Two-dimensional material membranes for critical separations
Pengchao
Liu
abc,
Junjun
Hou
bc,
Yi
Zhang
bc,
Lianshan
Li
 *bc,
Xiaoquan
Lu
*a and
Zhiyong
Tang
*bc,
Xiaoquan
Lu
*a and
Zhiyong
Tang
 bc
bc
aTianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic, Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, P. R. China. E-mail: luxq@tju.edu.cn
bCAS Key Laboratory of Nanosystem and Hierarchical Fabrication & CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing 100190, China. E-mail: lils@nanoctr.cn
cUniversity of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 A Yuquan Rd, Shijingshan District, Beijing 100049, P. R. China
First published on 15th May 2020
Abstract
Separation technology is of great importance to the chemical industries which involve many steps of purification. Compared to the traditional thermal-based purification processes such as evaporation and distillation, membrane technology has attracted increasing attention due to its low energy consumption and continuous operation. Two-dimensional (2D) material membranes formed by stacking various kinds of 2D nanosheets, including graphene, graphene oxide (GO), MXenes, layered transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), layered zeolites, 2D metal organic frameworks (MOFs), 2D covalent organic frameworks (COFs), etc., represent a burgeoning class of separation membranes. Owing to their easy fabrication, controllable pore size, that is the stacking space between neighbouring layers, and diverse functionalization, these 2D material membranes show great potential for precise and high-efficiency separation through the synergy of the pore size and surface properties of nanopores or nanochannels. To date, 2D material membranes have been widely used in a broad range of critical separations, including ion separation, mixed organic solvent separation, gas separation, nanofiltration, and chiral molecular separation. In this review, we first summarize the separation mechanism adopted in 2D material membranes, followed by the introduction of the most widely used 2D materials and the synthetic strategies for their single or few layer structures. Finally, we summarize the applications of 2D material membranes in various critical separations, including ion sieving, nanofiltration, gas separation and chiral separation.
1. Introduction
Separation technology, which can separate mixtures into pure substances, is significantly important for the chemical industry. According to the statistics, separation and purification processes account for half of the energy usage in the chemical industry, that is 10–15% of the total energy consumption of the whole world.1 Unfortunately, 80% of the separations still rely heavily on traditional high cost thermal-based processes such as evaporation and distillation.2 Unlike the thermal-based processes, membrane technology has emerged as a new promising separation technology due to its low energy consumption (accounting for only one tenth of the thermal-based process), environmental compatibility, small footprint, continuous operation, etc.2,3 Since 1960s, membrane technology has been widely used in water purification,4,5 sea water desalination6,7 and gas separation.8 Most recently, it was further used in the separation of organic mixtures, such as organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN),9 organic solvent reverse osmosis (OSRO),10 organic solvent forward osmosis (OSFO),11 chiral molecule separations,12etc.From the materials point of view, various materials have been adopted for membrane fabrication, including traditional flexible polymers,13 three-dimensional (3D) rigid polymers,14 carbon molecular sieves (CMSs),10 metal organic frameworks (MOFs),15 covalent organic frameworks (COFs),16 two-dimensional (2D) material membranes,17,18etc. Among those, 2D material membranes represent an important class of separation membranes, which are formed by the stacking of single-layer 2D materials, including graphene,19 graphene oxide (GO),20 MXenes (2D transition metal carbides and/or nitrides),21 layered transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs),22 layered zeolites,23 2D MOFs,24,25 and 2D COFs.26 Different from the intrinsic micropores in microporous materials (such as MOFs, COFs and CMSs), the porosity of the 2D material membranes mainly results from the stacking spaces between neighbouring layers, namely, the interlayer spacing. This interlayer spacing can be precisely controlled to accommodate molecules or ions with different sizes, and is thus used for highly efficient ion or molecule separations.27 To date, 2D material membranes have been widely used in ion separation,28,29 gas separation,30 nanofiltration,31 chiral molecule separation15 and so on.
In this review, we will focus on the separation mechanisms, preparation strategies, and applications of the 2D material membranes, summarize the recent progress and problems of the 2D material membranes in critical separations, and look forward to the future research directions of the 2D materials as efficient separation membranes.
2. Separation mechanisms
From the separation or rejection point of view, two main mechanisms are adopted. The first one is physical exclusion, in which molecules or ions that are smaller than the pores can pass through while larger ones are rejected. Since no chemical interactions are involved, the rejection totally depends on the relative size of the nanopores in the membrane and the passing species. Generally, there are two types of nanopores in 2D material membranes: nanoholes in single layer membranes and the stacking space between neighbouring layers in the stacking membranes (Fig. 1a and b).32 Nanoholes can be created on single layer membranes, such as graphene, by means of electron beam irradiation,33,34 oxidative etching,35,36 ion beam bombardment,37 plasma treatment,38,39 or nanolithography,40 while the stacking of 2D material single layers can form uniform interlayer space with size comparable to those of ions or molecules.41 In addition, ions, molecules, nanoparticles and polymers can also be incorporated into the interlayers to adjust the stacking distance. For instance, the interlayer distance of GO membranes can be controlled at the Angstrom level by the insertion of different cations.27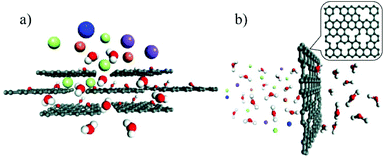 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) The interlayer space of the stacking GO membrane, in which the hydrated ions are blocked while the water molecules pass through.32 (b) The nanoholes created on single-layer graphene can selectively reject large hydrated ions32 (C: black, H: white, O: red, K+: blue, Na+: purple, Mg2+: orange, and Cl−: cyan). Copyright, 2016 Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
