported that an increase of catalyst weight from 1.0 to 4.0 g L−1 increases the dye decolourization sharply from 69.27% to 95.23% at 60 minutes and dye degradation from 74.54% to 97.29% at 150 min. A similar observation has been made by other authors, as well.137,148,160
It is evident that initially photodegradation rate increases with an increase in the amount of photocatalyst and then decreases with increase in catalyst concentration (Fig. 5). This trend can be explained by three possibilities:
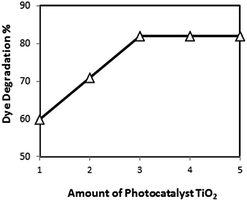 | ||
| Fig. 5 Effect of increasing TiO2 catalyst loadings (in grams) on rate of dye degradation.141 | ||
1 When all dye molecules are adsorbed on photocatalyst surface, the addition of higher quantities of photocatalyst would have no further enhancing effect on the degradation efficiency.
2 Another possible reason could be due to the fact that an excess of photocatalyst particles may increase opacity of the suspension which may retard the degradation rate.161 Zhu et al.130 reported in their study that as the amount of photocatalyst was increased from 0.05 to 0.5 g L−1 the number of absorbed photons increased indicating 97% photocatalytic decolorization of methyl orange solution. However, it was found that at photocatalyst dosages above 0.5 g L−1, the rate constants decreased due to the blocking of light penetration by the excessive amount of photocatalysts.162
3 Moreover, particle–particle interaction becomes significant as the amount of particles in solution increases. This may result in an enhanced rate of deactivation of activated molecules by collision with ground state titanium dioxide particles and hence decreases in dye concentration.141,163
Effect of the initial dye concentration
It has been reported earlier that by increasing the dye concentration, the decolourization rate constant (k) decreases.138 The initial dye concentration can affect the rate of photodegradation based upon two main aspects.(1) In high dye concentrations, more active sites may be covered with dye ions. This further may lead to the decrease in the production of OH radicals on the surface of catalyst. Illinous et al.164 studied the influence of various initial dye concentrations for reactive yellow 125 dye on the photocatalytic discolouration and degradation in the concentration range of 0.025–0.1 g L−1. They concluded that increasing the dye concentration will render the process less efficient by decreasing degradation efficiency.
(2) Zhu et al.130 reported that the path length of the photons entering the solution decreases as the initial concentration of methyl orange increased. The reversal occurred for the lower concentration, thereby increasing the number of photons absorbed by the catalyst.132 The same {Zhu, 2005 #167} effect was reported by Wang et al.165 during their study of the photocatalytic degradation of commercial dyes using zinc oxide power as photocatalyst.
Effect of inorganic salts
The presence of mineral ions in dye contents of wastewater is common. Some cations such as copper, phosphate and iron have been reported to have the ability to decrease the photodegradation efficiency present in certain concentration. One of the major reasons is that these substances may compete with dyes for the active sites on the TiO2 surface and thus deactivate the photocatalyst resulting in decreased degradation of targeted dyes. Whereas calcium, magnesium and zinc have been studied to have little effect on the photodegradation of organic compounds which is associated to the fact that these cations are present in their highest oxidation states causing no inhibitory effect.166The dye industry wastewater contains a considerable amount of inorganic anions such as carbonates, chlorides, nitrate, and sulphates. The presence of these salts causes colloidal instability, increases mass transfer and decrease in the surface contact between the target dye molecule and the photocatalyst.166 Degradation of dyes decreases in the presence of these ions. These CO32− and HCO3− ions may scavenge the HO˙ radicals.24
| CO32− + OH˙ → CO3−˙ + OH− | (14) |
| HCO3− + OH˙ → CO3−˙ + H2O | (15) |
| CO3−˙ + OH˙ → HCO3− | (16) |
The decrease in degradation efficiency in the presence of chloride ion is due to the hole scavenging properties of chloride ion.
| Cl− + h+(VB) → Cl˙ | (17) |
| OH˙ + Cl− → HOCl˙− | (18) |
| HOCl˙− + H+ → Cl˙ + H2O | (19) |
The chloride radical anions formed can also block the active sites of the catalyst surface. The inhibitory effect of chloride and phosphate ions on the photocatalytic degradation has also already been reported.167 The inhibiting effect of CO32− ion is greater than the inhibiting effect of Cl− ion.
Wang et al.168 reported the effect of NO3− and SO42− on the photodegradation of reactive red 2 dye under UV irradiation, stating an increased in dye removal. Zhu et al.169 also reported the same results that the presence of NO3− accelerated the photocatalytic degradation of an azo dye under visible light irradiation in their experiment. This can be attributed to the direct or indirect hydroxyl radical formation as follow:
| NO3− + hν → NO2− + O | (20) |
| NO3− + H2O + hν → NO2− + 2OH˙ | (21) |
| O + H2O → 2OH˙ | (22) |
SO42− in photocatalytic dye degradation has two important roles. SO42−, by driving the dye molecule to bulk interface, increases aqueous ionic strength that results into enhanced photocatalytic efficiency. Also, the adsorbed SO42− reacts with generated valence band holes forming SO4−. This reaction between SO42− and photogenerated hVB+ on the photocatalyst surface can prevent the electrons and holes recombination, enhancing photodegradation rate as:
| SO42− + h+(VB) → SO4−˙ | (23) |
| SO4−˙ + H2O → SO24− + OH˙ + H+ | (24) |
SO4−˙ is a very strong oxidant with redox potential of +2.6 V, which can enhance dye degradation. Further, the degradation rates also depend on type of salt used. This effect has been studied by various authors.109,133,138,170–172
Effect of addition of oxidizing species
Addition of powerful oxidizing species, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and potassium peroxydisulfate (K2S2O8) to TiO2 suspensions is a well-known procedure which increases rate of photooxidation.47,95,148,160,173 Hydrogen peroxide is believed to have a dual role during the process of photocatalytic degradation. It accepts an electron from the conduction band, thus, promotes the charge separation and it also forms OH˙ radicals.| H2O2 + e− → OH− + OH˙ | (25) |
| H2O2 + O2− → OH− + OH˙ + O2 | (26) |
At H2O2 concentration greater than critical concentration, it may act as hole or OH˙ scavenger or react with TiO2 to form peroxy compounds, which are detrimental to the photocatalytic action.148,174–177 Bizani et al.142 reported that the addition of oxidants such as H2O2 appears to be more effective in photocatalytic degradation of dyes than K2S2O8 comparatively, although their effectiveness in decolourizing the solutions can be reversed. Dye intermediates showed higher toxicity values involving K2S2O8 than photocatalytic process involving H2O2, indicating partial DOC (dissolved organic carbon) and toxicity removal efficiency.
Strategies for enhancing photocatalytic properties of TiO2
Photocatalysis by adopting advanced oxidation procedures
Recently cavitation methods have attracted attention as AOPs for the removal of carcinogenic chemicals present in water.178,179 Cavitation involves the growth, nucleation and implosive collapse of micro-bubbles and cavities that occur in fractions of microseconds, releasing large amount of energy over a small location that behave as micro-reactors.168 In acoustic cavitation, pressure variations in liquid are effected through sound waves (16 kHz to 100 MHz) using ultrasonic transducers as represented in Fig. 6. This produces oscillating bubbles of various size moving at different velocities.180 The motion of the bubbles and their radial pulsation can be controlled by acoustic field in the resonating system.181 It has been observed that enhancement due to such synergistic mechanism is due to the de-agglomerating effect of photocatalyst through ultrasound, resulting into increased surface area and catalytic performance.182–185 However, industrial application of ultrasonically induced cavitation is a problem due to ineffective distribution of the cavitational activity on a large scale.186,187 Wang et al.168 studied the efficiency of combined treatment in which they used photocatalysis and water jet cavitation on reactive red 2 dye degradation. The results showed a significant enhancement of photocatalytic activity up to ca. 136%.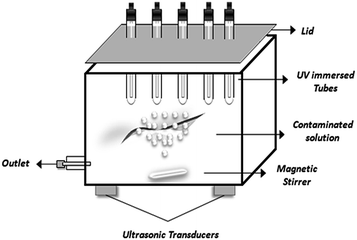 | ||
| Fig. 6 Application of cavitation technology to photocatalysis by using ultrasonic transducers for efficient treatment of organic contaminants. | ||
In hydrodynamic cavitation, cavitation is produced by pressure variations obtained by creating velocity variation and decrease in static pressure that occurs when the fluid passes through a constriction.188 Saharan et al.189 reported that hydrodynamic cavitation is more energy efficient compared to acoustic cavitation and has a higher degradation as for equivalent power/energy dissipation. In addition, other AOTs including organic contaminants degradation using SO4−˙ have recently been introduced.190–193 These include radiolytic or photolytic or thermal activation of persulfate or peroxide bond to break it down to produce SO4−˙. SO4−˙ showed a higher reduction potential of 2.5–3.1 V as compared with OH˙ having a standard reduction potential of 1.8–2.7 V. Moreover, it is more selective for the oxidation of organic contaminants over a wide range of pH.194,195 In addition, SO4−˙ have a longer half-life, depending on its preference for reactions related to electron transfer, whereas OH˙ with an equal preference participates in every reaction.172,194,196
Development of efficient TiO2 photocatalysts by doping
There are various research studies on photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2 in several modified forms for performance enhancement under visible light. These include adsorption and surface complexation on TiO2, non-metal doping, lanthanide ion doping, transition metal doping, noble metal doping and multi-atom doping. The main purpose of doping is to decrease the band gap of pure TiO2 (3.2 eV for anatase phase) to bring the absorption band from UV to visible region. The Fig. 7 below represents the simplified and relative band position and band gap of pure, metal and non-metal doped TiO2. The details about the doping methodologies and photocatalysis mechanisms can be found elsewhere.197–199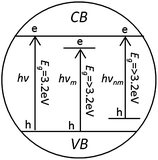 | ||
| Fig. 7 Simplified relative energy bad positions and band widths for pure (hν) metal doped (hνm) and non-metal doped (hνnm) TiO2 anatase.197 | ||
Non-metal doping
There are various reports available on non-metal doping of TiO2, especially with boron,200 carbon,201 sulfur, nitrogen and fluorine.202 The main objective of non-metal doping is to bring the absorption band of TiO2 to visible region. Apart from its advantages, however, long-term instability of the photocatalyst is a major drawback.202 The detail about the dye degradation including nitrogen and carbon doped TiO2 is given below under separate headings.| Catalyst | Dyes used for analysis | Techniques for preparation of N-doped TiO2 catalysts | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-Doped TiO2 | Rhodamine B | Microemulsion-hydrothermal method | 208 |
| N-Doped anatase and rutile | Methyl blue | Calcination of acidified TiCl3 in presence of urea and oxalic acid | 209 |
| N-Doped TiO2 nanotubes | Methyl orange | Solvothermal process | 210 |
| Microarrays of N-doped flower-like TiO2 | Methyl orange | Electrochemical anodization of Ti in NH4F aqueous solution | 211 |
| N-TiO2 | Methyl orange and phenol | Microwave method | 212 |
| N-TiO2 nano colloid | Methyl blue | Nitridation of a porous TiO2 | 213 |
| N-TiO2 | Ethyl blue and 4-chlorophenol | Sol gel using NH4Cl as nitrogen source | 207 |
| N-TiO2 | Methyl blue | Simple method | 214 |
| N-TiO2 | Rhodamine B | Plasma based ion implantation | 215 |
Asahi et al. and others reported that nitrogen due to its comparable size and electronegativity to that of oxygen is the most suitable element for reducing the band gap width of TiO2.216,217 Irie et al.218 proposed that an isolated narrow band formed above the valence band in TiO2−xNx powder is responsible for the visible light response. In addition, increasing nitrogen concentration lowered the quantum yield under UV illumination, indicating that the doping sites could also work as recombination centers. Parida and Naik219 reported the degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange using N-doped TiO2 showing 67% and 59% of degradation after 4 hours irradiation under visible light source. Selvaraj et al.220 measured the photocatalytic degradation of the reactive triazine dyes including reactive yellow 84, reactive red 120 and reactive blue 160 on N-doped TiO2 anatase and P25 in the presence of natural sunlight. It was reported that reactive yellow 84 indicated a faster degradation on N-doped TiO2 in sunlight thanthe commercial Aeroxide P25. However, the P25 indicated higher photocatalytic activity for the other two dyes. The COD level within 3 h sunlight exposure, reduced to 65.1, 73.1, and 69.6% for reactive yellow-84, reactive red 120 and reactive blue 160 respectively. In two separate studies, Ihara et al.221 and Serpone222 argued that synthesized nitrogen doped TiO2 with the sites that were oxygen deficient formed in the grain boundaries were responsible for the visible light response, whereas presence of nitrogen had only enhanced the stabilization of these oxygen vacancies. Songkhum and Tantirungrotechai223 prepared nitrogen and iron(III) co-doped TiO2 (N–Fe–TiO2) and reported active for the photodegradation of methyl orange. However, corresponding to the absorption spectra the synthesized TiO2 photocatalysts except, under UV irradiation, were not found to be photocatalytically active under visible light irradiation. In summary, it can be concluded that, apart from vague understanding of dye degradation mechanism under visible light and various disadvantages, use of nitrogen doped TiO2 may outweigh non-doped TiO2 in near future due to its dye degradation activity under practically available sunlight.224
Ren et al.228 prepared doped TiO2 using outside preparation approach. They added required amounts of amorphous TiO2, glucose, deionized water in a Teflon lined stainless steel autoclave by marinating the temperature at 160 °C for 12 hours.
