Enzyme-mimicking redox-active vitamin B12 functionalized MWCNT catalyst for nearly 100% faradaic efficiency in electrochemical CO2 reduction†
Yashly
Yesudas K.
ab,
Mani
Balamurugan
 c,
Ki Tae
Nam
c,
Ki Tae
Nam
 c,
Buvaneswari
Gopal
c,
Buvaneswari
Gopal
 *b and
Annamalai
Senthil Kumar
*b and
Annamalai
Senthil Kumar
 *ab
*ab
aCarbon Dioxide Research and Green Technology Centre, Vellore Institute of Technology University, Vellore 632 014, India. E-mail: askumar@vit.ac.in; askumarchem@yahoo.com
bDepartment of Chemistry, School of Advanced Sciences, Vellore Institute of Technology University, Vellore 632 014, India. E-mail: gbhuvaneswari@vit.ac.in
cDepartment of Materials Science and Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea
First published on 9th September 2024
Abstract
Due to the detrimental effects of CO2 on the atmosphere, including climate change, the development of environmentally friendly electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction is crucial for mitigation. Inspired by carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH) enzymes, where an active centre is surrounded by a protein scaffold, this work introduces a biomimetic system featuring a vitamin B12 cluster protected by a matrix of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). Unlike literature-based vitamin B12 systems with no redox activity, we have developed multi-walled nanotubes (MWCNTs) functionalized with vitamin B12 (MWCNT@B12) as a highly redox-active system and explored it for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction at room temperature in an aqueous medium. The presence of vitamin B12 in the matrix was confirmed through a series of characterizations by employing FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, FESEM, EDAX, ultrapressure liquid chromatography (UPLC), scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) and cyclic voltammetry. This new electrocatalyst demonstrates high faradaic efficiency (∼100%), low overpotential (ηCO2 = 242 mV), and a significant current density (43.5 mA cm−2) for the electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 to CO in a 0.5 M NaHCO3 solution. In situ SECM reveals that clusters of vitamin B12 embedded on the modified electrode are the active sites for the overall electrocatalytic reaction. Compared to previously reported heterogeneous molecular catalyst electrodes, this system exhibits a lower peak-reduction potential of 100–600 mV and current densities 2–40 times higher for the CO2 reduction reaction. Furthermore, vitamin B12 is a naturally occurring, non-toxic redox mediator. Therefore, the B12-modified electrode presented herein is a promising development for future green CO2 reduction applications.
1. Introduction
Global emissions of CO2 have been steadily increasing, reaching a value of 424.55 ppm in 2024, which marks a high record of 37.5 gigatons of CO2 emissions for the year.1–3 This surge in CO2 levels has not been observed in the past 2 million years. In response to this concerning trend, various countries have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, as evidenced by initiatives such as the EU Green Deal and the UK's 2019 pledge to reach net-zero.4,5 Consequently, there is an urgent need to decarbonize the global economy by adopting green, sustainable, and environmentally friendly technologies across all sectors. In this connection, various processes for CO2 capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies have been explored,6,7 including thermochemical,8 photochemical,9–11 biochemical,12,13 and electrochemical14–16 methods. Among these methods, electrochemical methods stand out as particularly promising due to their efficiency, environmental friendliness and extension to real-time fuel-cell applications, which makes them a superior choice for CO2 conversion into value-added products, such as CO, hydrocarbons, and alcohols.17–19 The development of a highly functional and green electrocatalyst mimicking the natural enzymes for 100% efficiency, selectivity, utilization of low concentration and low overpotential (ηCO2)-based facile operation is the ultimate aim for the success of future electrochemical CO2 reduction-based carbon net-zero technologies.20–22 In this context, various metals (Cu, Zn, Ni, Pd, and Sn),23–26 metal oxide,27,28 nanoparticles,29,30 single-atoms31,32 and metal complexes33–35 based on porphyrin, phthalocyanines, and bipyridine have been explored for the electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction. Any one or more obstacles such as high ηCO2 (400–1000 mV with respect to the carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH) enzyme, ECO2-to-CO = −0.1 V vs. RHE),36,37 poor faradaic efficiency, non-selective (multiple products: CH4, CO, C2H4, C2H5OH, and CH3OH) and serious parallel reactions such as hydrogen gas evolution reaction are common with the electrocatalysts. For instance, dual-atom Ag2/graphene,38 Pd2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 39 and Fe–Cu40 catalysts were reported for the effective CO2-to-CO conversion with 93–99% faradaic efficiency (FE) at −0.7–1.0 V vs. RHE (7–13 mA cm−2) but with 400 mV overpotential value. To overcome the overpotential problem, molecular system-anchored heterogeneous catalysts were developed.33–35 Overpotential values of ∼300–800 mV are common in the reported systems (Table 1).41–50 This is true for recent reports, with few electrocatalysts having nearly 100% faradaic efficiency.51–55 Further, most electrocatalysts reported in the literature are synthetic chemicals, and their associated carbon footprint is a serious concern. In 2020, our group first reported as a preliminary communication for vitamin B12 (B12; cyanocobalamin) anchored graphene oxide (GO) for the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 with FE = 93% (29.4 mA cm−2 at −0.8 V vs. RHE in 0.5 M KHCO3).50 The advantage of using B12 as a catalyst is its two key properties: it is environmentally friendly and naturally occurs in animal-derived sources, such as fish, meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy products.56,57 There are two more reports available in the literature utilizing the B12 as an electrocatalyst with achievement in the FE% 94 and 99.3% (use of ionic liquid and preconcentrating membrane on the interface). Unfortunately, there was no redox activity of the active site, particularly B12-CoII/I and B12-CoIII/II, which are expected to occur at Eo′ of −0.74 V and −0.18 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.11 V and 0.45 V vs. RHE).47,50 In addition, the ηCO2 observed with the reports is 300–600 mV. The absence of any redox response noted in the above reports is the likely reason for the high overpotential observed. In this work, we report a highly redox-active B12-anchored multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) composite, designated as MWCNT@B12 (surface excess: ΓB12 = 24.7 nmol cm−2). This MWCNT@B12 composite was prepared by applying an innovative electrochemical method. The MWCNT@B12 mimics natural CODH's function, achieves a green electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 with near 100% faradaic efficiency and minimum overpotential (ηCO2 = 242 mV) and exhibits near zero activity overpotential.