To further improve the selectivity or separation efficiency of the 2D material membranes, it is necessary to make full use of the various interactions between the 2D materials and the passing ions or molecules, such as electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, local dipole interactions and chiral recognition. The electrostatic interactions between ions and functional groups on the surfaces of the 2D materials can be used to separate charged ions.42,43 For instance, owing to the negatively charged functional groups (e.g., carboxyl group) on the surface of the GO layer, the GO membrane can inhibit the passage of negatively charged molecules or ions and facilitate the migration of positively charged ones via electrostatic interactions.31 Wen et al.44 reported the synthesis of Ti3C2Tx nanosheets under mild etching conditions. The dispersed Ti3C2Tx nanosheets were subsequently filtered on a polycarbonate (PC) substrate to obtain stacking Ti3C2Tx membranes. With the presence of oxygen-containing groups on the surface, the nanochannels in the Ti3C2Tx membrane are negatively charged and thus show good cation selectivity, allowing cations to pass while rejecting anions. Hydrogen bonding is another interaction that can help selectively transport molecules or ions. Peng et al.45 developed a laminar MoS2 membrane through the vacuum filtration technique. The presence of a large number of sulfur atoms on the surfaces of the MoS2 layers makes the membrane hydrophilic and show good affinity to water through hydrogen bonding. These hydrogen-bonded water molecules act as spacers, providing a large number of nanochannels for the efficient transport of water molecules. As a result, the water permeance through the MoS2 membrane is 3–5 times higher than that of the GO membrane with almost the same rejection level for small molecules. Wang et al.46 simulated the transport of ions through multiple layers of a TpHZ COF, and found that due to the polarity of the COF, Na+ hydrates with the pore wall of the COF and forms hydrogen bonds, resulting in a significantly slower migration speed of Na+ ions than that of water molecules. Beyond the liquid phase, chemical interactions can also be used to tune the gas permeation through a membrane that can interact with the passing gas molecules. Shen et al.47 dispersed GO nanosheets into a polyether block amide (PEBA) block copolymer to prepare a GO/PEBA mixed matrix membrane (MMM). The oxygen-containing group on the surfaces of the GO nanosheets strongly interacts with the polar C–O bonds of CO2, leading to preferential adsorption and diffusion of CO2 molecules through the GO-based membrane (Fig. 2a). Last but not least, the chiral recognition between the chiral functional groups in the 2D material membrane and the passing chiral molecules can be used for the separation of chiral substances. Liu et al.48 prepared a L-glutamic modified GO membrane and used for the separation of 3,4-dihydroxy-D,L-phenylalanine (D-,L-DOPA). Due to the higher binding affinity between D-DOPA and L-glutamic acid, D-DOPA is preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the modified GO layers, leading to the preferential transport of D-DOPA through the membrane (Fig. 2b).
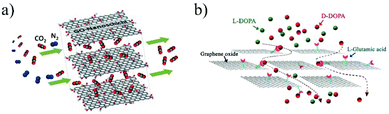 | ||
| Fig. 2 (a) Schematic illustration of the facilitated transport of CO2 through the GO membrane via the chemical interaction between CO2 molecules and the oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the GO layers.43 (b) Chiral separation of D- and L-DOPA by the L-glutamic acid functionalized GO membrane through the chiral interaction between L-glutamic acid and D-DOPA.44 Copyright, 2014 Wiley-VCH and 2016 Elsevier. | ||
In addition to various interactions, the hydrophilic or hydrophobic properties of the membrane surface can influence the efficiency of the mass transport in a membrane. For example, the high hydrophobicity of the graphene surface can greatly reduce the friction between single layer water and the graphene membranes, leading to an ultra-fast water permeation rate.49,50 Jiang et al.51 prepared polyimide (PI) porous membranes and modified the inner pore surface with hydrophobic azobenzene derivatives to achieve hydrophobic nanochannels. The wettability of membranes can be controlled by light and an electric field, endowing them with the ability of regulating the transport of ions and water across the membrane.
Although discussed separately, the precise discrimination of ions, gases, and organic molecules by 2D material membranes usually relies on the synergistic effect between the pore size and pore surface. Thus, preparation of 2D material membranes with precisely regulated pore size and specific surface properties is urgently required for their further application in critical separations.
3. 2D materials for membrane fabrication
3.1 Graphene and graphene derivatives
Graphene, a typical 2D material with only one-atom thickness, is predicted to have a range of unique properties.52 Since Novoselov et al. reported the successful synthesis of graphene by simply exfoliating graphite in 2004,53 great efforts have been devoted towards studying this fascinating material.54 Intensive research studies on graphene have also prompted studies on graphene derivatives,55,56 including GO,57,58 fluorographene,59 graphyne and graphdiyne.60 Among them, graphene and GO are the two most important 2D nanomaterials for membrane fabrication,61 which have been widely studied in the fields of seawater desalination,62 gas permeation,63 nanofiltration,31etc.There are two main strategies for the production of graphene. The first one is a bottom-up method, in which graphene is directly grown on Cu foil at high temperature with hydrocarbon gases (e.g., CH4 mixed with Ar and H2) as the carbon source.64 The as-prepared graphene can be easily transferred to other substrates with polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), enabling them to be used in various applications (Fig. 3).65 The second strategy is a top-down method, in which single layer graphene is exfoliated from the bulk graphite by mechanical exfoliation.66 Since no chemical reactions are involved in mechanical exfoliation, single layer graphene with a clean surface is usually obtained. However, due to the lack of surface charges or other protection, it is highly challenging to produce a stable graphene dispersion on a large scale.67
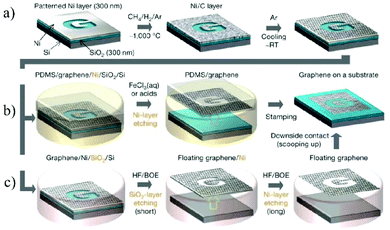 | ||
| Fig. 3 The process of synthesizing, etching, and transferring the CVD-grown large-area and patterned graphene membranes.65 (a) Synthesis of the patterned graphene on a thin nickel substrate. (b and c) Etching and subsequent transfer of the graphene membrane on other substrates. Copyright, 2009 Springer Nature. | ||
GO is an oxidized form of graphene with high density of oxygen-containing functional groups on its surface, such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, and epoxy groups. In contrast to graphene obtained by either chemical vapor deposition (CVD)68 or mechanical exfoliation,69 GO is usually synthesized via chemical exfoliation, in which the graphite is oxidized by strong oxidation reagents to produce hydrophilic groups on the surface of graphene. Due to the hydrophilic feature of GO, it can be well dispersed in aqueous solution and produced inexpensively on a large scale.70 Hummers et al.71 pioneered the chemical exfoliation of graphite into GO in high yield using strong oxidation reagents, such as KMnO4, NaNO3, and H2SO4. Afterward, Tour et al.72 further improved the oxidation efficiency by carrying out the exfoliation process in a 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of H2SO4/H3PO4, with increasing the amount of KMnO4 and excluding NaNO3. Although more oxidized, the GO produced by this improved method shows similar electrical conductivity to that from Hummers’ method after reduction by hydrazine (Fig. 4).