Velmurugan et al.229 recently synthesized carbon nanoparticle loaded TiO2 (CNP–TiO2) through sonochemical method. CNP–TiO2 was found to be stable and reusable. Comparatively, photocatalytic activity of CNP–TiO2 under solar light for degradation of reactive red 120 was found higher than TiO2 P-25 and as prepared TiO2. Increase in activity was related to suppression in recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pair by loaded CNP indicated by a decrease of measured photoluminescence intensity.
Lanthanide ions doping
Lanthanide ions are known for their complex formation with various Lewis bases e.g. aldehydes, acids, amines, alcohols, thiols. These Lewis bases interact with the f-orbitals of the lanthanides through their functional groups. Thus, incorporation of lanthanide ions into a TiO2 matrix could provide a mean to concentrate the organic pollutant at the semiconductor surface and consequently enhance the photoactivity of TiO2.230–232 It has been reported in literature that the optimum level of rare earth metal doping is 1–2% to hinder the crystal growth of TiO2 during calcinations.202 Although doping of lanthanide ions into TiO2 attracted some attentions still such works are little so far. Additionally, lanthanides ions can in fact trap conductive band electrons when restricted to the TiO2 surface.233 Recently, La3+, Nd3+, Sm3+, Eu3+, Gd3+, and Yb3+ modified TiO2 nanoparticles with their ability to increase the anatase phase stability and preventing the segregation of TiO2 have excessively been investigated for maximizing the efficiency of photocatalytic reactions.234–236 Xie et al.237,238 prepared three types of lanthanide ion-modified titanium dioxide i.e. Eu3+–TiO2, Nd3+–TiO2 and Ce4+–TiO2 and tested for the photodegradation of azo dye X–3B under visible light irradiation. The results showed that Lnn+–TiO2 system had a higher photocurrent generation. They ranked reaction rates as Nd3+–TiO2 sol > Eu3+–TiO2 sol > Ce4+–TiO2 sol > TiO2 sol > P-25 TiO2 powder. Zhang et al.239 prepared TiO2 particles co-doped with boron and lanthanum (B–La–TiO2) at a molar ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 and investigated their photocatalytic performance to photodegrade methyl orange dye. The result showed organic dye degradation to 98% within 90 min compared to 24% with undoped TiO2. It was speculated that the reason behind enhanced photocatalytic activity of B–La–TiO2 photocatalyts is its excellent photocatalytic effect under the visible light region.
4 and investigated their photocatalytic performance to photodegrade methyl orange dye. The result showed organic dye degradation to 98% within 90 min compared to 24% with undoped TiO2. It was speculated that the reason behind enhanced photocatalytic activity of B–La–TiO2 photocatalyts is its excellent photocatalytic effect under the visible light region.
Very recently, Lan et al.240 successfully prepared lanthanum and boron co-doped TiO2 (La–B–TiO2) by modified sol–gel method to enhance the visible-light photocatalytic performance by improving the quantum efficiency of the photocatalytic reaction. 1% La–B–TiO2 catalysts showed highest photocatalytic degradation of acid orange 7 up to 93% under visible-light irradiation for 5 h. Nasir et al.241 synthesized 0.1 Ce/C codoped TiO2 via hydrothermal method for the efficient degradation of an aqueous solution of acid orange 7 dye under visible light irradiation. Co-doped catalysts showed higher photocatalytic activity compared to C-doped catalyst. However, increasing Ce concentration above 0.1 Ce/C–TiO2 resulted in an increase of electrons and holes recombination. In another study Nasir et al.242 again used Ce to prepared Ce–S co-doped TiO2 because of its Ce3+/Ce4+ redox couple, which contains the ability to shift between Ce2O3 and CeO2 under reducing and oxidizing conditions.243 Results indicated that decrease in the particle size, increase in the surface area, abundance of surface hydroxyl groups, and reduction of recombination of e− and h+ assisted the enhanced photocatalytic degradation of acid orange dye.
Transition metal doping
Incorporating transition metals in the TiO2 crystal lattice may result in the formation of new energy levels between valence and conduction band, inducing a shift of light absorption towards the visible light region. However, it has been reported as well that transition metals may cause thermal instability for the anatase phase of TiO2.244![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) TiO2 ratio. The best results were achieved under UV irradiation, when H2O2 is added in photocatalytic process at CuxS
TiO2 ratio. The best results were achieved under UV irradiation, when H2O2 is added in photocatalytic process at CuxS![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) TiO2 = 3
TiO2 = 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7, with high degradation efficiency of almost 99% using methyl orange in 300 min and methylene blue in 180 min. This semiconductors association and the films homogeneity have the ability to limit the electron–hole recombination facilitating good efficiency in dyes photodegradation even under visible light irradiation. Huang et al.253 prepared Cu2O nanoparticles and microparpicles. They tested these particles for the photodegradation of methyl orange. It was observed that nanoparticles were stable in ambient atmosphere, whereas microparticles were found stable as a Cu2O/CuO core structure. The Cu2O microparticles with very slow photocorrosion rate exhibited a higher photocatalytic activity for methyl orange dye than that of the deactivated nanoparticles during the photocatalytic reaction.
7, with high degradation efficiency of almost 99% using methyl orange in 300 min and methylene blue in 180 min. This semiconductors association and the films homogeneity have the ability to limit the electron–hole recombination facilitating good efficiency in dyes photodegradation even under visible light irradiation. Huang et al.253 prepared Cu2O nanoparticles and microparpicles. They tested these particles for the photodegradation of methyl orange. It was observed that nanoparticles were stable in ambient atmosphere, whereas microparticles were found stable as a Cu2O/CuO core structure. The Cu2O microparticles with very slow photocorrosion rate exhibited a higher photocatalytic activity for methyl orange dye than that of the deactivated nanoparticles during the photocatalytic reaction.Noble metal modified TiO2
Deposition of noble metals on TiO2 surface has been reported to improve the photocatalytic efficiency by acting as an electron trap due to the Schottky barrier formation thereby reducing electron–hole recombination process and helping interfacial charge transfer.79,255–261 TiO2 modified with noble metal exhibits excellent stability as well as high reproducibility. Doping of TiO2 with noble metals for photo-oxidation has been studied for at least two decades. However, the detail about the most recent dye degradation work including Silver and Platinum doped TiO2 is given below under separate headings.Multi-atom doped TiO2
Many studies have revealed that TiO2 mono-doping may lead to recombination centers thereby inhibiting light-induced migration of charge carriers to the surface.270 However, it has been recognized that co-doping of TiO2 with both nonmetal and metal can reduce the number of recombination centers by neutralizing positive and negative charges inside the TiO2, which can effectively improve the efficiency of migration of the charge carriers and thus enhance photocatalytic activity.271 Xing et al.272 prepared carbon and lanthanum co-doped TiO2 by a hydrothermal method and reported their high photocatalytic activity under both UV and visible-light irradiation. Recently, Yang et al.273 synthesized Mo and C co-doped TiO2 photocatalysts and reported that 1% Mo–C4/TiO2 showed an excellent visible light photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye. The prepared co-doped catalysts showed greater photocatalytic activity than pure anatase TiO2 and the mono-doped catalysts, because a synergistic effect between molybdenum and carbon increases absorption of visible light and affects separation of photoinduced electrons and holes. Also, Yan et al.274 investigated photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by TiO2–SiO2–NiFe2O4 suspensions and reported that OH˙ radicals and h+ plays important roles in the degradation by TiO2–SiO2–NiFe2O4. Akpan and Hameed275 compared electronically stable composite photocatalyst of the type Ti(1−x−y)Ca(3x−y)Ce(2x−y)–W(y/6)O2(1−2(y−x)) (at y < 2x and x + y < 1) prepared by sol–gel method with commercially available Degussa P-25 and TiO2 photocatalysts for acid red 1 (AR1) photocatalytic degradation. The performance of the composite catalyst excelled that of TiO2, but was as good as Degussa P-25 in terms of the solar photodegradation. However, composite photocatalyst was found better than Degussa P-25 in terms of reusability since it could settle out of solution in less than one hour after solar experiment. The composite photocatalyst was found to have narrowed band gap as compared to TiO2 by 0.26 eV with its activities more into visible region.Dye sensitization in photocatalysis
On a broader scale, waste water remediation with dye sensitization method is beneficial in two ways. Firstly, the adsorption of the dye on the surface of TiO2 catalyst extends the absorption spectrum of TiO2 from UV to visible regime.102 Secondly, the system containing the dye and the phenolic compound represents a classic model of a real effluent stream, which is usually a mixture of different organic compounds, surfactants and metal ions. Dye sensitized degradation is primarily aided by enhanced adherence of the dye molecule onto TiO2 surface in the presence of O2 that can easily scavenge the injected electrons from the conduction band of TiO2.76 General mechanism of dye sensitized photocatalysis has been explained in detail in basic principles and mechanism section of this review. Zhang et al.276 recently studied the aerobic selective oxidation of alcohols in the presence of an anthraquinonic dye (alizarin red S) sensitized TiO2, and a nitroxyl radical (2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidinyloxyl). They found that the whole mechanism involved was the formation of a dye radical cation, which oxidized the nitroxyl radical. This oxidized radical species was found to be mainly responsible for the selective oxidation of alcohols into aldehydes. Other conjugated polymers such as poly(aniline)277 and poly(thiophene)278 has also been used as TiO2 sensitizers for the degradation of dyes.Recently, there have been new discoveries related to the adsorption of complexants on TiO2 surface leading to a sharp enhancement in its activity under visible light by using absorbent such as salicylic acid.279 In a study, Moser et al.280 proved that surface complexation of colloidal semiconductors strongly enhance interfacial electron transfer rates. Ikeda et al.281 demonstrated that phenolic compounds with TiO2 can work as catalyst under visible light below ca. 550–600 nm for water reduction in the presence of a sacrificial donor. Also, Zhang et al.282 chemically modified TiO2 nanoparticles with catechol (4.0 wt% catechol/TiO2) without changing the crystalline structure of TiO2. Surface complexation of catechol lead to an enhanced acid orange 7 dye photocatalytic degradation by shifting onset wavelength of the optical absorption to the visible range.
