Vladimir Yu. Torbeev and Stephen B. H. Kent
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2012,10, 5887-5891
DOI:
10.1039/C2OB25569C,
Paper
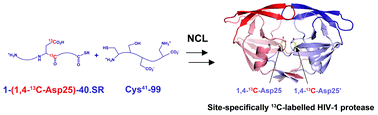
Total chemical synthesis was used to site-specifically 13C-label active site Asp25 and Asp25′ residues in HIV-1 protease and in several chemically synthesized analogues of the enzyme molecule.