1 mixture of H2SO4/H3PO4, with increasing the amount of KMnO4 and excluding NaNO3. Although more oxidized, the GO produced by this improved method shows similar electrical conductivity to that from Hummers’ method after reduction by hydrazine (Fig. 4).
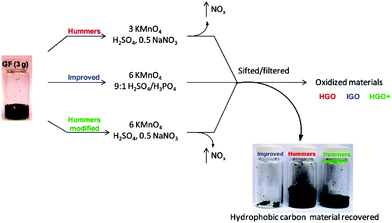 | ||
| Fig. 4 Different synthesis procedures of GO and comparison of the unoxidized hydrophobic carbon material recovered during the purification of improved GO (IGO), GO prepared by Hummers’ method (HGO), and Hummers’ method with additional KMnO4 (HGO+). The increased efficiency of the IGO method is indicated by the very small amount of unoxidized material produced.72 Copyright, 2010 American Chemical Society. | ||
The well-dispersed GO layers can be assembled into membranes by vacuum filtration,73,74 spin coating,75 drop coating76 or layer-by-layer deposition77 for further applications. The interlayer spacing can be effectively controlled to accommodate molecules with different sizes and thus precisely tune the selectivity, making it very intriguing in various separations such as gas separation and water purification/desalination.
3.2 MXenes
MXene, a new type of 2D material, is usually expressed as Mn+1XnTx (n could range from 1 to 3), where M represents early transition metals (Ti, V, Cr, Nb, etc.), X refers to carbon and/or nitrogen and Tx can be functional groups such as –OH,![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O or –F. MXenes could be obtained by etching the A layers of MAX, such as Ti2AlC, Ti3AlC2, and Ta4AlC3, where A refers to a group of elements (such as Al, Si, Sn, etc.).78,79 Since the first MXene was reported in 2011,80 the name of “MXene” has been used to emphasize the loss of the A element in MAX and its 2D feature similar to graphene.81
O or –F. MXenes could be obtained by etching the A layers of MAX, such as Ti2AlC, Ti3AlC2, and Ta4AlC3, where A refers to a group of elements (such as Al, Si, Sn, etc.).78,79 Since the first MXene was reported in 2011,80 the name of “MXene” has been used to emphasize the loss of the A element in MAX and its 2D feature similar to graphene.81
The most widely used strategy for exfoliating MAX into a 2D MXene is chemical etching with hydrofluoric acid (HF) accompanied by ion or organic molecule intercalation. Compared with the stronger M–X bond, the M–A bond shows much higher chemical activity, which makes it possible to prepare an MXene by selective etching of the A elemental layer.82,83 Gogotsi et al.81 used HF aqueous solution to exfoliate the bulk MAX powder, in which the element A layer was selectively etched and replaced with O, OH and F. The removal of the A layer greatly weakened the interaction between the Mn+1Xn layers, leading to high-yield production of the MXene by further simple sonication treatment (Fig. 5). It is noteworthy that appropriate etching conditions play an important role in achieving high yield and full exfoliation of MAX to MXene. Although exfoliation of MAX can be successfully achieved by HF etching, the yield of the single layer MXene is usually low. To further improve the exfoliation yield, HF etching combined with ion or organic molecule intercalation has been developed, in which the ions or organic molecules insert into the interlayers of the HF etched MXene to further increase the interlayer spacing.84,85 Sinitskii et al.86 reported a Li+-insertion assisted method for the exfoliation of MAX, in which the bulk MAX was first etched in a mixture of HCl and LiF, followed by washing with water to adjust the pH around 6 to produce high-yield single-layer or multi-layer Ti3C2Tx nanosheets. The advantage of this method over pure HF etching is that the MXene can be delaminated without an additional step of sonication, because the insertion of Li+ further increases the spacing between the MXene layers (Fig. 6). Beside ions, organic molecules could also be used in MXene intercalation. For example, Gogotsi et al.87 reported the exfoliation of Nb2CTx in isopropylamine (i-PrA), allowing the insertion of the i-PrA molecules into the layered structure of Nb2CTx, and then sonication in a suitable solvent to boost the formation of a single-layer or multi-layer MXene (Fig. 7). In addition to the traditional MXene, a new MXene can also be synthesized from non-MAX materials. Zhou et al.88 found that, in Zr3Al3C5, it is more advantageous to etch Al–C units than to etch Al layers from the energy perspective. This discovery makes it possible to synthesize new MXenes from non-MAX precursors.
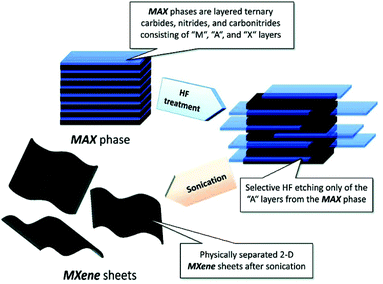 | ||
| Fig. 5 Schematic illustration of the exfoliation of MAX and the formation of an MXene by HF etching and sonication treatment.81 Copyright, 2012 American Chemical Society. | ||
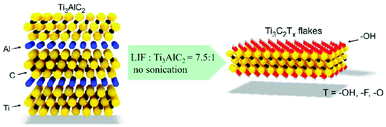 | ||
| Fig. 6 Preparation of an MXene by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2 in a mixture of HCl and LiF without sonication.86 Copyright, 2016 Wiley-VCH. | ||
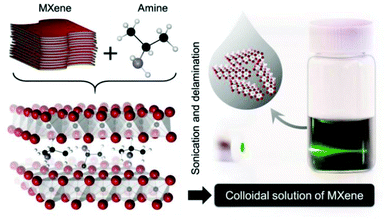 | ||
| Fig. 7 Schematic illustration of the exfoliation of Nb2CTx by isopropylamine (i-PrA) insertion.87 Copyright, 2015 Wiley-VCH. | ||
Similar to graphene and GO membranes, MXene membranes with a controllable interlayer distance can also be obtained by restacking the single layer or few layer MXene. For example, Shen et al.89 reported the fabrication of an MXene membrane, in which the stacking behavior and interlayer spacing of the MXene layers were precisely controlled by modifying the surface of the MXene with borate and PEI molecules. After crosslinking with borate and PEI molecules, the packing of the 2D layers of the MXene becomes denser and more stable, leading to the reduction of the interlayer spacing from 0.52 nm to 0.34 nm which is much smaller than that of pristine MXene membranes. In this case, the interlocked borate and PEI molecules play the roles of both crosslinking the MXene layers and being CO2-philic nanodomains, giving rise to an enhanced solubility and transport of CO2 molecules.