Structurally modified TiO2
For enhancement of photocatalysis, nanostructured materials with different shapes of TiO2 including nanoparticles, nanotubes, nanofibers, nanocages, nanorods, nanorings, nanosheets, nanocombs, nanobowls, nanosprings and nanobelts have been employed.283 The discussion below illustrates the use of most common TiO2 structural modification to enhance its photocatalytic activity. TiO2 can be synthesized in the form a nanometer scale tube like structure called TiO2 nanotubes.284 The photoactivity of the TiO2 nanotube films has been found as strongly influenced by the tube diameter and thickness.285,286 Increasing tube thickness increases the photodegradation efficiency till a maximum and then decreases till a steady value. In much longer tubes active species have a longer diffusion path that may cause the decrease in photocatalytic degradation rate. The nanotube arrays have been found to be more active than anatase or P-25 TiO2 nanoparticulate films with similar thickness and geometric area. The enhanced dye degradation activity is attributed to a more effective separation of electron–hole pairs taking place in a well ordered way in TiO2 nanotube array film and due to higher internal surface area of the nanotube structure.285–290Graphene modified TiO2
Carbon can also be used in the form of graphene to synthesize graphene/TiO2 photocatalysts.291 Graphene is an atomic sheet of sp2-bonded carbon atoms with unique properties having high conductivity, large specific surface area and high transparency due to its one-atom thickness.292 Zhang et al.293 prepared a P-25–graphene composite by hydrothermal treatment of a suspension of P-25 and graphene oxide. Graphene oxide was reduced to graphene and then P-25 nanoparticles were deposited simultaneously on this graphene sheet. The P-25–graphene composite was found more active than P-25 for the photodegradation of methylene blue due to reduced charge recombination and enhanced absorptivity. The P-25–graphene composite exhibited higher efficiency than P-25 having same carbon content, due to its giant two-dimensional planar structure, which facilitated a better platform for the adsorption of the dye and charge transportation.283 Moreover, TiO2/graphene composites have been well studied as a solar light photocatalysts and electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Recent reports have shown that ultralight 3D-graphene aerogels (GAs) can better adsorb organic pollutants and can provide multidimensional electron transport pathways. Qiu et al.294 prepared 3D-structured TiO2/GA composites by one-step hydrothermal method using glucose. Glucose acts as facet-controlling agent to achieve in situ growth of TiO2 nanocrystals on GAs surfaces. TiO2 nanocrystals exposed with {001} facets and mesoporous structure were highly dispersed on the GAs surface. Affording high surface area, massive appearance, and hydrophobic properties determine its high recyclability and to efficiently photodegrade methyl orange dye.Fullerenes modified TiO2
A fullerene is anymolecule composed entirely of carbon, in the form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, tube, and many other shapes. Spherical fullerenes are also called buckyballs. Cylindrical fullerenes are calledcarbon nanotubes or buckytubes. Fullerenes are similar instructure to graphite, which is composed of stackedgraphene sheets of linked hexagonal rings; but they may also contain pentagonal or sometimes heptagonal rings. Fullerenes are extremely hydrophobic, therefore, their use in aqueous media is quite limited. However functionalizing the molecules with hydroxyl groups can improve water solubilizing properties of fullerenes.283 Krishna et al.295 employed polyhydroxy fullerenes (PHF) to enhance the photocatalytic efficiency of TiO2 for the degradation of the procion red dye. The PHF molecules adsorbed on the surface of TiO2 by electrostatic forces enabled the scavenging of the photogenerated electrons decreasing the electron/hole recombination. The surface coverage of the TiO2 nanoparticles by the PHF molecules (C60(OH)n, n = 18–24) determined the extent of enhancement in dye degradation, with an optimum PHF/TiO2 weight ratio equal to 0.001.296,297Improvement by enhancing TiO2 reactive facets
For anatase TiO2, theoretical and experimental studies have so far revealed that {001} facet compared to thermodynamically stable {101} facet is much more reactive being the dominant source of active sites for various applications.298 Whereas, most of the synthetic anatase crystals due to its crystal growing process are dominated by the less-reactive {101} facets diminishing the reactive {001} facets to minimize the surface energy. Chen et al.299 presented a simple hydrothermal approach for synthesizing uniform, hierarchical spheres self-organized from ultrathin anatase TiO2 nanosheets with nearly 100% exposed {001} facets. Also, Liu et al.300 reported fabricating hollow TiO2 microspheres composed of anatase polyhedra with 20% exposed {001} facets by fluoride-mediated self-transformation method, exhibiting tunable photocatalytic selectivity in decomposing azo dyes in water. Very recently, Yu et al.301 synthesized of layered TiO2, composed of nanosheets with exposed {001} facets, by a simple hydrothermal method. It was observed that layered TiO2 with {001} facet nanosheets exhibited excellent photocatalytic activity for the degradation of rhodamine B dye.Practical aspects of TiO2 photo-processes
Limitations of TiO2 photo-processes
Performance of a catalyst depends upon its configurations i.e. suspended or fixed-bed catalyst impart different performances. Although, coating a catalyst eliminates the need for its post-filtration and centrifugation but it generally reduces the system efficiency significantly largely due to loss in exposed surface area.302,303 On the other hand disadvantages using powder form of catalyst include stirring during the reaction and separation of catalyst from the treated water after each run. To address the later, filtration, sedimentation and centrifugation processes have been used to recover highly dispersed and suspended catalyst from the treated water. However, with this method a fraction of TiO2 particles usually remains in the treated water and a further microfiltration step is usually required for final purification. Besides its time consuming problem, the filtration process become increasingly inefficient as the particle size diminishes. Smaller particles suspended in the water may penetrate through filtration materials causing membranes filter clogging.304The other common way to perform the separation is by sedimentation of TiO2 particles after pH adjustment by coagulation–flocculation process. Separation by sedimentation has been enhanced by attaching TiO2 particles onto other support particles like quartz, silica gel, alumina, zeolites, activated carbon or glass spheres but the loss of photocatalytic activity has usually been observed.305 In addition to this the fast aggregation of TiO2 in suspension leads to a decrease in effective surface area which reduces its catalytic efficiency. A filtration step after photocatalytic reaction is still required because of TiO2 suspension.164 Moreover, TiO2 absorption wavelength corresponding to the band-gap energy of 3.02 eV is at near ultraviolet radiation.306 Thus either the need of an UV excitation source or ability of TiO2 to absorb only 5% energy of the solar spectrum has restricted its technological applications.
Trends in improving TiO2 photo-processes
Despite of drawbacks discussed in the above section, more coated photocatalysts and immobilization techniques are still been investigated.164,307–311 In many cases TiO2 coated on a support is found to be more efficient for organic compound removal in contrast to uncoated TiO2, reducing overall operating costs.312 Many researchers have examined some methods for fixing TiO2 on supporting materials including glass beads,313 fiber glass,161,314 activated carbon,315 silica316 and zeolite317 as given in Table 3.| Support type | Dye used for degradation | Technique used for preparation | Performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinoptilolite (CP) (Iranian Natural Zeolite) | Acid red 114 | — | TiO2/clinoptilolite (SSD) proved to be an active photocatalyst with a first order reaction, k = 0.0108 min−1. With increasing dye conc. photodegradation conversion of AR 114 decreased | 318 |
| Chitosan [β-(1→4)-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose] | Methyl orange | Solution casting technology | The TiO2/ZnO/chitosan NTFs showed high photocatalytic activity under solar irradiation | 319 |
| Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) rings | Methylene blue | Ultrasonically spray-coated with TiO2 sol | Results showed 80% degradation of methylene blue after 10 min at pH 9 | 320 |
| Polyamide 6 (PA6) fiber | Methylene blue | Low temperature hydrothermal method | Compared with the untreated fabric, the protection against UV radiation improved. The titanium dioxide coated fabric could degrade methylene blue efficiently dye under UV irradiation | 321 |
| Glass plates | Acid red 27 (AR27) | Immobilized | Outlet stream from photoreactor was mineralized with products such as NH4+, NO3−, O2− and SO42− ions | 322 |
| Non-woven paper with SiO2 | Reactive black 5 (RB5) | — | Degradation of RB5 azo dye was strongly influenced by the ionic strength of the solution. Above pH PZC of SiO2, the cations of the solution increased the amount of dye adsorbed onto the photocatalyst support | 170 |
| Sand | Methylene blue, rhodamine B and methyl orange | — | TiO2/UV process supported on sand is effective in totally mineralizing these compounds | 323 |
Zeolite as TiO2 support
Zeolites are thealuminosilicate members of the family of microporous solids known as molecular sieves. The termmolecular sieve refers to the ability to selectively sort molecules based primarily on a size exclusion process. This is due to a very regular pore structure of molecular dimensions. Among variety of supports available, zeolites are considered to provide an effective electric field of their framework for separation of photogenerated electrons and holes.318,324 However care should be taken while using zeolite as TiO2 support so that it may not affect the TiO2 photoactivity and the adsorptive properties of zeolite. Mathews325 reported that photoefficiency of TiO2 is suppressed when Ti interacts with zeolite. The OH˙ available on the surface of TiO2 can be easily transferred onto zeolite surface as shown in Fig. 8. Additionally, the presence of zeolite on TiO2 maintains dye molecules near the photocatalyst (local concentration effect) which may result in an increase of degradation rate.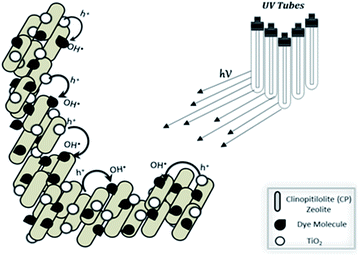 | ||
| Fig. 8 Synergistic effect of TiO2 and clinopitilolite catalyst on dye degradation by producing OH˙ free radicals.318 | ||
TiO2 loaded hydrophobic mesocellualr foams
Hydrophobic materials based on zeolites and mesoporous silicas such as hexagonal mesoporous silica (HMS), SBA-15 and mesocelluar foams could offer excellent ability of adsorption of organic compounds owing to their weak adsorption of water molecules and the large surface areas.326 Though simple surface fluorination on TiO2 can induce an enhanced UV light photocatalytic oxidation activity, however it is difficult to improve the visible light photocatalytic activity of TiO2, owing to the lack of photo-excited holes in the visible light irradiation.327In 2012, Xing et al.328 prepared a novel hydrophobic TiO2 photocatalyst, which can enhance visible light response by using cheaper and low-toxic inorganic NH4F. They prepare the super-hydrophobic mesocellular foams loaded with nanosized TiO2 photocatalyst. Mesoporous catalyst greatly facilitated the surface fluorination, which together with Ti3+ (a self-doped TiO2 catalyst) generation promoted its visible light photocatalytic activity329 and the surface fluorination enhanced UV light photocatalytic activity. It was reported that the catalyst exhibit permanent and excellent super-hydrophobic property, high adsorption capacity, and enhanced photocatalytic activity for rhodamine B (RhB) degradation. Recently, Qi et al.330 prepared carbon-doped TiO2/mesocellular-F photocatalysts hydrophobically modified by the hydrothermal method. Catalyst indicated an efficient visible light photodegradation of methyl orange solution because of the synergistic effect of small crystal size, carbon dopants, and hydrophobic modification due to the fluorination of NH4F.