39 and Fe–Cu40 catalysts were reported for the effective CO2-to-CO conversion with 93–99% faradaic efficiency (FE) at −0.7–1.0 V vs. RHE (7–13 mA cm−2) but with 400 mV overpotential value. To overcome the overpotential problem, molecular system-anchored heterogeneous catalysts were developed.33–35 Overpotential values of ∼300–800 mV are common in the reported systems (Table 1).41–50 This is true for recent reports, with few electrocatalysts having nearly 100% faradaic efficiency.51–55 Further, most electrocatalysts reported in the literature are synthetic chemicals, and their associated carbon footprint is a serious concern. In 2020, our group first reported as a preliminary communication for vitamin B12 (B12; cyanocobalamin) anchored graphene oxide (GO) for the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 with FE = 93% (29.4 mA cm−2 at −0.8 V vs. RHE in 0.5 M KHCO3).50 The advantage of using B12 as a catalyst is its two key properties: it is environmentally friendly and naturally occurs in animal-derived sources, such as fish, meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy products.56,57 There are two more reports available in the literature utilizing the B12 as an electrocatalyst with achievement in the FE% 94 and 99.3% (use of ionic liquid and preconcentrating membrane on the interface). Unfortunately, there was no redox activity of the active site, particularly B12-CoII/I and B12-CoIII/II, which are expected to occur at Eo′ of −0.74 V and −0.18 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.11 V and 0.45 V vs. RHE).47,50 In addition, the ηCO2 observed with the reports is 300–600 mV. The absence of any redox response noted in the above reports is the likely reason for the high overpotential observed. In this work, we report a highly redox-active B12-anchored multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) composite, designated as MWCNT@B12 (surface excess: ΓB12 = 24.7 nmol cm−2). This MWCNT@B12 composite was prepared by applying an innovative electrochemical method. The MWCNT@B12 mimics natural CODH's function, achieves a green electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 with near 100% faradaic efficiency and minimum overpotential (ηCO2 = 242 mV) and exhibits near zero activity overpotential.
| Electrocatalyst | Electrolyte | E onset (ηCO2) (mV vs. RHE) | FE/CO (%) | j (mA cm−2) | Redox peak | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Solution phase studies; TTC – COF prepared by tetraphenyl-p-phenylenediamine and 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-formylphenyl)-metalloporphyrin combined with cobalt metal center; VCB – Vulcan carbon black; Nf –Nafion; CC – carbon cloth; MCoPc – modified cobalt phthalocyanine; FePc-GNC – iron phthalocyanine – graphene nanocomposite; CMOF – cobalt based metallocene implanted metalloporphyrin organic framework; GCE – glassy carbon electrode; FePGF-Fe(III) tetraphenyltrimethylammonium porphyrin/graphene frame work; CoPcPy – cobalt phthalocyanine (pyridine) complex; GE – graphite electrode; FePor – iron porphyrin; MWCNT – multi-walled carbon nanotube; GDE – gas diffusion electrode; GO – graphene oxide; PBS – 0.1 M phosphate buffer; CODH – carbon monoxide dehydrogenase; GCDE – glassy carbon disk electrode. | |||||||
| 1. | FePGF/GCP | KCl | −900 (800) | 98.7 | 1.68 | No | 41 |
| 2. | FePor/MWCNT/GCE | NaHCO3 | −890 (790) | 80.0 | — | No | 42 |
| 3. | MCoPc + Nf/CP | KHCO3 | −800 (700) | 98.4 | 22.4 | No | 43 |
| 4. | B12 + rGO/GCE | KHCO3 | −650 (550) | 94.0 | 6.24 | No | 44 |
| 5. | TTC + VCB + Nf/CC | KHCO3 | −590 (490) | 92.0 | −29.2 | No | 45 |
| 6. | NiP + CNT/GDE | KHCO3 | −550 (450) | 98.0 | 353 | No | 46 |
| 7. | B12 + MWCNT/GCE | KHCO3 | −450 (350) | 95.9 | 40.85 | No | 47 |
| 8. | CoPcPy/GE | NaH2PO4 | −445 (345) | 90.0 | 2.00 | Yes | 48 |
| 9. | FePc-GNC + Nf/CP | KHCO3 | −400 (300) | 92.0 | 1.70 | No | 49 |
| 10. | B12@GO/CP | KHCO3 | −389 (289) | 93.0 | 29.4 | No | 50 |
| 11. | CODH + GCDE (enzymatic system)a | PBS | −100 (0) | 100 | — | No | 37 |
| 12 | B12@MWCNT/CP | NaHCO3 | −342 (242) | 99.4 | 43.5 | Yes | This work |
The CODH is a specific enzyme that catalyzes the reversible conversion of CO2-to-CO through a proton-coupled electron transfer pathway.36,37 In general, the enzyme contains an active prosthetic group bound to the protein scaffold.58 For instance, CODH enzymes have two main types: aerobic CODH with a Cu–Mo prosthetic group and anaerobic CODH with a Ni–Fe-based flavoenzyme prosthetic group.59,60 The surrounding protein structure facilitates CO2 binding, and the prosthetic group catalyses the selective reduction reaction. Similar to the structural interactions found in CODH, B12-stabilized MWCNT analogues exhibit covalent, π–π, electrostatic, and multihydrogen bondings. The electroactivity and structure of this biomimicking system were analyzed using in situ scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM).61,62 This newly developed green and biomimicking electrocatalyst shows promising potential for next-generation CO2 reduction applications.
2. Experimental section
2.1. Chemicals and reagents
Vitamin B12 (≥98% purity) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (USA) and NaHCO3 from CDH Chemical, India. The stock solution of graphene oxide–ethanol dispersion (GO) (5 mg mL−1, approximately 80% carbon basis, with flake size in the range of 0.5–2.0 μm and thickness in the range of 0.6–1.2 nm, purity of 99%) and pristine multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs, approximately 90% purity on a carbon basis, with dimensions of 7–15 nm × 0.5–10 μm) were procured from SRL, India. Additionally, oxygen-functionalized MWCNT (FWCNT), carbon nanofiber (CNF) and graphite nanopowder (GNP, 400 nm, approximately 98% purity) were acquired from the same source. Carbon paper (CP) (Toray Sheets TGP H60) was purchased from Alfa Aesar. Acetonitrile (HPLC Grade) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, and formic acid (LC-MS grade) was obtained from Merck, Germany. All other chemicals used are ACS-certified reagent grade and used without further purification. Electrolyte solutions were prepared using double distilled (DD) water.2.2. Instrumentation
Electrochemical experiments were conducted using a three-electrode system comprising a glassy carbon electrode (GCE; surface area 0.0707 cm2) and carbon paper (CP; surface area 0.25 cm2) as the working electrodes, a platinum wire as the counter electrode, and a saturated KCl Ag/AgCl electrode as the reference electrode. Initial electrochemical measurements were performed using the CHI Model 660C electrochemical workstation. For the SECM analysis, a Versascan Potentiostat instrument with a Pt probe system provided by Princeton Applied Research (PAR), was utilized. A 10 μm Pt-tip ultramicroelectrode (UME) was used in conjunction with a glassy carbon electrode (GCE, 0.0707 cm2) chemically modified with MWCNT@B12. The Waters Acquity UPLC System, equipped with an Acquity UPLC BEH C8 1.7 μm column (2.1 × 150 mm) was used for the ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) analysis of B12. For bulk electrolysis and subsequent product analysis, the CHI Model 660D system was employed, which was integrated with a PerkinElmer gas chromatograph (NARL8502 model 4003) equipped with a thermal conductivity detector (TCD). To separate the gas products generated from the electrochemical reduction of CO2, a Hayesep N column and a Molesieve 13X column were utilized. The TCD detected hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen gases. Post bulk electrolysis, a 0.1 mL gas sample was extracted from the headspace of the electrochemical cell and injected into the gas chromatograph. The chromatographic peak areas were calibrated using a standard gas mixture containing 0.1 mol% of each target gas species, enabling the quantification of product moles. Furthermore, the faradaic efficiency (FE) of the products was calculated using the following equation:50 | (1) |
2.3. Electrocatalyst fabrication
First, 4 mg of MWCNT was added to 1 mL ethanol and sonicated for 15 ± 1 min (stock). The homogenous carbon dispersion was suitably drop-casted on the GCE or CP surface and allowed to air dry for ∼2 min. The modified electrode (designated as GCE/MWCNT) was then transferred into a 4 mM solution of B12 in 0.5 M NaHCO3 solution (N2 = purged) and potential cycled at the scan rate of 50 mV s−1 in a potential window ranging from 0.0 to −1.6 V vs. Ag/AgCl (0.67 to −0.92 V vs. RHE) for 60 segments. The as-prepared electrode was designated as GCE/MWCNT@B12 or CP/MWCNT@B12. For the case of CP/MWCNT@B12, 80 μL of the MWCNT dispersion (stock) was drop-casted onto the carbon paper (0.5 × 0.5 cm) and dried with a heat gun, resulting in a MWCNT loading of 0.1 mg![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cm−2. 2% Nafion was added as a binder to obtain homogenous carbon dispersion for preparing stable CME and minimizing surface fouling problems.