3.3 Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs)
Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) represent one of the typical inorganic 2D materials analogous to graphene, with the general formula of MX2 (where M could be Ti, Zr, Nb, Mo, W and other group IV, V or VI transition metals and X is a chalcogen element, including S, Se and Te).90 The structure of the TMDCs was first determined by Pauling et al.91 in 1923. Specifically, in the layered structure of TMDCs, each layer is typically 6–7 Å thick and consists of a hexagonal metal atom layer sandwiched between two layers of chalcogen atoms.92 The M–X bonds in the layer are essentially covalent bonds in nature, while the adjacent layers are connected by weak van der Waals forces, making it easy for TMDC crystals to split into separate layers.93 Frindt et al.94 first reported the exfoliation of ultra-thin MoS2 layers with tapes as early as 1963, followed by the preparation of the first single-layer MoS2 suspension in 1986.95 Beyond 2D TMDC suspensions, layered TMDCs have also been used for the preparation of ultra-thin membranes for separation applications.96 There are many methods for preparing single-layer or multi-layer TMDC nanosheets, including mechanical exfoliation,97 liquid phase exfoliation,98 the CVD method99 and so on.Mechanical exfoliation is a convenient, effective and fast technique for obtaining TMDC layers, in which a tape is used to adhere the TMDC bulk materials and then it is repeatedly torn to obtain few layer or even single layer TMDCs.100 Despite the advantages of mechanical exfoliation, this method is only suitable for laboratory synthesis rather than large-scale production of TMDCs. One of the effective ways to obtain large-scale thin-layer TMDCs is the liquid phase exfoliation method, which is usually assisted by either ultrasonication or intercalation processes in the liquid phase. The ultrasonication-assisted process is usually performed in a suitable solvent (e.g., N-methylpyrrolidone and acetone.) to weaken the van der Waals forces between layers in the bulk materials.101,102 The key of this technology is to choose an appropriate solvent with surface tension equivalent to the surface energy of TMDCs, in which the exfoliated layers can be dispersed. Coleman et al.103 reported the ultrasonic exfoliation of bulk TMDCs powders into mono- and few-layer nanosheets in N-methylpyrrolidone. This method demonstrates a universal strategy for the large-scale synthesis of various TMDC single layers, such as BN, MoS2, WS2, MoSe2, MoTe2, TaSe2, NbSe2, NiTe2, and Bi2Te3, in a number of solvents, and is expected to be applicable to all MX2 compounds (Fig. 8). In the intercalation process, organic molecules or ions are inserted into the bulk crystal interlayers, which increases the interlayer distance and makes TMDC crystals easier to delaminate. Taking MoS2 as an example, Dines et al.104 discovered in 1975 that lithium ions can be inserted into the MoS2 interlayers to form lithium-intercalated complexes. Based on this, Frindt et al.95 demonstrated the large-scale exfoliation of MoS2 by the intercalation method, in which the MoS2 powder was first immersed in a solution containing a lithium compound (such as n-butyllithium) for lithium intercalation, followed by reacting with water to produce gases to further increase the interlayer distance of MoS2, thereby obtaining a large scale of MoS2 in single or few layers. Zhang et al.105 developed a simple and effective method to prepare high-yield single-layer TMDCs through an electrochemical lithium ion intercalation process. Specifically, in an electrochemical device, the TMDC crystals (e.g., MoS2, WS2, and TiS2) were used as cathode, while the lithium foil serves as the anode to provide lithium ions. This method can finely control the intercalation speed of lithium into the bulk TMDC materials. Finally, a high-yield of single-layer TMDCs can be obtained by ultrasonication treatment (Fig. 9).
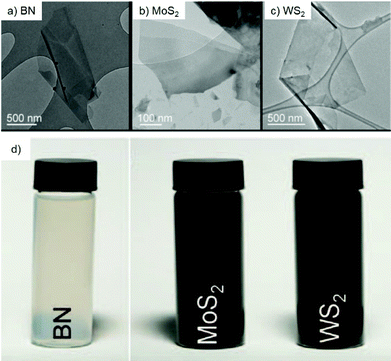 | ||
| Fig. 8 Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of the exfoliated BN (A), MoS2 (B) and WS2 (C) nanoflakes and their large-scale dispersion (D) in N-methylpyrrolidone.103 Copyright 2011, American Association for the Advancement of Science. | ||
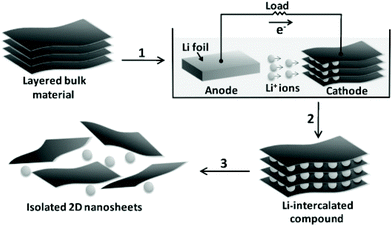 | ||
| Fig. 9 Preparation of 2D nanosheets (e.g., MoS2, WS2, and TiS2) by the electrochemical lithiation process.105 Copyright, 2011 Wiley-VCH. | ||
The CVD method represents a bottom-up strategy for preparing large area TMDCs with controllable thickness. Compared with exfoliation methods that usually require small molecules or ions as exfoliants, the thickness and size of TMDCs obtained by CVD can be precisely controlled. For instance, Lou et al.106 found that MoS2 membranes (form single layer to few layers) can be obtained on SiO2 substrates by reacting S vapor with Mo at high temperatures. The thickness and size of the MoS2 layer depend on the thickness of the Mo metal pre-deposited on the substrate and the size of the substrate, respectively.