Chitosan as TiO2 support
Chitosan [β-(1→4)-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose] is a natural cationic biopolymer that is produced by N-deacetylation of chitin. Chitin is considered as the second most abundant natural polysaccharide after cellulose.331 The extraction of chitin from shells and its subsequent deacetylation to chitosan is a relatively low cost process.332Chitosan molecules contain a large number of reactive hydroxyl (–OH) and amino (–NH2) groups. Also, chitosan has high affinity for metal ions and this property has been used to prepare metal–chitosan nanocomposites.333 This enables Chitosan to exhibit unique adsorption and chelating properties for all kinds of heavy metal ions,334–336 making chitosan an appropriate and excellent bio-matrix for synthesizing nanosized particles for various inorganic photocatalysts such as titanium oxide,337,338 cadmium sulfide,319,339 zinc sulfide,340 zinc oxide341 and cuprous oxide.342 In addition, immobilizing nanosized photocatalysts onto chitosan bio-matrix can effectively prevent agglomeration of nanoparticles during growth and can overcome the difficulties related to separation and recovery of nanosized powder materials.336
Activated carbon as TiO2 support
Activated carbon also known as activated charcoal (AC) is a highly porous form of carbon with porosity spanning the macro (λ > 50 nm), meso (0.5–1 μm) and micro (<1 μm) pore ranges116 and very high-surface typically up to 900–1200 m2 g−1.343 It is generally produced from cheap carbonaceous source materials such as nutshells, coconut husk, peat, wood, coir, lignite, coal, and petroleum pitch. Use of activated carbon is the most common method applied for dye removal by adsorption.344 In particular, activated carbon (AC) has been extensively researched as a support for heterogeneous catalysis,345 and there exists over 650 studies and well over 1000 patents346 concerning AC–TiO2 mixtures or composites.347–351 Due to its higher effectiveness, it has been applied on adsorbing cationic, mordant, and acid dyes and to dispersed, vat, direct, pigment and reactive dyes on a slightly lesser extent.26,352Effective performance using activated carbon mainly dependents upon the type of carbon being used and the characteristics of the aqueous solution containing various chemicals and non-targeted contaminants. Regeneration or reuse can result in a steep reduction in performance, and efficiency of dye removal. Activated carbon, like many other dye-removal treatments is considered suitable for one particular type of pollutant or waste system and ineffective on another. Although, activated carbon is expensive it comes with the advantage of regeneration. However, this reactivation usually results into 10–15% loss of the sorbent. Arana et al.353 prepared AC and TiO2 catalysts having varying proportion. The results showed that the AC in addition to increasing surface area can also modify the acid–base properties and the UV spectrum of TiO2. It was reported that activity of AC was increased under solar irradiation.
In AC–TiO2 system, the adsorption capacity of AC enhances the chances of high concentration of reactants to come in contact with TiO2 and possibly turning them into their intermediates as explained in the Fig. 9. Zhang et al.236 proposed a similar illustration for the photocatalyzed mineralization of methyl orange to understand the effect of presence of AC onto TiO2 for effective dye degradation. On the other hand, a disadvantage of using AC is the excessive formation of nanosized pores resulting into rare infiltration, leaving TiO2 on the outer macropores.116,354,355 Moreover, the band gap tuning problem of TiO2 is not resolved by the use of AC as a support.
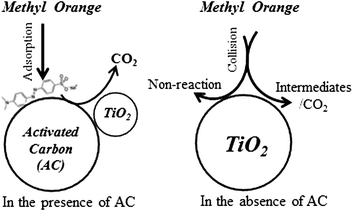 | ||
| Fig. 9 Synergistic mechanism between AC–TiO2 composites. The arrow labelling un-reacted emphasizes that in the absence of Absorbent the reactants may remain un-reacted into the solution resulting in low photoactivity of methyl orange.236 | ||
Silica as TiO2 support
Use of supported TiO2 catalysts depends on the nature of supports, one of the most important factors influencing photocatalytic performance.169,356,357 Recently, amorphous SiO2 due to its special physicochemical properties such as high adsorption capacity has been studied showing advantages towards highly active support for catalysts. The presence of considerably large number of acid sites and hydroxyl groups on the surface of amorphous SiO2 material make it more absorptive.358,359 Studies have shown that silica gel can be an effective support for binding TiO2 that is effective for removal of basic dyes. However, in such processes, there can be side reaction taking place along with photocatalysis and therefore such limiting factors can prevent its commercial application.26 Additionally, immobilization TiO2 on a suitable and inert matrix has shown an advanced organic and inorganic pollutant photodecomposition than that of pure TiO2.169,360Sun et al.361 investigated the catalytic properties of three porous amorphous silica including diatomite, opal and porous supported photocatalysts (TiO2/SiO2) by UV-assisted degradation of rhodamine B. Through morphology and physical properties of the resulting TiO2/amorphous SiO2 catalysts, it was suggested that the nature of silica supports could affect the particle size and the crystal form of TiO2. TiO2/diatomite photocatalyst, compared with pure TiO2 (P-25) and the other two TiO2/amorphous SiO2 catalysts, exhibited better catalytic performance at different calcination temperatures with a discolouration rate of up to over 85%. Photocatalytic properties such as mixed-phase TiO2 with small particle size might be responsible for efficient performance. Furthermore, its stable and inert porous structure improves its activity.
Carbon nanotubes as TiO2 support
The carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are interesting materials having unique electronic properties associated with their special 1D structure which facilitates the charge transfer.362 The CNTs are described as tubular assemblies made exclusively of rolled-up films of interlocked carbon atoms. These are classified as single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) which consist of a single layer of graphene sheet rolled into a cylindrical tube or multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), which contain multiple concentric tubes. CNTs have a large specific surface area due to their hollow geometry. CNTs–TiO2 hybrids have been tested for the photodegradation of acetone,363 methylene blue364,365 and phenol.366,367 All such studies emphasized that the addition of CNTs had enhanced the photocatalytic effectiveness of TiO2.Yu et al.368 compared the effect of MWCNTs on the adsorption and the photocatalytic properties of TiO2 P-25. The results showed that the mixture of CNTs and TiO2 significantly improved the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 for the treatment of three azo dyes and was found more efficient than the mixture of TiO2 with activated carbon. Luo et al.369 prepared short MWCNTs that can be suspended, sorted and manipulated more easily so that the light can well penetrate into the inner tubes. The short MWCNTs were used as initial materials to fabricate TiO2/short MWCNTs nano-composites that were tested for the photodegradation of reactive brilliant red X-3B. The photoactivity of the TiO2/short MWCNTs samples with optimum weight ratio (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100) was studied and rates much higher than that of various active photocatalysts (TiO2/short MWCNTs > TiO2/MWCNTs > TiO2> P-25) were reported.
100) was studied and rates much higher than that of various active photocatalysts (TiO2/short MWCNTs > TiO2/MWCNTs > TiO2> P-25) were reported.
TiO2 embedded in polymer matrix
Difficulties such as low quantum yield and low adsorption capacity of TiO2 photocatalyst limits its practical application.122 Among multiple techniques to overcome these issues, incorporation of semiconductors into the polymer matrix have been achieved. Example such as polypyrrole (PPy)–TiO2 composite films, polyethylene–TiO2, and polyvinylchloride (PVC)–TiO2 as resulting composites were found to enhance degradation reactions more effectively than a suspension of TiO2 nanoparticles.370 Cheng et al.371 report efficient adsorption and photodegradation of textile dyes orange II and methyl orange under UV irradiation using polyaniline (PANI) and PANI–TiO2 composite nanotubes as photocatalyst, respectively. Decolorization up to 98.6% of orange II and 98.1% of methyl orange in the presence of PANI–TiO2 composite nanotubes were reported. Addition of TiO2 nanoparticles to the one-dimensional polymer matrix gradually increased the removal rate of organic dyes due to higher specific surface area and the positive form of titania at the interface.Conclusion
Owing to its many advantages mainly involving most stable and active naturally occurring photocatalyst, TiO2 is, so for, seen as the best catalytic material for degradation of various contaminants and sustainable environmental remediation technology. It has been widely employed in dye photodegradation studies. Photodegradation of industrial dyes using improved TiO2 has presented a somewhat promising and effective treatment technology. However, in order to overcome constraint such as sensitivity towards operational parameters i.e. pH, temperature, catalyst dose, amount of dye, inability for high photon efficiency to utilize wider solar spectra, and separation after treatment inhibits the ability of TiO2 from its real time application on a vast scale. Therefore, more advanced level research studies are needed to address TiO2 shortfalls or to formulate potential alternative for TiO2.Acknowledgements
The authors of this work acknowledge the financial support from Department of Environmental Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad and Higher Education Commission of Pakistan.Notes and references
- R. J. Fessenden and J. S. Fessenden, Adv. Drug Res., 1967, 4, 95–132 CAS.