cm−2. 2% Nafion was added as a binder to obtain homogenous carbon dispersion for preparing stable CME and minimizing surface fouling problems.
2.4. UPLC analysis of vitamin B12
UPLC analysis was performed using a gradient elution method. The mobile phase consisted of 0.025% formic acid in water (mobile phase A) and acetonitrile (mobile phase B). Detection was conducted using a photodiode array (PDA) detector set at a wavelength of 361 nm, with a sample injection volume of 10 μL and a constant flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1. A 25 ng mL−1 B12 standard solution was used as a reference. Subsequently, the extract from the chemically modified electrode was analyzed. The electrode, optimized as GCE/MWCNT@B12, was immersed in 1 mL of distilled water and sonicated for approximately 5 minutes to release the electro-adsorbed B12 into the solution. This extraction process was repeated twice to ensure the sufficient detectability of B12 in the final extract. The extract was then filtered through a 0.22 μm syringe filter to remove any solid particles before injection.3. Results and discussion
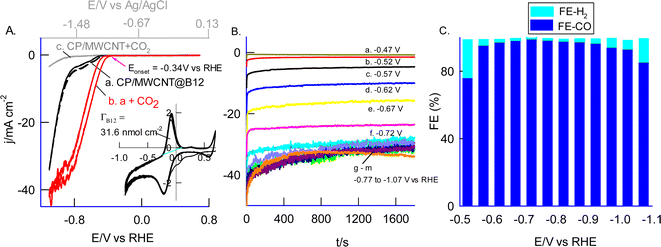
Initial experiments investigated immobilizing high-redox-active B12 onto various graphitic materials (GNP, CNF, GO, FWCNT, and MWCNTs) for enhanced stability and activity (see ESI Fig. S3†). An MWCNT-modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE/MWCNT) achieved optimal immobilization. The electrode was prepared by exposing GCE/MWCNT to 4 mM B12 in 0.5 M NaHCO3, followed by 30 continuous potential cycles between −1.6 V and 0 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.92 and 0.67 V vs. RHE) using cyclic voltammetry. The resulting GCE/MWCNT@B12 electrode exhibited a stable redox response, arising from B12-CoII/I redox couple (Scheme 1) characterized by a standard electrode potential (E°) of −820 ± 5 mV vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.14 V vs. RHE).44,47 This value was calculated using the formula E° = (Epa + Epc)/2, where Epa and Epc are the anodic and cathodic peak potentials measured as −717 mV and −923 mV vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.04 V and −0.24 V vs. RHE) in a N2-purged 0.5 M NaHCO3 solution (pH 8.1), respectively. It exhibited a peak-to-peak separation (ΔEp = Epa − Epc) of 206 ± 5 mV (at 50 mV s−1) and a high surface excess of B12 (ΓB12 = 24.7 nmol cm−2) (Fig. 1A, curve b). The surface excess value was calculated utilizing the following formula: ΓB12 = Q/nFA, where Q represents the charge associated with the redox peak of the modified electrode surface (1.68 × 10−4 C), n denotes the number of electrons involved in the process (1), F is the faradaic constant (96![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 485 C mol−1), and A signifies the surface area of the electrode (0.0707 cm−2). This ΓB12 value is significantly higher than those reported in the existing literature (4.28 nmol cm−2).50 A control experiment employing MWCNT in the absence of B12 yielded no discernible redox peak, thereby furnishing direct electrochemical evidence for the successful immobilization of B12 on MWCNT (Fig. 1A, curve a). It is also noteworthy that the stable immobilization of B12 is not achievable in the absence of MWCNT, as demonstrated by the poor and unstable redox response (Fig. 1A, curve c) associated with B12. This observation underscores the necessity of combining B12 with MWCNT to create an optimal and highly active catalytic site characterized by efficient electron transfer properties. The effect of the CV scan rate of the GCE/MWCNT@B12 showed a systematic increase in both anodic (ipa) and cathodic (ipc) peak currents with increasing scan rate (Fig. 1B). The linear relationship between ipa and ipcversus scan rate suggests surface-confined electron transfer behavior (inset Fig. 1B). Kinetic parameters, electron transfer coefficient (α) and heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (ks) are calculated using the following Laviron equation:63
485 C mol−1), and A signifies the surface area of the electrode (0.0707 cm−2). This ΓB12 value is significantly higher than those reported in the existing literature (4.28 nmol cm−2).50 A control experiment employing MWCNT in the absence of B12 yielded no discernible redox peak, thereby furnishing direct electrochemical evidence for the successful immobilization of B12 on MWCNT (Fig. 1A, curve a). It is also noteworthy that the stable immobilization of B12 is not achievable in the absence of MWCNT, as demonstrated by the poor and unstable redox response (Fig. 1A, curve c) associated with B12. This observation underscores the necessity of combining B12 with MWCNT to create an optimal and highly active catalytic site characterized by efficient electron transfer properties. The effect of the CV scan rate of the GCE/MWCNT@B12 showed a systematic increase in both anodic (ipa) and cathodic (ipc) peak currents with increasing scan rate (Fig. 1B). The linear relationship between ipa and ipcversus scan rate suggests surface-confined electron transfer behavior (inset Fig. 1B). Kinetic parameters, electron transfer coefficient (α) and heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (ks) are calculated using the following Laviron equation:63| Slpa/Slpc = α/1 − α, | (2) |
log(ks) = α![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) log(1 − α) + (1 − α)log log(1 − α) + (1 − α)log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) α − log[(RT/{nF(V)})] − α(1 − α)nFΔEp/2.3RT, α − log[(RT/{nF(V)})] − α(1 − α)nFΔEp/2.3RT, | (3) |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) v (Fig. 1C), respectively; n = total number of electron transfer (n = 1) and other symbols have their significant. Other symbols have their specific meanings (where R = universal gas constant, T = absolute temperature, and F = Faraday constant). The calculated α is 0.52 and ks is 0.13 s−1. These values are comparable to those reported for a hydroquinone-based redox molecule immobilized on a carbon surface (α = 0.54, ks = 0.24 s−1).61 B12 likely interacts with MWCNTs through multiple mechanisms on the edge and basal planes of the MWCNT.62 These include π–π stacking, where the aromatic electrons of B12 interact with the sp2 carbons of MWCNTs (Scheme 1), and hydrogen bonding between the carbon-oxygen functional groups of MWCNTs and the various hydrogenated functional groups of B12, which helps to stabilize B12 on MWCNT.