3.4 Zeolites
A zeolite is an aluminosilicate mineral containing aqueous alkali or alkaline earth metals.107,108 Because of its high hydrothermal stability, adsorption, ion exchange, and molecular selectivity, it has a wide range of applications in the fields of catalysis,109 adsorption,110 and separation.111,112 2D zeolites have a complete crystalline and microporous structure with inherent intercrystalline pores between 0.25 and 1 nm.113,114 By stacking the zeolite nanosheets into a molecular sieve membrane, the intercrystalline pores can be further minimized or eliminated, providing ample imagination space for the development of 2D zeolite membranes as ultra-thin molecular sieve membranes.115,116 At present, the synthesis methods for a 2D zeolite are mainly divided into three types: hydrothermal synthesis,117 surfactant-templated synthesis118 and ADOR (assembly–disassembly–organization–reassembly).119Hydrothermal synthesis is the earliest method used for preparing layered zeolites. Tsapatsis et al.120 reported the synthesis of zeolite nanoflakes/polystyrene nanocomposites by melting polystyrene and zeolite precursors. Subsequently, ultrasonication and centrifugation are performed in an organic solvent, such as toluene and chlorobenzene, to remove the polymers and large particles, leading to the formation of single-layer zeolite nanosheets. The zeolite nanosheets obtained by this method are suitable for membrane fabrication, providing an effective strategy for low-cost and large-scale membrane formation. Organic structure-oriented agents (OSDAs) such as cyclic amine derivatives or quaternary ammonium cations can be used as templates to synthesize 2D zeolites. Ryoo et al.121 developed a new bifunctional OSDA molecule as a template. The hydrophilic quaternary ammonium group of the OSDA interacts with the charged silica in the gel, directing the 2D crystallization of the zeolite, while the hydrophobic tail of the quaternary ammonium group prevents the crystallization in the 3D direction. In this way, 2D zeolite nanosheets can be directly synthesized in solution (Fig. 10). Based on Ryoo's work, Tsapatsis et al.122 optimized the chemical structure of the OSDA with different quaternary ammonium salts and variable alkane chains to synthesize layered MWW (MCM-22) and MFI (zeolite socony Mobil-5) nanosheets, and further exfoliated the nanosheets to produce a single-layer zeolite. Although this method can effectively avoid the formation of 3D aggregates from the existing 2D zeolite layers, the intrinsic micropores of the layered zeolite might be blocked, thereby reducing the permeation and selectivity of the membrane. To solve this problem, Tsapatsis et al.123 used a piranha solution (a mixture of H2SO4 and H2O2) to remove OSDAs from the detached MFI zeolite to obtain OSDA-free MFI nanosheets. Since the method does not require the steps of secondary growth and high temperature activation, such OSDA-free nanosheets are suitable for the fabrication of membranes on a polymer substrate on a large scale, greatly reducing the blockage of the nanopores in the membrane.
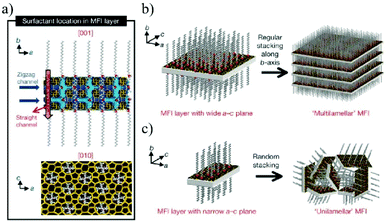 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a) The structural model proposed for the single MFI nanosheet. Surfactant molecules are aligned along the straight channel of the MFI framework. Two quaternary ammonium groups (indicated as a red sphere) are located at the channel intersections; one is inside the framework, and the other is at the pore mouth of the external surface. The MFI nanosheets form either multilamellar stacking along the b-axis (b), or a random assembly of a unilamellar structure (c).121 Copyright, 2009 Springer Nature. | ||
ADOR is a top-down strategy for the synthesis of 2D zeolites, in which four steps are successively involved. First, prepare the initial bulk 3D zeolite (assembly), then exfoliate the bulk zeolite into 2D separate layers (disassembly), subsequently, organize these layers in a suitable way (organization), and finally calcine the material to obtain a novel 3D zeolite with a new topological structure (reassembly).124 Morris et al.125 prepared two types of 2D zeolites, IPC-9 and IPC-10, by the ADOR method. In the fourth step of reassembling the layered structures, different 2D zeolites can be generated by different methods. If the material is simply calcined, the layers are connected only by oxygen bridges to form IPC-9, while if dimethyldiethoxysilane is added and inserted between the layers, a silicon bridge between different layers can be formed, leading to the formation of a single tetracyclic unit structure to generate IPC-10. This method makes it possible to prepare materials with the same layer topology but different layer connectivity.
3.5 Metal organic frameworks (MOFs)
MOFs represent a new crystalline porous material formed by organic linkers and metal nodes.126 Due to their high surface area, high porosity, and controllable topological structures, they have been widely used for a wide range of applications, such as gas separation,127 gas storage,128 catalysis,129 energy storage and conversion,130etc. Although thousands of MOFs with specific sizes, shapes and compositions have been synthesized, it is still highly challenging to realize high-quality 2D MOFs with single layer or few-layer thicknesses.131,132Two main strategies are adopted for synthesizing 2D MOF nanosheets: top-down and bottom-up methods.133,134 Starting from the bulk 2D MOFs, single-layer or few-layer 2D MOF nanosheets can be obtained by breaking the interlayer interactions, such as the weak van der Waals forces or hydrogen bonding, which is known as top-down method. Gallego et al.135 first reported the successful synthesis of 2D MOF nanosheets by solvent-assisted exfoliation. The exfoliated 2D MOF nanosheets possess the same crystal structure as their bulk precursors. Peng et al.136 reported a physical ball-milling process, in which the original bulk MOF, Zn2(bim)4 crystals, was first wet-milled at a very low milling speed, and then exfoliated with the help of ultrasonication in a volatile solvent such as methanol and propanol. The grinding process can promote the penetration of methanol molecules in between the layers of Zn2(bim)4 and thus facilitate the exfoliation process. Zhao et al.137 reported the preparation of MAMS-1 (Mesh Adjustable Molecular Sieve, Ni8(5-bbdc)6(μ-OH)4)) MOF nanosheets using a mild freeze–thaw exfoliation method. During the freezing and thawing processes in a liquid nitrogen bath, the interlayer bonds of the bulk MOF were broken due to the shear force caused by the volume change of the solvent between the liquid and solid phases. In this way, 2D MOF nanosheets with a thickness of 4 nm can be finally obtained by thawing the MOF powders in a hot water bath (Fig. 11).