- H. Park and W. Choi, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2003, 159, 241–247 CrossRef CAS.
- I. A. Alaton, I. A. Balcioglu and D. W. Bahnemann, Water Res., 2002, 36, 1143–1154 CrossRef CAS.
- U. Pagga and D. Brown, Chemosphere, 1986, 15, 479–491 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Bensalah, M. Alfaro and C. Martínez-Huitle, Chem. Eng. J., 2009, 149, 348–352 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Turhan and Z. Turgut, Desalination, 2009, 242, 256–263 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Gosetti, V. Gianotti, S. Angioi, S. Polati, E. Marengo and M. C. Gennaro, J. Chromatogr. A, 2004, 1054, 379–387 CAS.
- A. Houas, H. Lachheb, M. Ksibi, E. Elaloui, C. Guillard and J.-M. Herrmann, Appl. Catal., B, 2001, 31, 145–157 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zollinger, Color chemistry: syntheses, properties, and applications of organic dyes and pigments, Wiley-VCH, 2003 Search PubMed.
- W. S. Perkins, Textile Chemist and Colorist and American Dyestuff Reporter, 1999, vol. 1, pp. 33–37 Search PubMed.
- I. K. Konstantinou and T. A. Albanis, Appl. Catal., B, 2004, 49, 1–14 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Kant, Nat. Sci., 2012, 04, 22–26 CAS.
- R. Anliker, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 1979, 3, 59–74 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Shore, Indian Journal of Fiber and Textile Research, 1996, 21, 1–29 CAS.
- C. Carliell, S. Barclay and C. Buckley, Water SA, 1996, 22, 225–233 CAS.
- N. Willmott, J. Guthrie and G. Nelson, J. Soc. Dyers Colour., 1998, 114, 38–41 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Mishra and M. Tripathy, Colourage, 1993, 40, 35 CAS.
- M. Senthilkumar and M. Muthukumar, Dyes Pigm., 2007, 72, 251–255 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Leena and S. Raj, Afr. J. Biotechnol., 2008, 71(8), 3309–3313 Search PubMed.
- G. L. Baughman and T. A. Perenich, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 1988, 7, 183–199 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K.-T. Chung, G. E. Fulk and M. Egan, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1978, 35, 558–562 CAS.
- E. J. Weber and R. L. Adams, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1995, 29, 1163–1170 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Bali, E. Catalkaya and F. Sengul, J. Hazard. Mater., 2004, 114, 159–166 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Rauf and S. S. Ashraf, Chem. Eng. J., 2009, 151, 10–18 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Daneshvar, M. Rasoulifard, A. Khataee and F. Hosseinzadeh, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 143, 95–101 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Robinson, G. McMullan, R. Marchant and P. Nigam, Bioresour. Technol., 2001, 77, 247–255 CrossRef CAS.
- A. G. Prado, L. B. Bolzon, C. P. Pedroso, A. O. Moura and L. L. Costa, Appl. Catal., B, 2008, 82, 219–224 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Cassano, R. Molinari, M. Romano and E. Drioli, J. Membr. Sci., 2001, 181, 111–126 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Crini, Bioresour. Technol., 2006, 97, 1061–1085 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Perez-Urquiza and J. Beltran, J. Chromatogr. A, 2000, 898, 271–275 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Hueber-Becker, G. J. Nohynek, E. K. Dufour, W. J. Meuling, A. T. H. de Bie, H. Toutain and H. M. Bolt, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2007, 45, 160–169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Wróbel, A. Boguta and R. M. Ion, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2001, 138, 7–22 CrossRef.
- L. Yang, Y. Lin, J. Jia, X. Xiao, X. Li and X. Zhou, J. Power Sources, 2008, 182, 370–376 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. I. Georgiev, V. B. Bojinov and P. S. Nikolov, Dyes Pigm., 2009, 81, 18–26 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Nilsson, R. Nordlinder, U. Wass, B. Meding and L. Belin, Br. J. Ind. Med., 1993, 50, 65–70 CAS.
- W. Walthall and J. Stark, Environ. Pollut., 1999, 104, 207–215 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Tsuda, M. Murakami, N. Matsusaka, K. Kano, K. Taniguchi and Y. F. Sasaki, Toxicol. Sci., 2001, 61, 92–99 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zaharia and D. Suteu, Adsorption of cationic dye on cellolignin, BioResources, 2012, 8(1), 427–446 Search PubMed.
- A. Price, A. C. Cohen and I. Johnson, J.J. Pizzuto's fabric science, Fairchild Publications, New York, 8th edn, 2005 Search PubMed.
- R. M. Christie, Colour chemistry, Royal Society of Chemistry, 2001 Search PubMed.
- B. P. Corbman and M. D. Potter, Textiles: Fiber to Fabric, McGraw-Hill New York, NY, USA, 1975 Search PubMed.
- A. Datyner, Rev. Prog. Color. Relat. Top., 1993, 23, 40–50 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Stead, Dyes Pigm., 1982, 3, 161–171 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Golob and A. Ojstršek, Dyes Pigm., 2005, 64, 57–61 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. E. McGovern and R. H. Michel, Acc. Chem. Res., 1990, 23, 152–158 CrossRef CAS.
- H. L. Needles, Handbook of textile fibers, dyes and finishes, Garland STPM Press, 1981 Search PubMed.
- W. Z. Tang and A. Huren, Chemosphere, 1995, 31, 4157–4170 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Brown and S. C. De Vito, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 1993, 23, 249–324 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. M. Slokar and A. Majcen Le Marechal, Dyes Pigm., 1998, 37, 335–356 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sleiman, D. Vildozo, C. Ferronato and J.-M. Chovelon, Appl. Catal., B, 2007, 77, 1–11 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Kuo, Water Res., 1992, 26, 881–886 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Ince and D. Gönenç, Environ. Technol., 1997, 18, 179–185 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Tünay, I. Kabdasli, G. Eremektar and D. Orhon, Water Sci. Technol., 1996, 34, 9–16 CrossRef.
- M. Saquib and M. Muneer, Dyes Pigm., 2003, 56, 37–49 CrossRef CAS.
- E. P. Reddy, L. Davydov and P. Smirniotis, Appl. Catal., B, 2003, 42, 1–11 CrossRef CAS.
- O. J. Hao, H. Kim and P.-C. Chiang, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2000, 30, 449–505 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Moutaouakkil, Y. Zeroual, F. Zohra Dzayri, M. Talbi, K. Lee and M. Blaghen, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2003, 413, 139–146 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Shaw, C. Carliell and A. Wheatley, Water Res., 2002, 36, 1993–2001 CrossRef CAS.
- G. M. Bonser, L. Bradshaw, D. Clayson and J. Jull, Br. J. Cancer, 1956, 10, 539 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Arslan and I. A. Balcioğlu, Dyes Pigm., 1999, 43, 95–108 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kunitou, S. Maeda, S. Hongyou and K. Mishima, Can. J. Chem. Eng., 2002, 80, 208–213 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chakrabarti and B. K. Dutta, J. Hazard. Mater., 2004, 112, 269–278 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Sun, X. Wang, J. Sun, R. Sun, S. Sun and L. Qiao, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2006, 260, 241–246 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Madhavan, P. Maruthamuthu, S. Murugesan and S. Anandan, Appl. Catal., B, 2008, 83, 8–14 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-H. Qi, Y.-Y. Zhuang, Y.-C. Yuan and W.-X. Gu, J. Hazard. Mater., 2002, 90, 51–62 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Pizarro, C. Guillard, N. Perol and J.-M. Herrmann, Catal. Today, 2005, 101, 211–218 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yates, M. Nolan, D. Sheel and M. Pemble, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2006, 179, 213–223 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ni, M. K. Leung, D. Y. Leung and K. Sumathy, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2007, 11, 401–425 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L.-C. Chen and T.-C. Chou, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1994, 33, 1436–1443 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Annadurai, T. Sivakumar and S. R. Babu, Bioprocess Eng., 2000, 23, 167–173 CrossRef CAS.
- W. A. Sadik, A. W. Nashed and A.-G. M. El-Demerdash, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2007, 189, 135–140 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Jiang, Y. Sun, H. Liu, F. Zhu and H. Yin, Dyes Pigm., 2008, 78, 77–83 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Bizani, K. Fytianos, I. Poulios and V. Tsiridis, J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, 136, 85–94 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Vinodgopal and P. V. Kamat, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1995, 29, 841–845 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Chen, X. Li, W. Ma, J. Zhao, H. Hidaka and N. Serpone, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106, 318–324 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Vinodgopal, D. E. Wynkoop and P. V. Kamat, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1996, 30, 1660–1666 CrossRef CAS.
- U. G. Akpan and B. H. Hameed, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 170, 520–529 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Tang, Z. Zhang, H. An, M. Quintana and D. Torres, Environ. Technol., 1997, 18, 1–12 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li and F. Li, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, 35, 2381–2387 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, Water Res., 2000, 34, 990–994 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Stylidi, D. I. Kondarides and X. E. Verykios, Appl. Catal., B, 2003, 40, 271–286 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Tanaka, K. Padermpole and T. Hisanaga, Water Res., 2000, 34, 327–333 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Lachheb, E. Puzenat, A. Houas, M. Ksibi, E. Elaloui, C. Guillard and J.-M. Herrmann, Appl. Catal., B, 2002, 39, 75–90 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. K. Gouvêa, F. Wypych, S. G. Moraes, N. Durán, N. Nagata and P. Peralta-Zamora, Chemosphere, 2000, 40, 433–440 CrossRef.
- A. Bianco Prevot, C. Baiocchi, M. C. Brussino, E. Pramauro, P. Savarino, V. Augugliaro, G. Marcì and L. Palmisano, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, 35, 971–976 CrossRef.
- F. Zhang, J. Zhao, T. Shen, H. Hidaka, E. Pelizzetti and N. Serpone, Appl. Catal., B, 1998, 15, 147–156 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhao, T. Wu, K. Wu, K. Oikawa, H. Hidaka and N. Serpone, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1998, 32, 2394–2400 CrossRef CAS.
- J. T. Spadaro, L. Isabelle and V. Renganathan, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1994, 28, 1389–1393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Neppolian, H. C. Choi, S. Sakthivel, B. Arabindoo and V. Murugesan, Chemosphere, 2002, 46, 1173–1181 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Sakthivel, B. Neppolian, M. V. Shankar, B. Arabindoo, M. Palanichamy and V. Murugesan, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2003, 77, 65–82 CrossRef CAS.
- C. M. So, M. Y. Cheng, J. C. Yu and P. K. Wong, Chemosphere, 2002, 46, 905–912 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Hu, J. C. Yu, Z. Hao and P. K. Wong, Appl. Catal., B, 2003, 42, 47–55 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Minero, V. Maurino and E. Pelizzetti, Res. Chem. Intermed., 1997, 23, 291–310 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Chun and W. Yizhong, Chemosphere, 1999, 39, 2107–2115 CrossRef.
