PEGylation as an efficient tool to enhance cytochrome c thermostability: a kinetic and thermodynamic study†
Abstract
Cytochrome-c from equine heart was kinetically and thermodynamically investigated either in its native (Cyt-c) or PEGylated forms with different PEGylation degrees (Cyt-c–PEG-4 and Cyt-c–PEG-8). Maximum activities were observed at 80 °C, and the irreversible deactivation was well described by first-order kinetics. The results of activity at different temperatures were used to estimate the activation energy of the catalysed Cyt-c reaction (E* = 10.22 ± 0.40, 7.51 ± 0.06 and 8.87 ± 0.29 kJ mol−1 for Cyt-c, Cyt-c–PEG-4 and Cyt-c–PEG-8) and the standard enthalpy variation of enzyme unfolding (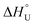 = 33.82 ± 4.92, 109.4 ± 13.1 and 58.43 ± 3.11 kJ mol−1 for Cyt-c, Cyt-c–PEG-4 and Cyt-c–PEG-8, respectively). The results of residual activity tests allowed estimating the activation energy (Ed* = 50.51 ± 1.71, 72.63 ± 0.89 and 63.36 ± 1.66 kJ mol−1 for Cyt-c, Cyt-c–PEG-4 and Cyt-c–PEG-8), enthalpy (ΔH‡), entropy (ΔS‡) and Gibbs free energy (ΔG‡) of the enzyme irreversible denaturation. The higher enthalpic contributions of PEGylated conjugates and the increase in ΔG‡, compared to the native protein, indorsed the protective role of PEGylation. Negative values of ΔS‡ suggested the occurrence of an aggregation phenomenon by increasing the temperature, which was confirmed by circular dichroism. The estimated thermodynamic parameters suggest that PEGylated Cyt-c forms have enhanced thermostability, which would be of great significance for industrial biosensing applications.
= 33.82 ± 4.92, 109.4 ± 13.1 and 58.43 ± 3.11 kJ mol−1 for Cyt-c, Cyt-c–PEG-4 and Cyt-c–PEG-8, respectively). The results of residual activity tests allowed estimating the activation energy (Ed* = 50.51 ± 1.71, 72.63 ± 0.89 and 63.36 ± 1.66 kJ mol−1 for Cyt-c, Cyt-c–PEG-4 and Cyt-c–PEG-8), enthalpy (ΔH‡), entropy (ΔS‡) and Gibbs free energy (ΔG‡) of the enzyme irreversible denaturation. The higher enthalpic contributions of PEGylated conjugates and the increase in ΔG‡, compared to the native protein, indorsed the protective role of PEGylation. Negative values of ΔS‡ suggested the occurrence of an aggregation phenomenon by increasing the temperature, which was confirmed by circular dichroism. The estimated thermodynamic parameters suggest that PEGylated Cyt-c forms have enhanced thermostability, which would be of great significance for industrial biosensing applications.

- This article is part of the themed collection: Materials and Nano Research in Brazil


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...