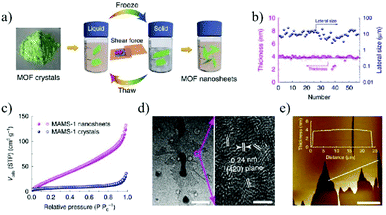 | ||
| Fig. 11 Exfoliation and purification of MAMS-1 nanosheets.137 (a) The freeze–thaw exfoliation of MAMS-1 crystals into dispersed nanosheets. (b) Thickness and lateral size distribution of exfoliated MAMS-1 nanosheets after 10-cycle freeze–thaw in hexane. (c) N2 sorption isotherms of MAMS-1 crystals and exfoliated MAMS-1 nanosheets (filled, adsorption; and open, desorption). (d) TEM image of MAMS-1 nanosheets. Scale bars, 1 mm (left) and 3 nm (right). (e) AFM image of purified MAMS-1 nanosheets. Scale bar, 10 μm. Copyright, 2016 Springer Nature. | ||
In addition to the top-down method, the bottom-up method is also widely used to synthesize 2D MOFs, in which the 2D MOF nanosheets are directly formed by metal ions and organic linkers. Kitagawa et al.138 reported the synthesis of NAFS-1 (nanofilms of MOFs on surface no. 1) MOF nanosheets by surface-confined growth, in which a mixture of CoTCPP and pyridine was first dispersed in a CuCl2·2H2O aqueous solution. Subsequently, the mixture solution was deposited on a substrate by a horizontal dipping method at room temperature, giving rise to the formation of 2D nanosheets. Interestingly, the NAFS-1 nanosheets with different thicknesses can be generated by repeating the above growth process. Despite the controllable synthesis of 2D MOF nanosheets, the surface-confined strategy is greatly limited by low yield and poor dispersion. To synthesize well dispersed 2D MOFs on a large scale, Zhang et al.139 first reported a surfactant-assisted synthesis method to prepare a series of ultra-thin 2D MOF nanosheets, namely, M-TCPP (M = Zn, Cu, Cd or Co, TCPP = tetrakis (4-carboxyphenylporphyrin)) nanosheets. As a surfactant, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) can selectively attach to a specific crystalline surface of an MOF to control the anisotropic growth, resulting in ultra-thin MOF nanosheets with thicknesses down to sub-10 nm (Fig. 12). Tang et al.140 reported the synthesis of ultra-thin metal organic framework nanoflakes (UMOFNs) via an ultrasonication-assisted method. The Ni2+, Co2+, and benzenedicarboxylic (BDC) acid ligands were separately dissolved, and stirred at room temperature to form a colloidal suspension. After continuous ultrasonication for 8 hours, UMOFNs were obtained. This method represents a fast, energy-saving and environmentally friendly approach for synthesizing well-dispersed 2D MOF nanosheets.
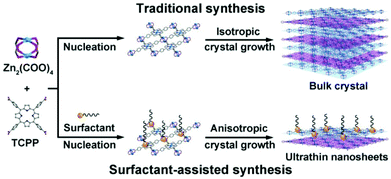 | ||
| Fig. 12 Preparation of MOFs by traditional synthesis and surfactant-assisted synthesis. In the traditional method, isotropic growth produces large crystals of MOFs, while in the surfactant-assisted synthesis, the surfactant causes anisotropic growth of MOFs to form uniform ultra-thin MOF nanosheets.139 Blue and purple are used to draw MOF layers separately. Copyright, 2015 Wiley-VCH. | ||
3.6 Covalent organic frameworks (COFs)
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) refer to porous crystalline materials formed by organic linkers with light atoms (hydrogen, boron, carbon, nitrogen, etc.) and symmetrically connected by covalent bonds.141,142 Considering the large specific surface area, low density, superior thermal stability and intrinsic microporosity with designable architectures at the molecular level, COFs have shown promising applications in desalination,143,144 nanofiltration,9,145 gas separation,146etc.Strategies for synthesizing 2D COFs can be divided into two classes, top-down and bottom-up methods.147,148 Exfoliation is the most widely adopted approach in the typical top-down strategy. Zamora et al.149 reported the preparation of fluorinated borate-linked COF-8 and its liquid phase exfoliation for the first time in 2011. The layered crystals of COF-8 were sonicated in dichloromethane, and the resulting suspension was centrifuged to remove large aggregates, leading to the formation of 2D nanosheets with lateral dimensions exceeding a few microns and a thickness of 4 nm (Fig. 13a). Later in 2013, Banerjee et al.150 reported the synthesis of 7 different COF powders including TpPa-2, TpPaNO2, TpBD-me2, TpPa-F4, TpPa-1, TpBD-(OMe)2 and TpBD-(NO2)2 and their further mechanical exfoliation. After grinding these COF powders in methanol for 30 minutes, 2D COF nanosheets with thicknesses of several nanometers can be obtained without changing or degrading the chemical bonds and crystal structure (Fig. 13b). Despite the feasibility of the top-down method, it is highly challenging to accurately control the thickness of the obtained nanosheets.