v (Fig. 1C), respectively; n = total number of electron transfer (n = 1) and other symbols have their significant. Other symbols have their specific meanings (where R = universal gas constant, T = absolute temperature, and F = Faraday constant). The calculated α is 0.52 and ks is 0.13 s−1. These values are comparable to those reported for a hydroquinone-based redox molecule immobilized on a carbon surface (α = 0.54, ks = 0.24 s−1).61 B12 likely interacts with MWCNTs through multiple mechanisms on the edge and basal planes of the MWCNT.62 These include π–π stacking, where the aromatic electrons of B12 interact with the sp2 carbons of MWCNTs (Scheme 1), and hydrogen bonding between the carbon-oxygen functional groups of MWCNTs and the various hydrogenated functional groups of B12, which helps to stabilize B12 on MWCNT.
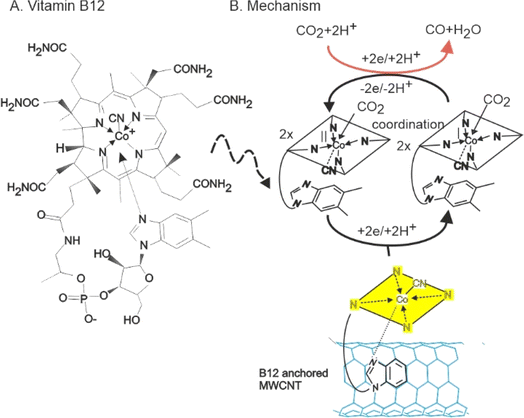 | ||
| Scheme 1 (A) Structure of vitamin B12 and (B) Illustration of vitamin B12-anchored MWCNT, redox property and its mediated CO2 reduction reaction. | ||
To further understand the interaction, MWCNT@B12 was prepared on a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPE) and characterized by Raman and FTIR spectroscopy (Fig. 1D and E). Raman spectra showed characteristic peaks corresponding to disordered (D-band, sp3 sites) and ordered (G-band, sp2 sites) graphitic structures (Fig. 1D).64 The intensity ratio of the bands (ID/IG) increased from 0.57 for MWCNTs to 0.69 for MWCNT@B12, suggesting a higher concentration of defects or functional groups introduced onto the MWCNT surface due to B12 immobilization. FTIR analysis revealed specific peaks at 3353 cm−1 (indicating alkene/alkyne groups), 3013 cm−1 (aromatic C–H stretching vibrations), and 1653 cm−1 (potentially amide-I C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching) in MWCNT@B12 compared to control samples (Fig. 1E). These peaks, with slightly shifted frequencies, support vitamin B12 immobilization on MWCNTs. Fig. 2A and B show FESEM images of needle-like MWCNTs embedded with clusters of B12. This structure resembles the active site-stabilized protein structure of enzymatic systems,36,37 potentially influencing biocatalytic activity. Next, EDAX analysis and elemental mapping were conducted, showing significant differences in the composition of MWCNT and MWCNT@B12. The pristine MWCNT displayed approximately 100% carbon content, indicating a pure carbon nanotube structure with a uniform carbon distribution. In contrast, MWCNT@B12 exhibited a distinct elemental profile, including nitrogen, oxygen, and 0.6% cobalt, confirming the successful immobilization of B12 on the MWCNT surface. Elemental mapping showed a uniform distribution of these elements, indicating homogeneous B12 immobilization (see ESI Fig. S1†).
O stretching) in MWCNT@B12 compared to control samples (Fig. 1E). These peaks, with slightly shifted frequencies, support vitamin B12 immobilization on MWCNTs. Fig. 2A and B show FESEM images of needle-like MWCNTs embedded with clusters of B12. This structure resembles the active site-stabilized protein structure of enzymatic systems,36,37 potentially influencing biocatalytic activity. Next, EDAX analysis and elemental mapping were conducted, showing significant differences in the composition of MWCNT and MWCNT@B12. The pristine MWCNT displayed approximately 100% carbon content, indicating a pure carbon nanotube structure with a uniform carbon distribution. In contrast, MWCNT@B12 exhibited a distinct elemental profile, including nitrogen, oxygen, and 0.6% cobalt, confirming the successful immobilization of B12 on the MWCNT surface. Elemental mapping showed a uniform distribution of these elements, indicating homogeneous B12 immobilization (see ESI Fig. S1†).
To confirm the presence of B12, the MWCNT@B12 electrode was analyzed using UPLC. The modified electrode was disassembled through ultrasonication in an aqueous solution, and the resulting extract was analyzed using UPLC, a gold standard technique. For comparison, a control B12 sample was also analyzed (Fig. 1F, curve a). In the UPLC analysis, a specific signal was observed at a retention time (RT) of 6.1 minutes with the extract from the MWCNT@B12 electrode (Fig. 1F, curve b). This RT value matches the RT value of 6.1 minutes for the control B12 sample (Fig. 1F, curve a). Quantitative analysis of the UPLC chromatogram revealed a total B12 concentration of 4.9 ng mL−1 (3.61 nmol) on the surface of the modified electrode. Additionally, both the extract and standard B12 were subjected to UV-vis spectroscopic analysis, showing a characteristic peak at λmax = 360 nm for B12 with no other interference (Fig. S2†).65 This confirms the successful entrapment of B12 on the modified electrode. Furthermore, based on the CV redox peak surface excess analysis (ΓB12 = 24.7 nmol cm−2), the calculated B12 concentration is 1.74 nmol. This indicates that only 48% of the immobilized B12 on the surface is electroactive. Further experiments using SECM support this observation.