- V. Augugliaro, C. Baiocchi, A. Bianco Prevot, E. García-López, V. Loddo, S. Malato, G. Marcí, L. Palmisano, M. Pazzi and E. Pramauro, Chemosphere, 2002, 49, 1223–1230 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Nohara, H. Hidaka, E. Pelizzetti and N. Serpone, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 1997, 102, 265–272 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Maurino, C. Minero, E. Pelizzetti, P. Piccinini, N. Serpone and H. Hidaka, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 1997, 109, 171–176 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Abdullah, G. K. C. Low and R. W. Matthews, J. Phys. Chem., 1990, 94, 6820–6825 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Kerzhentsev, C. Guillard, J.-M. Herrmann and P. Pichat, Catal. Today, 1996, 27, 215–220 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Pirkanniemi and M. Sillanpää, Chemosphere, 2002, 48, 1047–1060 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Stylidi, D. I. Kondarides and X. E. Verykios, Appl. Catal., B, 2004, 47, 189–201 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Kaur and V. Singh, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 141, 230–236 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Kormann, D. Bahnemann and M. R. Hoffmann, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1991, 25, 494–500 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Liu, S. Chen, W. Zhao and S. Zhang, Desalination, 2009, 249, 1288–1293 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Peralta-Hernández, Y. Meas-Vong, F. J. Rodríguez, T. W. Chapman, M. I. Maldonado and L. A. Godínez, Water Res., 2006, 40, 1754–1762 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Lakshmi, R. Renganathan and S. Fujita, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 1995, 88, 163–167 CrossRef CAS.
- D. C. Hurum, A. G. Agrios, K. A. Gray, T. Rajh and M. C. Thurnauer, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107, 4545–4549 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Yin, Y. Wada, T. Kitamura, S. Kambe, S. Murasawa, H. Mori, T. Sakata and S. Yanagida, J. Mater. Chem., 2001, 11, 1694–1703 RSC.
- A. Riga, K. Soutsas, K. Ntampegliotis, V. Karayannis and G. Papapolymerou, Desalination, 2007, 211, 72–86 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. K. Gupta, R. Jain, A. Nayak, S. Agarwal and M. Shrivastava, Mater. Sci. Eng., C, 2011, 31, 1062–1067 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Nadeem, K. A. Connelly and H. Idriss, Int. J. Nanotechnol., 2012, 9, 121–162 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Shiga, A. Tsujiko, S. Yae and Y. Nakato, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 1998, 71, 2119–2125 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Riegel and J. R. Bolton, J. Phys. Chem., 1995, 99, 4215–4224 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Abdullah, G. K. Low and R. W. Matthews, J. Phys. Chem., 1990, 94, 6820–6825 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhang, W. Wang, M. Shang and W. Yin, J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 177, 1013–1018 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. F. Velasco, J. B. Parra and C. O. Ania, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2010, 256, 5254–5258 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Khataee, M. Fathinia, S. Aber and M. Zarei, J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 181, 886–897 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sreekantan and L. C. Wei, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 490, 436–442 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-F. Yu and S.-T. Yang, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 492, 695–700 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Naeem and F. Ouyang, Phys. B, 2010, 405, 221–226 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Fox and M. T. Dulay, Chem. Rev., 1993, 93, 341–357 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Hoffmann, S. T. Martin, W. Choi and D. W. Bahnemann, Chem. Rev., 1995, 95, 69–96 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Peral, X. Domènech and D. F. Ollis, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 1997, 70, 117–140 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Saien and A. R. Soleymani, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2012, 18, 1683–1688 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhao, C. Chen and W. Ma, Top. Catal., 2005, 35, 269–278 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Galindo, P. Jacques and A. Kalt, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2000, 130, 35–47 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ma and J.-n. Yao, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 1998, 116, 167–170 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Chen, Y. Xie, J. Zhao and G. Lu, Chemosphere, 2001, 44, 1159–1168 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zhang, J. Zhao, T. Shen, H. Hidaka, E. Pelizzetti and N. Serpone, Appl. Catal., B, 1998, 15, 147–156 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhu, R. Jiang, Y. Fu, Y. Guan, J. Yao, L. Xiao and G. Zeng, Desalination, 2012, 286, 41–48 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla and R. Hamzavi, J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, 133, 226–232 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. K. Kansal, M. Singh and D. Sud, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 153, 412–417 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Muruganandham and M. Swaminathan, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2004, 81, 439–457 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sakthivel, B. Neppolian, M. Shankar, B. Arabindoo, M. Palanichamy and V. Murugesan, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2003, 77, 65–82 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Qamar, M. Saquib and M. Muneer, Dyes Pigm., 2005, 65, 1–9 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Tunesi and M. Anderson, J. Phys. Chem., 1991, 95, 3399–3405 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. Goncalves, A. M. Oliveira-Campos, E. M. Pinto, P. Plasência and M. J. R. Queiroz, Chemosphere, 1999, 39, 781–786 CrossRef CAS.
- A. H. Mahvi, M. Ghanbarian, S. Nasseri and A. Khairi, Desalination, 2009, 239, 309–316 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Baran, A. Makowski and W. Wardas, Chemosphere, 2003, 53, 87–95 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Z. Tang and R. Z. Chen, Chemosphere, 1996, 32, 947–958 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Neppolian, H. Choi, S. Sakthivel, B. Arabindoo and V. Murugesan, Chemosphere, 2002, 46, 1173–1181 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Bizani, K. Fytianos, I. Poulios and V. Tsiridis, J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, 136, 85–94 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wiszniowski, D. Robert, J. Surmacz-Gorska, K. Miksch and J.-V. Weber, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2002, 152, 267–273 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Raillard, V. Héquet, P. Le Cloirec and J. Legrand, Water Sci. Technol., 2004, 50, 241–250 CAS.
- D. Hufschmidt, D. Bahnemann, J. J. Testa, C. A. Emilio and M. I. Litter, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2002, 148, 223–231 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Vautier, J. Catal., 2001, 201, 46–59 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Poulios and I. Tsachpinis, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 1999, 74, 349–357 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Poulios, A. Avranas, E. Rekliti and A. Zouboulis, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2000, 75, 205–212 CrossRef CAS.
- L. B. Reutergådh and M. Iangphasuk, Chemosphere, 1997, 35, 585–596 CrossRef.
- D. Curcó, J. Gimenez, A. Addardak, S. Cervera-March and S. Esplugas, Catal. Today, 2002, 76, 177–188 CrossRef.
- M. Qamar, M. Muneer and D. Bahnemann, J. Environ. Manage., 2006, 80, 99–106 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Karunakaran and S. Senthilvelan, Catal. Commun., 2005, 6, 159–165 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. C. Collazzo, E. L. Foletto, S. L. Jahn and M. A. Villetti, J. Environ. Manage., 2012, 98, 107–111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. San, A. Hatipoǧlu, G. Koçtürk and Z. Çınar, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2001, 139, 225–232 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. Gouvea, F. Wypych, S. G. Moraes, N. Duran, N. Nagata and P. Peralta-Zamora, Chemosphere, 2000, 40, 433–440 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Saquib and M. Muneer, Dyes Pigm., 2002, 53, 237–249 CrossRef CAS.
- A. F. Caliman, C. Cojocaru, A. Antoniadis and I. Poulios, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 144, 265–273 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Percherancier, R. Chapelon and B. Pouyet, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 1995, 87, 261–266 CrossRef CAS.
- A. B. Prevot, M. Vincenti, B. A. and E. Pramauro, Appl. Catal., B, 1999, 22, 149–158 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Poulios and I. Aetopoulou, Environ. Technol., 1999, 20, 479–487 CrossRef CAS.
- R. W. Matthews, Sol. Energy, 1987, 38, 405–413 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Saquib, T. M. Abu, M. Haque and M. Muneer, J. Environ. Manage., 2008, 88, 300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Lung-Chyuan and C. Tse-Chuan, J. Mol. Catal., 1993, 85, 201–214 CrossRef.
- E. C. Ilinoiu, R. Pode, F. Manea, L. A. Colar, A. Jakab, C. Orha, C. Ratiu, C. Lazau and P. Sfarloaga, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2012, 44(2), 270–278 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Wang, C. Xie, W. Zhang, S. Cai, Z. Yang and Y. Gui, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 141, 645–652 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. N. Chong, B. Jin, C. W. Chow and C. Saint, Water Res., 2010, 44, 2997–3027 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-H. Liao, S.-F. Kang and F.-A. Wu, Chemosphere, 2001, 44, 1193–1200 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, J. Jia and Y. Wang, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 185, 315–321 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhu, J.-Y. Li, J.-C. Zhao and G. J. Churchman, Appl. Clay Sci., 2005, 28, 79–88 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Aguedach, S. Brosillon, J. Morvan and K. Lhadi El, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 150, 250–256 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Diebold, Surf. Sci. Rep., 2003, 48, 53–229 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Chen, W. Wang, H. Xiao, C. Hong, F. Zhu, Y. Yao and Z. Xue, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 193–194, 290–295 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Venkatadri and R. W. Peters, Hazard. Waste Hazard. Mater., 1993, 10, 107–149 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Fernandez, J. Bandara, A. Lopez, P. Buffat and J. Kiwi, Langmuir, 1999, 15, 185–192 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Dhananjeyan, E. Mielczarski, K. R. Thampi, P. Buffat, M. Bensimon, A. Kulik, J. Mielczarski and J. Kiwi, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105, 12046–12055 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Bozzi, M. Dhananjeyan, I. Guasaquillo, S. Parra, C. Pulgarin, C. Weins and J. Kiwi, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2004, 162, 179–185 CrossRef CAS.
- S. S. Reddy and B. Kotaiah, Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, 2, 245–251 CAS.
- X. Wang, Z. Yao, J. Wang, W. Guo and G. Li, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2008, 15, 43–48 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. K. Kim and C. P. Huang, J. Chin. Inst. Eng., 2005, 28, 1107–1118 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Mettin, S. Luther, C.-D. Ohl and W. Lauterborn, Ultrason. Sonochem., 1999, 6, 25–29 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Leighton, Ultrason. Sonochem., 1995, 2, S123–S136 CrossRef.
- S. Tangestaninejad, M. Moghadam, V. Mirkhani, I. Mohammadpoor-Baltork and H. Salavati, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2008, 15, 815–822 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Z. Shirgaonkar and A. B. Pandit, Ultrason. Sonochem., 1998, 5, 53–61 CrossRef CAS.
- N. L. Stock, J. Peller, K. Vinodgopal and P. V. Kamat, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2000, 34, 1747–1750 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mrowetz, C. Pirola and E. Selli, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2003, 10, 247–254 CrossRef CAS.
- K. M. Kalumuck and G. L. Chahine, http://resolver.caltech.edu/cav2001:sessionA4.006, 2001.
- M. Sivakumar and A. B. Pandit, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2002, 9, 123–131 CrossRef CAS.