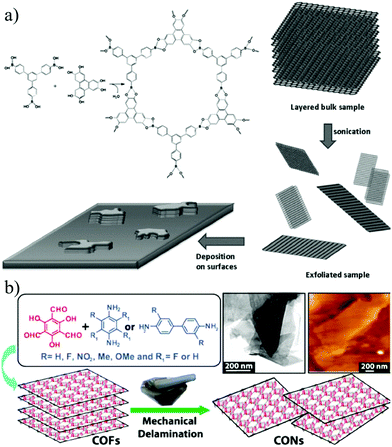 | ||
| Fig. 13 (a) Schematic illustration of the liquid phase exfoliation of COF-8.149 (b) Schematic illustration of COF synthesis by mechanical exfoliation.150 Copyright, 2011 Wiley-VCH and 2013 American Chemical Society. | ||
An alternative strategy is the bottom-up method, in which 2D COF nanosheets or even single molecule layers are formed through the reorganization and self-assembly of building units on a surface of a substrate or at the interface of two liquid phases. Chen et al.151 synthesized a 2D pyrene-based imine COF (Py-COF) by the self-condensation of a bifunctional monomer, 1,6-bis(4-formylphenyl)-3,8-bis(4-aminophenyl)pyrene (BFBAPy), on different substrates such as glass and silicon wafer (Fig. 14a–d). By controlling the initial concentration of the monomer, the membrane thickness can be easily adjusted. Ma et al.152 prepared a 2D cationic EB-COF: Br membrane by using a cationic monomer, through a Schiff base reaction at a liquid–liquid interface. The highly crystalline porous 2D cationic COF nanosheets formed at the liquid–liquid interface and can be easily transferred to various substrates. Then, through a convenient vacuum filtration of the nanosheet dispersion, a continuous and dense COF membrane with controllable thickness can be obtained (Fig. 14e).
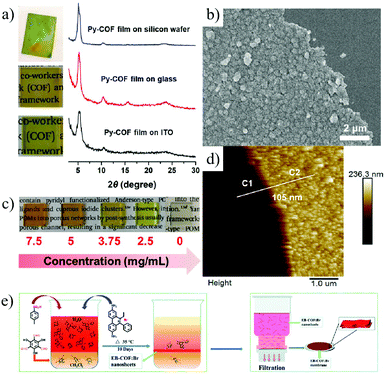 | ||
| Fig. 14 (a) Schematic illustration of Py-COF membranes grown on different substrates. (b) Schematic illustration of Py-COF membranes with different monomer concentrations on glass. (c and d) SEM image and AFM image of Py-COF membranes.151 (e) Schematic illustration of interfacial synthesis of EB-COF: Br nanosheets and preparation of membranes.152 Copyright, 2019 American Chemical Society and 2018 The Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
4. Critical separations
Membrane technology has been commonly used in applications such as ion sieving,153 water purification,154 desalination,155 gas separation,156,157 organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN)158 and so on. However, traditional membranes usually suffer from low permeation and selectivity, resulting in high operating cost. Advances in nanotechnology have inspired the design of new 2D material-based membranes with both higher permeability and selectivity.4.1 Ion sieving
The shortage of pure water all over the world continues to be a problem facing the society. Desalination, that is removal of salts from seawater with high energy-efficiency, will become a vital method to obtain fresh water. Due to their single atom thickness, 2D stacking structure, controllable stacking space and diverse surface functionalities, 2D material membranes are a promising candidate for ion sieving and discrimination.As the first investigated 2D material, graphene and GO have been widely used in water purification and seawater desalination. There are generally two types of graphene or GO membranes. The first one is the single layer graphene membrane with nanoholes. Due to the single atom thickness, the resistance for water permeability can be greatly reduced, leading to an ultrahigh water flux. In 2014, O'Hern et al.36 reported the introduction of reactive defects into the graphene lattice by ion bombardment, and then expanded the defects to small pores with a diameter of 0.40 ± 0.24 nm by oxidation etching. The resulting voids allow the transport of salts, while preventing the permeation of larger organic molecules, demonstrating an ion or molecule sieving ability originating from the small pores. In 2015, Mahurin et al.38 used an oxygen plasma etching process to create nanoscale pores in a single layer graphene, and subsequently adjusted the size of the pores. The resulting membrane exhibited nearly 100% salt (K+, Na+, Li+, and Cl−) rejection and a water flux up to 106 g m−2 s−1 (Fig. 15). Although the nanoporous graphene membrane shows its exceptionally high performance in ion sieving and water permeation, it is still limited to micro-scale sized flakes as enlarging the membrane area will inevitably introduce defects and weaken the mechanical strength. To overcome this dilemma, Duan et al.159 reported a large-area graphene-nanomesh/single-walled carbon nanotube (GNM/SWNT) composite membrane, ensuring the structural integrity of the atomic thick GNM. In this structure, the atomic thick GNM was supported and physically separated by the mechanically strong, interconnected SWNT webs, maintaining the large-area structural integrity of the GNM. The single-layer GNM has high-density, sub-nanometer pores, which can effectively transport water molecules, while preventing the passage of solute ions or organic molecules, and thus achieve size-selective separation. The salt rejection of the composite GNM/SWNT membrane was between 85.2 and 93.4%, with the rejection order of Na2SO4 > MgCl2 > NaCl > KCl (Fig. 16).
