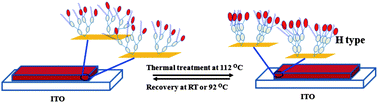
Nonlinear optical dendrons with alternating terminal groups of the stearyl group (C18) and chromophore were prepared through a convergent approach. These chromophore-containing dendrons were used as the intercalating agents for montmorillonite via an ion-exchange process. An orderly exfoliated morphology is obtained by mixing the dendritic structure intercalated layered silicates with a polyimide. As a result, optical nonlinearity, i.e. the Pockels effect was observed for these nanocomposites without resorting to the poling process. EO coefficients of 9–22 pm V−1 were achieved despite that relatively low NLO densities were present in the nanocomposites, particularly for the samples comprising the dendrons with alternating moieties. In addition, the hedging effects of the stearyl group on the self-alignment behavior, electro-optical (EO) coefficient and temporal stability of the dendron-intercalated montmorillonite/polyimide nanocomposites were also investigated.