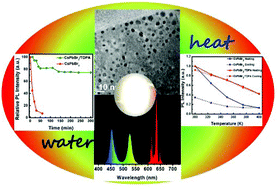
Inorganic halide perovskite quantum dots (QDs) suffer from problems related to poor water stability and poor thermal stability. Here we developed a simple strategy to synthesize alkyl phosphate (TDPA) coated CsPbBr3 QDs by using 1-tetradecylphosphonic acid both as the ligand for the CsPbBr3 QDs and as the precursor for the formation of alkyl phosphate. These QDs not only retain a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY, 68%) and narrow band emission (FHWM ∼ 22 nm) but also exhibit high stability against water and heat. The relative PL intensity of the QDs was maintained at 75% or 59% after being dispersed in water for 5 h or heated to 375 K (100 °C), respectively. Finally, white light-emitting diodes (WLEDs) with a high luminous efficiency of 63 lm W−1 and a wide color gamut (122% of NTSC) were fabricated by using green-emitting CsPbBr3/TDPA QDs and red-emitting K2SiF6:Mn4+ phosphors as color converters. The luminous efficiency of the WLEDs remained at 90% after working under a relative humidity (RH) of 60% for 15 h, thereby showing promise for use as backlight devices in LCDs.