Following our initial experiments on immobilizing high-redox-active B12 onto various graphitic materials, we extended our investigation to electrochemical CO2 reduction studies using these different carbon matrix-immobilized B12 systems (Fig. S4†). In these studies, GCE/MWCNT@B12 consistently yielded the highest CO2 reduction current values, indicating its superior performance with the highest CO2 reduction current value of ∼300 μA observed at −1.4 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.78 V vs. RHE) (Fig. S5A†). The ability to load higher active sites of B12 on the surface is the plausible reason for the superior electrocatalytic activity. Fig. 3A shows the CV response of carbon paper modified with MWCNT@B12 (i.e., CP/MWCNT@B12) in N2 (curve a) and CO2-saturated (curve b) 0.5 M NaHCO3 (pH 7.2) at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1. To enhance both stability and current sensitivity, a 2% Nafion solution (optimal) was drop-casted onto the modified electrode surface prior to the experiment. Nafion, an ionic polymer, creates additional conductive channels within the molecular electrode, thereby improving its sensitivity and stability. A well-defined cathodic (reduction) current peak is observed, starting at Eonset = −1.01 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.347 V vs. RHE) and reaching a maximum current density (jpc) of 43.5 mA cm−2 at Epc = −1.6 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.977 V vs. RHE). The control experiment with bare CP/MWCNT showed a nearly 40-fold decrease in peak current and a shift of about 600 mV in the reduction potential (Fig. 3A, curve c). This observation highlights the efficient electrocatalytic activity of the B12-modified electrode. The CO2 reduction potential observed in this work is ∼100 to 600 mV lower than the values reported for various molecular electrocatalysts, as shown in Table 1.41–50 Interestingly, this reduction potential is closer to the value observed for the CO dehydrogenase (CODH) enzyme, which is around −0.1 V vs. RHE.
The mechanism and electron transfer pathway for CO2 reduction on MWCNT@B12-modified GCE (without Nafion layer) were investigated by studying the effect of scan rate. A linear increase in the ipc with an increasing scan rate was observed (Fig. S5†). A plot of ipcvs. the square root of the scan rate (v1/2) was linear, indicating a diffusion-controlled electron transfer process for CO2 reduction. Furthermore, a plot of Epcvs. log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) v exhibited a linear relationship with a slope of 96.6 mV dec−1 (Fig. S5C†). Based on the equation Epc = K + (bc/2) log
v exhibited a linear relationship with a slope of 96.6 mV dec−1 (Fig. S5C†). Based on the equation Epc = K + (bc/2) log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) v, where K is a constant related to the universal gas constant (R), temperature (T), Faraday constant (F), and the diffusion coefficient of CO2 (DCO2); and bc is the Tafel slope (the calculated bc value is 185 mV dec−1).63 The Tafel slopes for the CO2 reduction reaction were obtained using two methods: potentiation polarization using CP/MWCNT@B12 (157 mV dec−1) and slow can rate CV (159 mV dec−1) experiments (Fig. S6†). This value is comparable to that for Co-porphyrin-modified CNT (∼120 mV dec−1)66 and significantly lower than that of cobalt meso-tetraphenyl porphyrin-modified CNT (∼258 mV dec−1)67 and perfluorinated cobalt phthalocyanine loaded carbon cloth-based electrocatalysts (∼277 mV dec−1).68
v, where K is a constant related to the universal gas constant (R), temperature (T), Faraday constant (F), and the diffusion coefficient of CO2 (DCO2); and bc is the Tafel slope (the calculated bc value is 185 mV dec−1).63 The Tafel slopes for the CO2 reduction reaction were obtained using two methods: potentiation polarization using CP/MWCNT@B12 (157 mV dec−1) and slow can rate CV (159 mV dec−1) experiments (Fig. S6†). This value is comparable to that for Co-porphyrin-modified CNT (∼120 mV dec−1)66 and significantly lower than that of cobalt meso-tetraphenyl porphyrin-modified CNT (∼258 mV dec−1)67 and perfluorinated cobalt phthalocyanine loaded carbon cloth-based electrocatalysts (∼277 mV dec−1).68
A plausible mechanism for the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 is proposed based on the active site associated with the dynamics and orientation of B12 on the MWCNT matrix. There are three possible immobilization methods, (i) physisorption, (ii) chemisorption, and (iii) cluster formation, via π–π interaction and hydrogen bonding. In physisorption and chemisorption, B12 molecules likely form a few monolayer thicknesses on the underlying graphitic surface (Spot 2). However, in cluster formation, a group of B12 molecules trapped on the porous sites of the CNT could facilitate a cooperative electrochemical reaction (Spot 3). There may be a chance of adsorption of B12 on the underlying GCE substrate (Spot 1). We investigated the plausible surface-active site involved in the electrochemical reaction using in situ SECM with dissolved oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) by the B12 site as a probe under substrate generation and tip-collection (SG-TC) mode.69 Prior to the experiments, the ORR conditions were optimized (see ESI Fig. S7†). Fig. 2C depicts a typical SG-TC SECM operation, where the substrate electrode (GCE/MWCNT@B12) is held at a potential of −1.0 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.32 V vs. RHE) for O2 to H2O2 conversion, while the SECM tip is set at +0.65 V vs. Ag/AgCl for H2O2 to H2O conversion. Fig. 2D and E are comparative SECM images of the MWCNT@B12 and MWCNT, respectively, showing a specific cluster-like image for the B12-modified system similar to the morphology noticed in the SEM analysis. The highest probe current signals (412 nA) are observed at these cluster-like sites, suggesting that B12-clustered CNTs are the active electrocatalytic sites for CO2 reduction (Spot 3). This finding supports the 48% of the active site of B12 on the electrode surface identified by applying a combined UPLC and CV approach.
The electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 was performed under various potentiostatic polarization conditions in a window ranging from −1.2 V to −1.7 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.57 V to 1.07 V vs. RHE) using CP/MWNCNT@B12 electrocatalyst. The resulting products were analyzed using gas chromatography equipped with a thermal conductivity detector. Fig. 3B and C show typical polarization and GC results, respectively. In the low and high potential regions, hydrogen gas evolution (H2 evolution) was observed, reaching up to 25%. However, at an applied potential of −1.35 V vs. Ag/AgCl (−0.727 V vs. RHE), nearly 100% faradaic efficiency (FE) for CO2 conversion to CO was achieved with negligible H2 production (ca. FECO2 = 99.4%). At the same applied potential, the MWCNT@B12 surface shows high catalytic efficiency, with a turnover number (TON) of 4559 and turnover frequency (TOF) of 2.5 s−1, enabling rapid CO2-to-CO conversion (calculation details are provided in the ESI†). Notably, vitamin B12 exhibits exceptional stability during the catalytic reaction, with its active site and redox properties remaining unchanged after prolong catalysis, as depicted in Fig. S8.† The anodic peak current density exhibits a minimal decrease of 90 μA cm−2 (around 5%), from an initial value of 1.71 mA cm−2 (before electrolysis, curve a) to 1.62 mA cm−2 (after electrolysis, curve b), indicating a stable response. Moreover, the redox peak persists, with a slight increase in background current likely due to minor molecular rearrangements or CO bubble formation on the electrode surface during electrolysis. Crucially, the catalytic site remains intact, ensuring the stability and durability of MWCNT@B12 as a high-performance catalyst for CO2RR. Ten hours of continuous usage in the electrochemical reduction also leads to over 96% retention of the electrocatalytic site. This performance is significantly better than recently reported non-redox-active B12 immobilized electrodes and other CoPc and metal-porphyrin-based chemically modified electrodes (FE 90–98.7%) (Table 1),41–50 which exhibit significant H2 formation. Furthermore, these results approach 100% efficiency, which is observed in enzymatic CO2 reduction by CO dehydrogenase (CODH).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we report the development of a green electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction in an aqueous solution. This catalyst consists of B12 immobilized on a multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)-modified electrode. The immobilized B12 exhibits high redox activity and achieves nearly 100% faradaic efficiency, making it an eco-friendly option. In situ SECM suggests that the active sites for CO2 reduction reside in cluster-like B12 agglomerates on the needle-like CNT structure. The overall structure and electrochemical performance of this new catalyst, in terms of overpotential and faradaic efficiency, are comparable to the enzymatic reaction catalysed by carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH).Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Author contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology − Science and Engineering Research Board (DST/CRG/2021/001048) scheme for financial support. Mani Balamurugan acknowledges the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) for the 2021 Creative and Challenging Research Foundation Support Project (NRF-2021R1I1A1A01059981). Yashly Yesudas K acknowledges DST-INSPIRE Fellowship (IF210177) for the financial support.References
- T. V. Ramachandra and S. Bharath, Carbon Sequestration Potential of the Forest Ecosystems in The Western Ghats, A Global Biodiversity Hotspot, Nat. Resour. Res., 2020, 29, 2753–2771 CrossRef CAS.
- NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, Monthly Global Climate Report for February 2024, NOAA, 2024 Search PubMed.
- B. E. Johansen, Climate Change and Oceans, Salem Press Encyclopedia, 2023, vol. 3, p. 1786 Search PubMed.
- International Energy Agency, Net Zero by 2050: A Roadmap for the Global Energy Sector, IEA, 2021 Search PubMed.
- J. E. T. Bistline, Roadmaps to Net-Zero Emissions Systems: Emerging Insights and Modeling Challenges, Joule, 2021, 5, 2551–2563 CrossRef.
- H. McLaughlin, A. A. Littlefield, M. Menefee, A. Kinzer, T. Hull, B. K. Sovacool, M. D. Bazilian, J. Kim and S. Griffiths, Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage in Review: Sociotechnical Implications for A Carbon Reliant World, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2023, 177, 113215 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Nagireddi, J. R. Agarwal and D. Vedapuri, Carbon Dioxide Capture, Utilization, and Sequestration: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Prospects for Global Decarbonization, ACS Eng. Au, 2024, 4, 22–48 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Pascual-Colino, Q. J. S. Virpurwala, S. Mena-Gutiérrez, S. Pérez-Yáñez, A. Luque, G. Beobide, V. K. Velisoju, P. Castaño and O. Castillo, Thermochemical CO2 Reduction Catalyzed by Homometallic and Heterometallic Nanoparticles Generated from the Thermolysis of Supramolecularly Assembled Porous Metal-Adenine Precursors, Inorg. Chem., 2023, 62, 17444–17453 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Imai, K. Kosugi, Y. Saga, M. Kondo and S. Masaoka, Introducing Proton/Electron Mediators Enhances the Catalytic Ability of an Iron Porphyrin Complex for Photochemical CO2 Reduction, Chem. Commun., 2023, 59, 10741–10744 RSC.
- L. Yuan, M.-Y. Qi, Z.-R. Tang and Y.-J. Xu, Coupling Strategy for CO2 Valorization Integrated with Organic Synthesis by Heterogeneous Photocatalysis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 2–25 CrossRef.
- L.-H. Gao, W.-Y. Xiao, M.-Y. Qi, J.-Y. Li, C.-L. Tan and Z.-R. Tang, Photoredox-catalyzed coupling of CO2 reduction and amines oxidation by Cu-doped CdS quantum dots, Mol. Catal., 2024, 554, 113858 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Karishma, R. Kamalesh, A. Saravanan, V. C. Deivayanai, P. R. Yaashikaa and A. S. Vickram, A Review on Recent Advancements in Biochemical Fixation and Transformation of CO2 into Constructive Products, Biochem. Eng. J., 2024, 208, 109366 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Tripathi, S. Choudhary, A. Meena and K. M. Poluri, Carbon Capture, Storage, and Usage With Microalgae: A Review, Environ. Chem. Lett., 2023, 21, 2085–2128 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Pei, B. Zhang and Y. Lu, Carbon capture and utilization via electrochemistry, what's next?, Next Nanotechnol., 2023, 3, 100020 CrossRef.
- Z. Q. Gao, Y. Gong, Y. T. Zhu, J. J. Li, L. Li, Y. X. Shi, M. Hou, X. J. Gao, Z. C. Zhang and W. P. Hu, Large Π-Conjugated Indium-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks for High-Performance Electrochemical Conversion of CO2, Nano Res., 2023, 16, 8743–8750 CrossRef CAS.
- C. He, Y. Zhang, Y. F. Zhang, L. Zhao, L. P. Yuan, J. N. Zhang, J. M. Ma and J. S. Hu, Molecular Evidence for Metallic Cobalt Boosting CO2 Electroreduction on Pyridineic Nitrogen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 4914–4949 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. B. Yeo, J. H. Jang, Y. I. Jo, J. W. Koo and K. T. Nam, Paired Electrosynthesis of Formaldehyde Derivatives from CO2 Reduction and Methanol Oxidation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202316020 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Qu, J. Hu, X. Dai, Q. Tan, Y. Liu, Y. Chen, S. Guo and Y. Liu, Electrospinning Highly Dispersed Ru Nanoparticle-Embedded Carbon Nanofibers Boost CO2 Reduction in a H2/CO2 Fuel Cell, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 23523–23531 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhou, X. Fang, Y. Zhang, W. Yang, W. Zhou, H. Zhou, Q. Liu, J. Wu, F. Qi and Y. Shen, Synergetic Effects of Cu Cluster-doped g-C3N4 with Multiple active Sites for CO2 Reduction to C2 Products: A DFT study, Fuel, 2023, 353, 129202 CrossRef CAS.
- V. M. Badiani, C. Casadevall, M. Miller, S. J. Cobb, R. R. Manuel, I. A. C. Pereira and E. Reisner, Engineering Electro- and Photocatalytic Carbon Materials for CO2 Reduction by Formate Dehydrogenase, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 14207–14216 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. J. Cobb, A. M. Dharani, A. R. Oliveira, I. A. C. Pereira and E. Reisner, Carboxysome-Inspired Electrocatalysis using Enzymes for the Reduction of CO2 at Low Concentrations, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202218782 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. J. Cobb, S. Rodríguez-Jiménez and E. Reisner, Connecting Biological and Synthetic Approaches for Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 136, e202310547 CrossRef.
- Y. Gwon, S. Y. Hwang, G. E. Park, S. Bae, G. Yun, C. K. Rhee and Y. Sohn, CuNiZn vs. CuZn Electrodes: Electrochemical CO2 Reduction, Role of Metal Elements, and Insights for C–C Coupling Chemistry, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2024, 7, 614–628 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Tsujiguchi, Y. Kawabe, S. Jeong, T. Ohto, S. Kukunuri, H. Kuramochi, Y. Takahashi, T. Nishiuchi, H. Masuda, M. Wakisaka, K. Hu, G. Elumalai, J.-I. Fujita and Y. Ito, Acceleration of Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to Formate at the Sn/Reduced Graphene Oxide Interface, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 3310–3318 CrossRef CAS.
