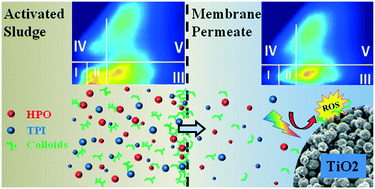
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) poses a serious challenge to applied photocatalysis. Membranes may offer a promising synergistic opportunity to enable efficient photocatalysis in the presence of DOM. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) effluent from a municipal treatment plant was studied to elucidate the effects of filtration and organic matter composition on photocatalysis. Effluent samples were collected from MBR units during routine operation and before/after chemical cleaning. Additional DOM samples from the bulk supernatant were separated into colloidal, hydrophobic and transphilic fractions, providing a novel examination of the inhibition potential of DOM. These DOM fractions and the effluent organic matter (EfOM) samples were then characterized utilizing three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix (3DEEM) fluorescence spectroscopy and assayed for their potential to inhibit TiO2-mediated photocatalytic degradation of a probe compound, para-chlorobenzoic acid (pCBA). The colloidal fraction of DOM was found to exert the strongest inhibition, followed by the transphilic, then the hydrophobic fractions; at 5 mgC L−1, these fractions reduced the photodegradation rates by approximately 75%, 27%, and 17%, respectively. Of the effluent samples, EfOM from the recently-cleaned membrane caused the greatest inhibition of photocatalysis (∼100% reduction at 0.5 to 2.0 mgC L−1), whereas the effluent from the fouled membrane provided the least inhibition (∼33% reduction at 2.0 mgC L−1). The 3DEEM analysis predicted inhibitory action of both DOM and EfOM, based on total fluorescence volumes. Results here demonstrate the prospective utility of combining membrane technologies with photocatalytic processes.