- P. R. Gogate and A. B. Pandit, Adv. Environ. Res., 2004, 8, 501–551 CrossRef CAS.
- V. K. Saharan, A. B. Pandit, P. S. Satish Kumar and S. Anandan, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2011, 51, 1981–1989 CrossRef.
- Y. Deng and C. M. Ezyske, Water Res., 2011, 45, 6189–6194 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Nfodzo and H. Choi, Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 174, 629–634 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Criquet and N. K. V. Leitner, Chemosphere, 2009, 77, 194–200 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. H. Waldemer, P. G. Tratnyek, R. L. Johnson and J. T. Nurmi, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2007, 41, 1010–1015 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Neta, V. Madhavan, H. Zemel and R. W. Fessenden, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1977, 99, 163–164 CrossRef CAS.
- G. P. Anipsitakis and D. D. Dionysiou, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, 38, 3705–3712 CrossRef CAS.
- K. B. Dhanalakshmi, S. Anandan, J. Madhavan and P. Maruthamuthu, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2008, 92, 457–463 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Zaleska, Recent Pat. Eng., 2008, 2, 157–164 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, Y. Wu, M. Xing, S. A. K. Leghari and S. Sajjad, Energy Environ. Sci., 2010, 3, 715–726 CAS.
- C. Ying, D. Hao and W. Lishi, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2008, 24, 675–689 Search PubMed.
- M. Fittipaldi, V. Gombac, A. Gasparotto, C. Deiana, G. Adami, D. Barreca, T. Montini, G. Martra, D. Gatteschi and P. Fornasiero, ChemPhysChem, 2011, 12, 2221–2224 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Chen, Z. Jiang, J. Geng, Q. Wang and D. Yang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2007, 46, 2741–2746 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, H. Xu, Y. Xu, H. Zhang and Y. Wang, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2005, 170, 279–285 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Balcerski, S. Y. Ryu and M. R. Hoffmann, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 15357–15362 CAS.
- T. Tachikawa, Y. Takai, S. Tojo, M. Fujitsuka, H. Irie, K. Hashimoto and T. Majima, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 13158–13165 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Meroni, S. Ardizzone, G. Cappelletti, C. Oliva, M. Ceotto, D. Poelman and H. Poelman, Catal. Today, 2011, 161, 169–174 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Emeline, X. Zhang, M. Jin, T. Murakami and A. Fujishima, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2009, 207, 13–19 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Wawrzyniak and A. W. Morawski, Appl. Catal., B, 2006, 62, 150–158 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Cong, J. Zhang, F. Chen and M. Anpo, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 6976–6982 CAS.
- A. R. Gandhe, S. P. Naik and J. B. Fernandes, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2005, 87, 103–109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. He and H. He, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 258, 972–976 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Wang, M. Wang, K. Xie, Q. Wu, L. Sun, Z. Lin and C. Lin, Nanotechnology, 2011, 22, 305607 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Peng, L. Cai, H. Yu, H. Wang and J. Yang, J. Solid State Chem., 2008, 181, 130–136 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Chen, Y. B. Lou, A. C. Samia, C. Burda and J. L. Gole, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2005, 15, 41–49 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Sobana and M. Swaminathan, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2007, 91, 727–734 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. J. Jang, C. Simer and T. Ohm, Mater. Res. Bull., 2006, 41, 67–77 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Asahi, T. Morikawa, T. Ohwaki, K. Aoki and Y. Taga, science, 2001, 293, 269–271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Di Valentin, E. Finazzi, G. Pacchioni, A. Selloni, S. Livraghi, M. C. Paganini and E. Giamello, Chem. Phys., 2007, 339, 44–56 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Irie, Y. Watanabe and K. Hashimoto, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107, 5483–5486 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Parida and B. Naik, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2009, 333, 269–276 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Selvaraj, S. Sivakumar, A. Ramasamy and V. Balasubramanian, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2013, 39, 2287–2302 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ihara, M. Miyoshi, Y. Iriyama, O. Matsumoto and S. Sugihara, Appl. Catal., B, 2003, 42, 403–409 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Serpone, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 24287–24293 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Songkhum and J. Tantirungrotechai, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2013, 39, 1555–1561 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Sun, L. Qiao, S. Sun and G. Wang, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 155, 312–319 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Neumann, P. Bogdanoff, H. Tributsch, S. Sakthivel and H. Kisch, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 16579–16586 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. U. Khan, M. Al-Shahry and W. B. Ingler, science, 2002, 297, 2243–2245 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sakthivel and H. Kisch, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 4908–4911 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Ren, Z. Aia, F. Jiaa, L. Zhanga, X. Fanb and Z. Zoub, Appl. Catal., B, 2007, 69, 138–144 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Velmurugan, B. Krishnakumar, B. Subash and M. Swaminathan, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2013, 108, 205–212 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Ranjit, I. Willner, S. Bossmann and A. Braun, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, 35, 1544–1549 CrossRef CAS.
- A.-W. Xu, Y. Gao and H.-Q. Liu, J. Catal., 2002, 207, 151–157 CrossRef CAS.
- D. W. Hwang, J. S. Lee, W. Li and S. H. Oh, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107, 4963–4970 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Matsuo, N. Sakaguchi, K. Yamada, T. Matsuo and H. Wakita, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2004, 228, 233–244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, H. Cheng, L. Zhang, Y. Hao, J. Ma, B. Xu and W. Li, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2000, 151, 205–216 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, Y. Xu and Y. Wang, J. Solid State Chem., 2004, 177, 3490–3498 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhang, M. Zhou and L. Lei, Carbon, 2005, 43, 1700–1708 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Xie, C. Yuan and X. Li, Colloids Surf., A, 2005, 252, 87–94 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Xie, C. Yuan and X. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2005, 117, 325–333 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Zhang, X. Li, G. Jia, Y. Gao, H. Wang, Z. Cao, C. Li and J. Liu, Catal. Commun., 2014, 45, 144–147 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Lan, L. Wang, B. Zhang, B. Tian and J. Zhang, Catal. Today, 2014, 224, 163–170 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Nasir, J. Zhang, F. Chen and B. Tian, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2013, 1–18 Search PubMed.
- M. Nasir, Z. Xi, M. Xing, J. Zhang, F. Chen, B. Tian and S. Bagwasi, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, 9520–9528 CAS.
- T. Yu, X. Tan, L. Zhao, Y. Yin, P. Chen and J. Wei, Chem. Eng. J., 2010, 157, 86–92 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Choi, A. Termin and M. R. Hoffmann, J. Phys. Chem., 1994, 98, 13669–13679 CrossRef.
- L. Andronic, A. Enesca, C. Vladuta and A. Duta, Chem. Eng. J., 2009, 152, 64–71 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. S. Li, G. E. Fryxell, M. H. Engelhard and C. Wang, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2007, 10, 639–641 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Chun, T. Yuchao and T. Hongxiao, Catal. Today, 2004, 90, 325–330 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Di Paola, P. Zaccagnino, G. Montedoro, T. Cocco and M. Lorusso, J. Bioenerg. Biomembr., 2004, 36, 165–170 CrossRef CAS.
- I. H. Tseng, J. C. S. Wu and H.-Y. Chou, J. Catal., 2004, 221, 432–440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhuge, X. Li, X. Gao, X. Gan and F. Zhou, Mater. Lett., 2009, 63, 652–654 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. A. Sagade and R. Sharma, Sens. Actuators, B, 2008, 133, 135–143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Andronic, L. Isac and A. Duta, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2011, 221, 30–37 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Huang, F. Peng, H. Yu and H. Wang, Solid State Sci., 2009, 11, 129–138 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Sayilkan, M. Asilturk, P. Tatar, N. Kiraz, E. Arpac and H. Sayilkan, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 144, 140–146 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. K. Seery, R. George, P. Floris and S. C. Pillai, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2007, 189, 258–263 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. V. Liga, E. L. Bryant, V. L. Colvin and Q. Li, Water Res., 2011, 45, 535–544 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Sun, Q. Li, S. Gao, L. Cao and J. K. Shang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 93, 3880–3885 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Wu, R. Xie, K. Imlay and J. K. Shang, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44, 6992–6997 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. L. Linsebigler, G. Lu and J. T. Yates Jr, Chem. Rev., 1995, 95, 735–758 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Behar and J. Rabani, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 8750–8755 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. You, F. Chen, J. Zhang and M. Anpo, Catal. Lett., 2005, 102, 247–250 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Gupta, A. Pal and C. Sahoo, Dyes Pigm., 2006, 69, 224–232 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Gunawan, W. Y. Teoh, C. P. Marquis, J. Lifia and R. Amal, Small, 2009, 5, 341–344 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. T. Hussain, Rashid, D. Anjum, A. Siddiqa and A. Badshah, Mater. Res. Bull., 2013, 48, 705–714 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sato, J. M. White and T. U. A. A. D. O. CHEMISTRY, Photodecomposition of Water Over Pt/TiO2 Catalysts, Defense Technical Information Center, 1980 Search PubMed.
- S. Sato and J. White, J. Phys. Chem., 1981, 85, 592–594 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Izumi, F.-R. F. Fan and A. J. Bard, J. Phys. Chem., 1981, 85, 218–223 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. John, A. Furgala and A. Sammells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1982, 129, 246–250 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Einaga, M. Harada, S. Futamura and T. Ibusuki, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107, 9290–9297 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Gai, J. Li, S.-S. Li, J.-B. Xia and S.-H. Wei, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 102, 036402 CrossRef.
- T. Ohno, Z. Miyamoto, K. Nishijima, H. Kanemitsu and F. Xueyuan, Appl. Catal., A, 2006, 302, 62–68 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Y. Xing, D. Y. Qi, J. L. Zhang and F. Chen, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 11432–11436 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Yang, H. Yang, B. Tian, J. Zhang and D. He, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2013, 39, 1685–1699 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Yan, Y. Cheng, S. Yuan, X. Yan, X. Hu and K. Oh, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2013, 39, 1673–1684 CrossRef CAS.
- U. G. Akpan and B. H. Hameed, Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 169, 91–99 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zhang, C. Chen, W. Ma and J. Zhao, Angew. Chem., 2008, 120, 9876–9879 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Zhang, R. Zong, J. Zhao and Y. Zhu, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2008, 42, 3803–3807 CrossRef CAS.
- H.-c. Liang and X.-z. Li, Appl. Catal., B, 2009, 86, 8–17 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Regazzoni, P. Mandelbaum, M. Matsuyoshi, S. Schiller, S. A. Bilmes and M. A. Blesa, Langmuir, 1998, 14, 868–874 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Moser, S. Punchihewa, P. P. Infelta and M. Graetzel, Langmuir, 1991, 7, 3012–3018 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Ikeda, C. Abe, T. Torimoto and B. Ohtani, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2003, 160, 61–67 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Zhang, W. Zou and J. Zhang, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2010, 1–14 Search PubMed.