- B. M. Tackett, J. H. Lee and J. G. Chen, Electrochemical Conversion of CO2 to Syngas with Palladium-Based Electrocatalysts, Acc. Chem. Res., 2020, 53, 1535–1544 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhu, T.-R. Kuo, Y.-H. Li, M.-Y. Qi, G. Chen, J. Wang, Y.-J. Xu and H. M. Chen, Emerging dynamic structure of electrocatalysts unveiled by in situ X-ray diffraction/absorption spectroscopy, Energy Environ. Sci., 2021, 14, 1928 RSC.
- S. S. A. Shah, M. S. Javed, T. Najam, C. Molochas, N. A. Khan, M. A. Nazir, M. Xu, P. Tsiakaras and S.-J. Bao, Metal Oxides for the Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide: Mechanism of Active Sites, Composites, Interface and Defect Engineering Strategies, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2022, 471, 214716 CrossRef CAS.
- H. A. Ahsaine and A. Baqais, Metal and Metal Oxide Electrocatalysts for the Electrochemical Reduction of CO2-to-C1 Chemicals: Are We There Yet?, Green Chem. Lett. Rev., 2023, 16, 2160215 CrossRef.
- B. Kumar, M. Asadi, D. Pisasale, S. Sinha-Ray, B. A. Rosen, R. Haasch, J. Abiade, A. L. Yarin and A. Salehi-Khojin, Renewable and Metal-Free Carbon Nanofibre Catalysts for Carbon Dioxide Reduction, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 2819 CrossRef.
- M. N. Hossain, J. Wen and A. Chen, Unique Copper and Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Toward the Efficient Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, 3184 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Han, S. Song, M. Liu, S. Yao, Z. Liang, H. Cheng, Z. Ren, W. Liu, R. Lin, G. Qi, X. Liu, Q. Wu, J. Luo and H. L. Xin, Stable and Efficient Single-Atom Zn Catalyst for CO2 Reduction to CH4, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 12563–12567 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-S. Hsu, J. Wang, Y.-C. Chu, J.-H. Chen, C.-Y. Chien, K.-H. Lin, L. D. Tsai, H.-C. Chen, Y.-F. Liao, N. Hiraoka, Y.-C. Cheng and H. M. Chen, Activating Dynamic Atomic-Configuration for Single-Site Electrocatalyst in Electrochemical CO2 Reduction, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 5245 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Abdinejad, A. Seifitokaldani, C. Dao, E. H. Sargent, X.-a. Zhang and H. B. Kraatz, Enhanced Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 Catalyzed by Cobalt and Iron Amino Porphyrin Complexes, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2019, 2, 1330–1335 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Hong, M. Luthra, J. B. Jakobsen, M. R. Madsen, A. C. Castro, H. C. D. Hammershøj, S. U. Pedersen, D. Balcells, T. Skrydstrup, K. Daasbjerg and A. Nova, Exploring the Parameters Controlling Product Selectivity in Electrochemical CO2 Reduction in Competition with Hydrogen Evolution Employing Manganese Bipyridine Complexes, ACS Catal., 2023, 13, 3109–3119 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Ertekin and M. D. Symes, Metal-Phthalocyanine Complexes as Electrocatalysts for The Multi-Electron Reduction of Carbon Dioxide, Appl. Catal., A, 2023, 666, 119388 CrossRef CAS.
- J. M. Becker, A. Lielpetere, J. Szczesny, J. R. C. Junqueira, P. Rodríguez-Maciá, J. A. Birrell, F. Conzuelo and W. Schuhmann, Bioelectrocatalytic CO2 Reduction by Redox Polymer-Wired Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenase Gas Diffusion Electrodes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 46421–46426 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Shin, S. H. Lee, J. W. Shin, S. P. Lee and Y. Kim, Highly Selective Electrocatalytic Conversion of CO2 to CO at −0.57 V (NHE) by Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenase from Moorella thermoacetica, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 14688–14689 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, C. Chen, R. Cao, Z. Pan, H. He and K. Zhou, Dual-Atom Ag2/Graphene Catalyst for Efficient Electroreduction of CO2 to CO, Appl. Catal., B, 2020, 268, 118747 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Kang, C. Ye, R. Jin, H. Yan, R. Lin, J. Yang, Q. Xu, Y. Wang, Q. Zhang, L. Gu, L. Liu, W. Song, J. Liu, D. Wang and Y. Li, A Supported Pd2 Dual-Atom Site Catalyst for Efficient Electrochemical CO2 Reduction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 13388–13393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Feng, X. Wu, H. Cheng, Z. Fan, X. Li, F. Cui, S. Fan, Y. Dai, G. Lei and G. He, Well-Defined Fe–Cu Diatomic Sites for Efficient Catalysis of CO2 Electroreduction, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 42, 23817–23827 RSC.
- J. Choi, P. Wagner, R. Jalili, J. Kim, D. R. MacFarlane, G. G. Wallace and D. L. Officer, A Porphyrin/Graphene Framework: A Highly Efficient and Robust Electrocatalyst for Carbon Dioxide Reduction, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1801280 CrossRef.
- A. Maurina and M. Robert, Catalytic CO2-to-CO Conversion in Water by Covalently Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes with a Molecular Iron Catalyst, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 12084–12087 RSC.
- Z. Sun, Y. Zhai, L. Zheng, W. Guo, W. Dong, Z. Fang, L. Jiao, Z. Zhu, X. Lu and J. Tang, Cobalt-Phthalocyanine-Modified Two-Dimensional Cobalt Hydroxide Complexes for Highly Selective Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to CO, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 1123–1128 RSC.
- C. Jia, K. Ching, P. V. Kumar, C. Zhao, N. Kumar, X. Chen and B. Das, Vitamin B12 on Graphene for Highly Efficient CO2 Electroreduction, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 41288–41293 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Gong, B. Chen, Y. Gao, B. Yu, Y. Wang, B. Han, C. Lin, Y. Bian, D. Qi and J. Jiang, Covalent Organic Frameworks Based on Tetraphenyl-P-Phenylenediamine and Metalloporphyrin for Electrochemical Conversion of CO2 to CO, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2022, 9, 3217–3223 RSC.
- Y. Jin, X. Zhan, Y. Zheng, H. Wang, X. Liu, B. Yu, X. Ding, T. Zheng, K. Wang, D. Qi and J. Jiang, In-situ Growing Nickel Phthalocyanine Supramolecular Structure on Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient Electrochemical CO2 Conversion, Appl. Catal., B, 2023, 327, 122446 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Xin, Y. Hu, W. Fang, J. Dang, Y. Wu, M. Li, W. Cui, Z. Li and H. Zhao, Vitamin B12/Carbon Nanotubes Composites for Highly Efficient CO2 Electroreduction with In- Situ Shell-Isolated Nanoparticle-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy, Electrochim. Acta, 2023, 466, 143024 CrossRef CAS.
- W. W. Kramer and C. C. L. McCrory, Polymer Coordination Promotes Selective CO2 Reduction by Cobalt Phthalocyanine, Chem. Sci., 2016, 7, 2506 RSC.
- X. Li, G. Chai, X. Xu, J. Liu, Z. Zhong, A. Cao, Z. Tao, W. You and L. Kang, Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to CO Over Iron Phthalocyanine-Modified Graphene Nanocomposites, Carbon, 2020, 167, 658–667 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Saravanan, M. Balamurugan, K. S. S. Devi, K. T. Nam and A. S. Kumar, Vitamin B12-Immobilized Graphene Oxide for Efficient Electrocatalytic Carbon Dioxide Reduction Reaction, ChemSusChem, 2020, 13, 5620–5624 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Pan, R. Lin, Y. Chen, S. Liu, W. Zhu, X. Cao, W. Chen, K. Wu, W.-C. Cheong, Y. Wang, L. Zheng, J. Luo, Y. Lin, Y. Liu, C. Liu, J. Li, Q. Lu, X. Chen, D. Wang, Q. Peng, C. Chen and Y. Li, Design of Single-Atom Co-N5 Catalytic Site: A Robust Electrocatalyst for CO2 Reduction with Nearly 100% CO Selectivity and Remarkable Stability, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 4218–4221 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L.-P. Chi, Z.-Z. Niu, X.-L. Zhang, P.-P. Yang, J. Liao, F.-Y. Gao, Z.-Z. Wu, K.-B. Tang and M.-R. Gao, Stabilizing Indium Sulfide for CO2 Electroreduction to Formate at High Rate by Zinc Incorporation, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 5835 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Q. Fu, J. Liu, N. M. Bedford, Y. Wang, J. W. Sun, Y. Zou, M. Dong, J. Wright, H. Diao, P. Liu, H. G. Yang and H. Zhao, Synergistic Cr2O3@Ag Heterostructure Enhanced Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2202854 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Xie, J. Wang, X. L. Du, N. Gao, T. Liu, Z. Li, G. Xiao, T. Li and J. Q. Wang, Metal–Organic Framework Derived Single-Atom Catalysts for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction, RSC Adv., 2022, 12, 32518–32525 RSC.
- Y. Han, S. An, X. Zhan, L. Hao, L. Xu, S. Hong, D. Park, Y. Chen, Y. Xu, J. Zhao, X. Tan, A. W. Robertson, Y. Jung and Z. Sun, Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to CO with Almost 100% Faradaic Efficiency Using Oxygen-Vacancy Enriched Two-Dimensional MgO, CCS Chem., 2023, 202303128 Search PubMed.
- B. Huang, J. Zhang, M. Wang and Z. Cai, Determination of Vitamin B12 in Milk and Dairy Products by Isotope-Dilution Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry, J. Food Qual., 2022, 7649228 CAS.
- D. Guggisberg, M. C. Risse and R. Hadorn, Determination of Vitamin B12 in Meat Products by RP-HPLC After Enrichment and Purification on an Immunoaffinity Column, Meat Sci., 2012, 90, 279–283 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Bährle, S. Böhnke, J. Englhard, J. Bachmann and M. Perner, Current Status of Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenases (CODH) and their Potential for Electrochemical Applications, Bioresour. Bioprocess., 2023, 10, 84 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Xu and H. Hirao, Revisiting the Catalytic Mechanism of Mo–Cu Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenase using QM/MM and DFT Calculations, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018, 20, 18938–18948 RSC.
- R. Breglia, F. Arrigoni, M. Sensi, C. Greco, P. Fantucci, L. De Gioia and M. Bruschi, First-Principles Calculations on Ni,Fe-Containing Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenases Reveal Key Stereoelectronic Features for Binding and Release of CO2 to/from the C-Cluster, Inorg. Chem., 2021, 60, 387–402 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Gandhi, D. Rajagopal and A. S. Kumar, Molecularly Wiring of Cytochrome C with Carboxylic Acid Functionalized Hydroquinone on MWCNT Surface and its Bioelectrocatalytic Reduction of H2O2 Relevance to Biomimetic Electron-Transport and Redox Signalling, Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 368, 137596 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Srinivas, S. M. Senthil Kumar and A. Senthil Kumar, Edge and Basal Plane Anisotropy of a Preanodized Pencil Graphite Electrode Surface Revealed Using Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy and Electrocatalytic Dopamine Oxidation as a Molecular Probe, Langmuir, 2023, 39, 12563–12575 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. S. Kumar, R. Shanmugam, N. Vishnu, K. C. Pillai and S. Kamaraj, Electrochemical Immobilization of Ellagic Acid Phytochemical on MWCNT Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode Surface and its Efficient Hydrazine Electrocatalytic Activity in Neutral pH, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2016, 782, 215–224 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Arthisree, W. Madhuri, N. Saravanan, B. Dinesh, S. Saikrithika and A. S. Kumar, A Ternary Polymer Nanocomposite Film Composed of Green-Synthesized Graphene Quantum Dots, Polyaniline, Polyvinyl Butyral and Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Polystyrene Sulfonate for Supercapacitor Application, J. Energy Storage, 2021, 35, 102333 CrossRef.
- K. Ó Proinsias, M. Giedyk and D. Gryko, Vitamin B12: chemical modifications, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 6605–6619 RSC.
- M. Zhu, J. Chen, L. Huang, R. Ye, J. Xu and Y.-F. Han, Covalently Grafting Cobalt Porphyrin onto Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient CO2 Electroreduction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 6595–6599 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-M. Hu, M. H. Rønne, S. U. Pedersen, T. Skrydstrup and K. Daasbjerg, Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Cobalt Porphyrin in CO2 Electroreduction upon Immobilization on Carbon Materials, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 6468–6472 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Morlanés, K. Takanabe and V. Rodionov, Simultaneous Reduction of CO2 and Splitting of H2O by a Single Immobilized Cobalt Phthalocyanine Electrocatalyst, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 3092–3095 CrossRef.
- S. Srinivas and A. Senthil Kumar, High-Performance Electrocatalytic Reduction and Sensing of Hazardous Hexavalent Chromium Using a Redox-Active Binol Species-Impregnated Carbon Nanofiber-Modified Electrode, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2022, 126, 8296–8311 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: The detailed calculation for turnover number (TON) and turnover frequency of (TOF) of MWCNT@B12 catalyst, EDAX studies and elemental mapping of MWCNT and MWCNT@B12, UV-vis spectrum corresponding to UPLC chromatogram samples confirming the presence of B12 on MWCNT@B12, effect of carbon nanomaterials for the preparation of B12 modified electrodes and their corresponding CO2 reduction activity by CV analysis, scan rate effect on the CV of GCE/MWCNT@B12 with dissolved CO2 and associated kinetic plots, Tafel slope for the CO2 reduction reaction, control experiments for SECM analysis data with dissolved oxygen. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ta04145c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |