Themed collection Food as Soft Matter

Demulsification of Pickering emulsions: advances in understanding mechanisms to applications
Demulsification approaches in particle-stabilised oil-in-water emulsions where coalescence occurs by changing the wettability of the Pickering particles via employing additives/processing conditions or dissolving the particles/reducing their size.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 7344-7356
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00600C
Simple and complex coacervation in systems involving plant proteins
This review covers simple and complex coacervation in plant proteins: legume, oil seed, and cereal. We grouped the proteins by sources and properties and examined how processing affects phase behaviors.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 1966-1977
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM01275A
Structured soft particulate matters for delivery of bioactive compounds in foods and functioning in the colon
The colon structure, factors significant to gut health, the fate of diet digesta entering the colon, and the functions of delivery systems in the colon.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 277-293
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00866E
Mixed cyclo di-amino acids structured edible oils: a potential hardstock fat mimic
Cyclizing two amino acids (CDAs) via condensation produces molecular gelators in numerous solvents, while mixtures of four or more non-gelling CDAs solidify canola oil after heating and cooling with altered microstructures from individual CDAs.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 6871-6874
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00849E
Pore development in viscoelastic foods during drying
In this paper, we present a numerical model that can describe the pore formation/cavitation in viscoelastic food materials during drying.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 5183-5194
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00201F
Multiscale analysis of triglycerides using X-ray scattering: implementing a shape-dependent model for CNP characterization
In this article, a shape-dependent model for the interpretation of USAXS data is proposed. CNPs are modeled as polydisperse parallelepipeds, and the aggregates are characterized by fractal dimensionality.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 5071-5085
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00259H
Combining fracture mechanics and rheology to investigate the impact of micro-aeration on chocolate oral processing
This study presents a rigorous mechanical characterisation investigation on milk chocolate with varying porosities, at different temperatures and strain rate levels.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 5134-5152
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM00264D
A hybrid approach to oil structuring – combining wax oleogels and capillary suspensions
Combination of wax oleogelation and capillary suspension gels oil. With no water, dispersed particles prevent wax oleogel formation; water load is key. Capillary suspensions increase oleogel firmness; this depends on particle polarity.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 4329-4336
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM01619F
Thermoresponsive oil-continuous gels based on double-interpenetrating colloidal-particle networks
Gels of multicomponent building blocks offer promising opportunities for the development of novel soft materials with unique and useful structures and properties.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 3033-3043
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM01582C
Pinching dynamics, extensional rheology, and stringiness of saliva substitutes
Saliva's response to extensional flows determine bolus cohesion during swallowing, growth of spit bubbles, stringiness observed during drooling or licking, and the size of drops released by coughing, singing, sneezing, or speaking.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 2547-2561
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM01662E
Interfacial assembly and rheology of multi-responsive glycyrrhizic acid at liquid interfaces
Multi-responsive glycyrrhizic acid shows varying and intriguing adsorption behaviors, structural reassembly, and interfacial rheological responses at liquid interfaces.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 1173-1185
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00973D
Structural characterization of solvent-based food preparation of jellyfish
Jellyfish were soaked in aqueous mixed solvents (ethanol or acetone) and were found to undergo gel collapse below a critical solvent polarity. Strong gel collapse resulted in both microstructural re-arrangements and mechanical reinforcement.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 495-510
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00620D
Enhancing the textural and rheological properties of fermentation-induced pea protein emulsion gels with transglutaminase
The aim of this study was to assess how transglutaminase (TG) impacts the microstructure, texture, and rheological properties of fermentation-induced pea protein emulsion gels.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 133-143
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM01001E
Long term water trapping in Pickering emulsions undergoing compositional ripening
Water-in-oil emulsions are a potential way to achieve low-calorie foods. We investigate compositional ripening in two water-in-oil Pickering systems using confocal microscopy and particle tracking, revealing two contrasting end fates.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 9428-9434
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00856H
Rheology and dispensing of real and vegan mayo: the chickpea or egg problem
Real mayonnaise and vegan mayo display striking differences in dispensing behavior, manifested in the size and shape of drops, neck shape, and pinching dynamics often not revealed by the characterization and analysis of shear rheology.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 9413-9427
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00946G
Emulsifier adsorption kinetics influences drop deformation and breakup in turbulent emulsification
We combine drop breakup simulations with adsorption kinetics to gain insight into how emulsifier dynamics control turbulent drop breakup.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 9059-9073
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM01213A
Characterising the mechanical properties of soft solids through acoustics and rheology, exemplified by anhydrous milk fat
Changing rheological (G′, G′′, longitudinal viscosity) and acoustic (Sound velocity) properties of anhydrous milk fat as it cools from the melt to a soft solid.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 8349-8359
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM01097J
Rheological study of nanoemulsions with repulsive and attractive interdroplet interactions
As the potential well between droplets becomes deeper, nanoemulsions show higher 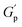 and σy. By superposition of rheological properties of nanoemulsions, a master curve is constructed for dynamic moduli at different volume fractions and interactions.
and σy. By superposition of rheological properties of nanoemulsions, a master curve is constructed for dynamic moduli at different volume fractions and interactions.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 8337-8348
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00932G
Water-resistance chitosan film through enzymatic treatment and layer-by-layer assembly with bacterial cellulose for food packaging materials
By interpreting bacterial cellulose (BC) through grafting chitosan with lauryl gallate (CT-LG), it exhibited exceptional hydrophobic properties while also employing a sustainable approach to chemical synthesis as a green packaging material.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 7696-7707
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00826F
Emulsifying properties of plant-derived polypeptide and their conjugates: a self-consistent-field calculation study of the impact of hydrolysis
By considering the hydrolysates of soy protein produced by trypsin as an example, the emulsion stabilizing properties of plant-based protein fragments, and their conjugates with polysaccharides, have been investigated theoretically.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 7443-7458
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00855J
Tea film formation in artificial tap water
On tea infusions, the formation of a transparent, shiny film which cracks upon disturbance can often be observed. The strength of this film depends on water hardness and tea variety.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 5967-5977
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00169E
Preparation and characterization of emulsion gels stabilized by adequately preprocessed insoluble soybean fiber from okara
Emulsion gels as soft materials were formulated by insoluble soybean fiber (ISF) assembled from okara in this study.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 4062-4072
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00189J
Non-linear properties and yielding of enzymatic milk gels
The enzymatic milk gel is a weak physical gel of casein micelles that displays strain-softening and strain-hardening before failure during stress sweep tests.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 3562-3569
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM01556K
About this collection
This collection, Guest Edited by Vivek Sharma (0000-0003-1152-1285) (University of Illinois Chicago), focuses both on understanding and analyzing food as soft matter, and on molecular gastronomy - the physicochemical basis for designing foods. Many food materials are rheologically-complex fluids that can be modeled as multicomponent colloidal dispersions, with a continuous liquid phase containing dispersed proteins, polysaccharides, drops, bubbles, particles, and self-assembled structures such as micelles. The lens of soft matter can be used to shed light on the science of cooking, food production, processing, and consumption by highlighting concepts from statistical thermodynamics, macromolecular and soft matter physics, interfacial science, fluid mechanics and rheology.
An understanding of current foods will also help us to develop a roadmap for sustainable, cost-effective, healthier, and tasteful alternatives, including meat and dairy alternatives with plant-based ingredients. To this end, the collection encompasses review and research articles relevant to understanding and analyzing food as soft matter.