- A. Di Paola, E. Garcia-Lopez, G. Marci and L. Palmisano, J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 211–212, 3–29 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. K. Mor, O. K. Varghese, M. Paulose, K. Shankar and C. A. Grimes, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2006, 90, 2011–2075 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-F. Zhuang, C.-J. Lin, Y.-K. Lai, L. Sun and J. Li, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2007, 41, 4735–4740 CrossRef CAS.
- L. K. Tan, M. K. Kumar, W. W. An and H. Gao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2010, 2, 498–503 CAS.
- J. Toledo Antonio, M. Cortes-Jacome, S. Orozco-Cerros, E. Montiel-Palacios, R. Suarez-Parra, C. Angeles-Chavez, J. Navarete and E. López-Salinas, Appl. Catal., B, 2010, 100, 47–54 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Xu, G. Vanamu, Z. Nie, H. Konishi, R. Yeredla, J. Phillips and Y. Wang, J. Nanomater., 2006, 2006, 23 Search PubMed.
- J. M. Macak, M. Zlamal, J. Krysa and P. Schmuki, Small, 2007, 3, 300–304 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Lai, L. Sun, Y. Chen, H. Zhuang, C. Lin and J. W. Chin, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2006, 153, D123–D127 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, R. Shi, J. Lin and Y. Zhu, Appl. Catal., B, 2010, 100, 179–183 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ishigami, J. Chen, W. Cullen, M. Fuhrer and E. Williams, Nano Lett., 2007, 7, 1643–1648 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang, X. Lv, Y. Li, Y. Wang and J. Li, ACS Nano, 2009, 4, 380–386 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Qiu, M. Xing and J. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 5852–5855 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Krishna, N. Noguchi, B. Koopman and B. Moudgil, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2006, 304, 166–171 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-C. Oh, A.-R. Jung and W.-B. Ko, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2007, 13, 1208–1214 CAS.
- S. Mu, Y. Long, S.-Z. Kang and J. Mu, Catal. Commun., 2010, 11, 741–744 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. G. Yang, G. Liu, S. Z. Qiao, C. H. Sun, Y. G. Jin, S. C. Smith, J. Zou, H. M. Cheng and G. Q. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 4078–4083 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. S. Chen, Y. L. Tan, C. M. Li, Y. L. Cheah, D. Luan, S. Madhavi, F. Y. C. Boey, L. A. Archer and X. W. Lou, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 6124–6130 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Liu, J. Yu and M. Jaroniec, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 11914–11916 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yu, B. Tian and J. Zhang, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 5499–5502 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. M. Arabatzis, S. Antonaraki, T. Stergiopoulos, A. Hiskia, E. Papaconstantinou, M. C. Bernard and P. Falaras, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2002, 149, 237–245 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kabra, R. Chaudhary and R. L. Sawhney, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2004, 43, 7683–7696 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Bao, X. Feng, Z. Yang, L. Shen and X. Lu, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, 38, 2729–2736 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Loddo, G. Marci, L. Palmisano and A. Sclafani, Mater. Chem. Phys., 1998, 53, 217–224 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. G. Adewuyi, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, 39, 8557–8570 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Masarwa, S. Rachmilovich-Calis, N. Meyerstein and D. Meyerstein, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2005, 249, 1937–1943 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Chamarro, A. Marco and S. Esplugas, Water Res., 2001, 35, 1047–1051 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Mounir, M.-N. Pons, O. Zahraa, A. Yaacoubi and A. Benhammou, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 148, 513–520 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Fukahori, H. Ichiura, T. Kitaoka and H. Tanaka, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, 37, 1048–1051 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Karches, M. Morstein, P. Rudolf von Rohr, R. L. Pozzo, J. L. Giombi and M. A. Baltanás, Catal. Today, 2002, 72, 267–279 CrossRef CAS.
- T.-H. Kim, C. Park and S. Kim, J. Cleaner Prod., 2005, 13, 779–786 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. A. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla, M. Shokri, H. Elham and A. Zeininezhad, J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng., 2008, 43, 460–467 CAS.
- Y. M. Xu, P. E. Ménassa and C. H. Langford, Chemosphere, 1988, 17, 1971–1976 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Y. Shan, T. I. M. Ghazi and S. A. Rashid, Appl. Catal., A, 2010, 389, 1–8 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-H. Huang, K.-P. Chang, H.-D. Ou, Y.-C. Chiang, E.-E. Chang and C.-F. Wang, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 186, 1174–1182 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-C. Wang, C.-K. Lee, M.-D. Lyu and L.-C. Juang, Dyes Pigm., 2008, 76, 817–824 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Nikazar, K. Gholivand and K. Mahanpoor, Desalination, 2008, 219, 293–300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhu, R. Jiang, L. Xiao, Y. Chang, Y. Guan, X. Li and G. Zeng, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 169, 933–940 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Rizzo, J. Koch, V. Belgiorno and M. A. Anderson, Desalination, 2007, 211, 1–9 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang and L. Yang, Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520, 5922–5927 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla, N. Daneshvar and M. Rabbani, Chem. Eng. J., 2007, 127, 167–176 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. W. Matthews, Water Res., 1991, 25, 1169–1176 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Carp, C. L. Huisman and A. Reller, Prog. Solid State Chem., 2004, 32, 33–177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. W. Matthews, J. Catal., 1988, 111, 264–272 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Kuwahara, T. Kamegawa, K. Mori and H. Yamashita, Chem. Commun., 2008, 2008, 4783–4785 RSC.
- N. O. Gopal, H.-H. Lo and S.-C. Ke, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 2760–2761 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Xing, D. Qi, J. Zhang, F. Chen, B. Tian, S. Bagwas and M. Anpo, J. Catal., 2012, 294, 37–46 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Xing, W. Fang, M. Nasir, Y. Ma, J. Zhang and M. Anpo, J. Catal., 2013, 297, 236–243 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Qi, M. Xing and J. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 7329–7336 CAS.
- G. A. Roberts, Chitin chemistry, Macmillan, 1992 Search PubMed.
- M. N. Ravi Kumar, React. Funct. Polym., 2000, 46, 1–27 CrossRef.
- I. Aranaz, M. Mengíbar, R. Harris, I. Paños, B. Miralles, N. Acosta, G. Galed and Á Heras, Curr. Chem. Biol., 2009, 3, 203–230 CAS.
- W. Ngah and S. Fatinathan, Chem. Eng. J., 2008, 143, 62–72 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Chauhan and N. Sankararamakrishnan, Bioresour. Technol., 2008, 99, 9021–9024 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A.-H. Chen, S.-C. Liu, C.-Y. Chen and C.-Y. Chen, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 154, 184–191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. E. Zubieta, P. V. Messina, C. Luengo, M. Dennehy, O. Pieroni and P. C. Schulz, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 152, 765–777 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zainal, L. K. Hui, M. Z. Hussein, A. H. Abdullah and I. R. Hamadneh, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 164, 138–145 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Jiang, H. Zhu, X. Li and L. Xiao, Chem. Eng. J., 2009, 152, 537–542 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, Y. Du, S. Ding, L. Fan, X. Shi, Q. Wang and G. Xiong, Phys. E, 2005, 30, 96–100 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Khan, A. Kaushik, P. R. Solanki, A. A. Ansari, M. K. Pandey and B. Malhotra, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2008, 616, 207–213 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-Y. Chen, P.-J. Zhou, J.-L. Li and Y. Wang, Carbohydr. Polym., 2008, 72, 128–132 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Serp, M. Corrias and P. Kalck, Appl. Catal., A, 2003, 253, 337–358 CrossRef CAS.
- M. M. Nassar and M. S. El-Geundi, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 1991, 50, 257–264 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, Carbon, 1998, 36, 159–175 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Li Puma, A. Bono, D. Krishnaiah and J. G. Collin, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 157, 209–219 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Tryba, Int. J. Photoenergy, 2008, 2008 Search PubMed.
- J. Matos, J. Laine and J.-M. Herrmann, J. Catal., 2001, 200, 10–20 CrossRef CAS.
- S. X. Liu, X. Y. Chen and X. Chen, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 143, 257–263 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Ao, J. Xu, S. Zhang and D. Fu, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2010, 256, 2754–2758 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Cordero, J.-M. Chovelon, C. Duchamp, C. Ferronato and J. Matos, Appl. Catal., B, 2007, 73, 227–235 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Raghavacharya, Chem. Eng. World, 1997, 32, 53–54 CAS.
- J. Araña, J. Dona-Rodrıguez, E. Tello Rendón, C. Garriga i Cabo, O. González-Dıaz, J. Herrera-Melián, J. Pérez-Peña, G. Colón and J. Navío, Appl. Catal., B, 2003, 44, 153–160 CrossRef.
- X. Zhang, M. Zhou and L. Lei, Carbon, 2006, 44, 325–333 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D.-K. Lee, S.-C. Kim, S.-J. Kim, I.-S. Chung and S.-W. Kim, Chem. Eng. J., 2004, 102, 93–98 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Ma, S. Wang, J. Gong, X. Yang and G. Xu, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2004, 222, 183–187 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Fernandez, G. Lassaletta, V. Jimenez, A. Justo, A. Gonzalez-Elipe, J.-M. Herrmann, H. Tahiri and Y. Ait-Ichou, Appl. Catal., B, 1995, 7, 49–63 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Yuan, D. Wu, H. He and Z. Lin, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2004, 227, 30–39 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Tian, H. Fu, L. Jing, B. Xin and K. Pan, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 3083–3089 CAS.
- J. Xu, Y. Ao, D. Fu and C. Yuan, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2008, 69, 2366–2370 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Sun, C. Bai, S. Zheng, X. Yang and R. L. Frost, Appl. Catal., A, 2013, 458, 103–110 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Eder, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 1348–1385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yu, J. C. Yu, J.-G. Yu, Y.-C. Kwok, Y.-K. Che, J.-C. Zhao, L. Ding, W.-K. Ge and P.-K. Wong, Appl. Catal., A, 2005, 289, 186–196 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wang, D. Yang, D. Chen, Y. Wang and Z. Jiang, J. Nanopart. Res., 2007, 9, 1087–1096 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Oh and M. Chen, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2008, 29, 159 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Yu, X. Quan, S. Chen, H. Zhao and Y. Zhang, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2008, 200, 301–306 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yao, G. Li, S. Ciston, R. M. Lueptow and K. A. Gray, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2008, 42, 4952–4957 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yu, J. C. Yu, C.-Y. Chan, Y.-K. Che, J.-C. Zhao, L. Ding, W.-K. Ge and P.-K. Wong, Appl. Catal., B, 2005, 61, 1–11 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Luo, J. Liu, X. Xia, X. Li, T. Fang, S. Li, Q. Ren, J. Li and Z. Jia, Mater. Lett., 2007, 61, 2467–2472 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Chowdhury, A. Paul and A. Chattopadhyay, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 4123–4128 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Cheng, L. An, F. Gao, G. Wang, X. Li and X. Chen, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2013, 39, 3969–3979 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |