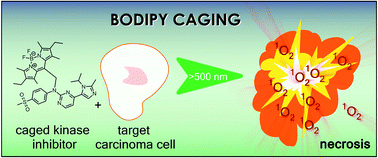
Recent studies report the boron-dipyrromethene (BODIPY) moiety to be interesting for caging applications in photopharmacology based on its response to irradiation with wavelengths in the biooptical window. Thus, in a model study, we investigated the meso-methyl-BODIPY caged CDK2 inhibitor AZD5438 and aimed to assess the usability of BODIPY as a photoremovable protecting group in photoresponsive kinase inhibitor applications. Photochemical analysis and biological characterisation in vitro revealed significant limitations of the BODIPY-caged inhibitor concept regarding solubility and uncaging in aqueous solution. Notably, we provide evidence for BODIPY-caged compounds generating singlet oxygen/radicals upon irradiation, followed by photodegradation of the caged compound system. Consequently, instead of caging, a non-specific induction of necrosis in cells suggests the potential usage of BODIPY derivatives for photodynamic approaches.