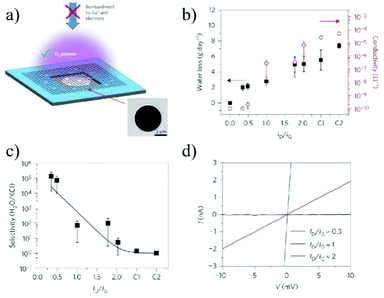 | ||
| Fig. 15 Porous graphene membrane and its water transport and desalination measurements.38 (a) Schematic illustration and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of single-layer graphene suspended on a 5 μm-diameter hole. (b) Water transport measurement through the same porous graphene membranes etched at various exposure times. (c) Water/salt selectivity as a function of the ID/IG ratio showing exceptionally high selectivity for a short etching time. (d) Examples of I–V curves measured in 1 M KCl solution across a porous graphene membrane for different plasma exposure times. Copyright, 2015 Springer Nature. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 16 Schematic illustration of a GNM/SWNT composite membrane and its application for efficient desalination.159 Copyright, 2019 American Association for the Advancement of Science. | ||
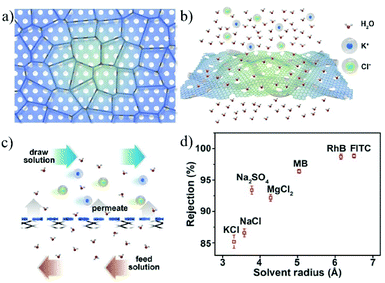
An alternative strategy is to fabricate bulk membranes by stacking the 2D material single layers, with a thickness range from several hundred nanometers to micrometers. GO is the most widely used 2D stacking membrane due to its good hydrophilicity and dispersity in water, as well as its precisely controllable stacking distance. Most importantly, GO can be produced reliably with the chemical exfoliation method, enabling the large-scale fabrication of membranes. In 2014, Nair et al.41 prepared GO membranes with micrometer thickness by vacuum filtering a GO suspension through a porous substrate. It was found that, in the dry state, the GO membrane is vacuum-sealed, while when immersed in water, it acts like a molecular sieve, blocking all solutes with a hydration radius larger than 4.5 Å. In the salt ion diffusion test, the conductivity of NaCl solution increases with time. However, for larger ions, e.g., [Fe(CN)6]3+ and [Ru(bipy)3]2+, with a hydration radius greater than 4.5 Å, the conductivity does not change, indicating that NaCl and [Fe(CN)6]3+ or [Ru(bipy)3]2+ can be completely separated. Impressively, smaller ions pass through the membrane several thousand times faster than simple free diffusion, indicating effective ion separation capability. To achieve more precise controllability on the stacking distance of 2D material membranes, Abraham et al.160 reported physically confined GO (PCGO) membranes, in which the swelling of the GO laminates was mechanically restricted by the epoxy groups. Thus, the interlayer spacing of the GO membranes can be controlled between 0.64 and 0.98 nm after treatment under different humidity conditions. The smaller channel size reduced the ion permeability exponentially; however, it greatly enhanced the rejection of NaCl up to 97%. Chen et al.27 reported the insertion of ions with different hydrated radii (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Li+, or Mg2+) in between the interlayers to precisely control the stacking distance of the GO membrane with an accuracy of 1 Å. The stacking space controlled by one cation can effectively exclude other cations with larger hydrated radii. The permeability of Na+, Mg2+ and Ca2+ through the GO membrane controlled by KCl is even lower than the detection limits, indicating its high ion rejection rate over 99%. This result demonstrates the excellent ion sieving effect of the KCl-controlled GO membrane when compared to the untreated GO membranes (Fig. 17).
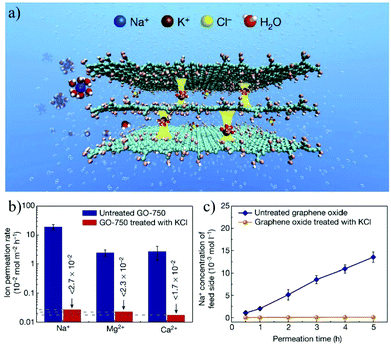 | ||
| Fig. 17 A freestanding GO membrane with cation-controlled interlayer spacing and its ion penetration testing.27 (a) Schematic illustration of the interlayer spacing fixed by K+ ions. (b) Permeability of Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ in untreated and KCl-controlled GO membranes. (c) Na+ permeation through the untreated GOMs and KCl-controlled GO membranes. Copyright, 2017 Springer Nature. | ||
In addition to graphene and GO, other 2D material membranes such as MoS2 and MXenes also show promising ability for effective ion sieving. Aluru et al.161 carried out molecular dynamics simulations to demonstrate that a nanopore in a single layer MoS2 can effectively repel ions, while allowing high-speed transport of water. Their results show that more than 88% of the ions can be rejected by membranes with a pore area of 20 to 60 Å2. Nanopores with only molybdenum atoms on the pore edges result in a higher water flux, which is 70% higher than that of graphene nanopores. Ries et al.162 reported a series of covalently functionalized MoS2 membranes, which can effectively improve the ion sieving performance by controlling the interlayer spacing of the membrane. Under reverse osmosis conditions, the rejection rate of NaCl and water flux are up to 87% and 45 L m−2 h−1 bar−1, respectively. MXene membranes are another recently developed 2D material membranes with thicknesses ranging from several hundred nanometers to several micrometers. They have good flexibility, high mechanical strength and hydrophilicity, which make them potentially promising in separation applications. Gogotsi et al.163 reported the self-assembly of 2D Ti3C2Tx nanosheets into self-standing membranes to selectively reject ions and molecules based on their charge and size, respectively. It was found that the permeation rates for different ions are in the order of Na+ > Li+ > K+ > Ca2+ > Ni2+ > Mg2+ > Al3+, and the micrometer thick MXene membrane showed an ultra-fast water flux of 37.4 L m−2 h−1 bar−1. Ding et al.164 prepared non-swelling MXene membranes by inserting Al3+ ions into the interlayers of the MXene. The strong interaction between Al3+ and the oxygen functional groups on the surface of the MXene can prevent the membrane from swelling, leading to a high rejection rate of 89.5–99.6% for NaCl, and a water flux of 1.1–8.5 L m−2 h−1.
Distinct from the inorganic 2D materials, MOFs possess high surface area and intrinsic microporosity, in which high mass transport efficiency can be expected. Farimani et al.165 used molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the desalination performance of the Ni/Cu-HAB MOF, which indicate that water fluxes through single-layer Ni/Cu-HAB are about one order higher than those of graphene and the MoS2 membrane, and almost 100% of ions can be successfully rejected with the 2 layer MOF membrane. However, the current research studies are mainly focused on the bulk MOF membranes rather than layered MOF membranes, due to the difficulty in obtaining high quality single- or few-layer MOFs.
4.2 Nanofiltration
Nanofiltration is thought to be able to separate monovalent and divalent ions in aqueous solution or separate large organic molecules with molecular weights of 200–1000 g mol−1 from organic solvents.166 Among various membrane separation technologies, nanofiltration has the characteristics of a large solvent flux and low operating pressure when compared with the reverse osmosis process.167 With the features of the stacking structure with tunable interlayer space and surface properties, 2D material membranes have become one of the most promising nanofiltration membranes for water purification and chemical and pharmaceutical separations.168,169Due to their nanoscale pores and hydrophilic pore surfaces, 2D material membranes find wide applications in the removal of large organic molecules from aqueous solutions.170,171 Gao et al.31 prepared 22–53 nm thick ultra-thin graphene nanofiltration membranes (uGNMs) by a vacuum assisted assembly strategy. The as-prepared graphene membrane is highly efficient at removing organic dyes (such as methyl blue and direct red) from water with a rejection rate of more than 99% and a pure water flux up to 21.8 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 (Fig. 18). Owing to the ultra-thin characteristic, 34 mg of the raw material is sufficient to produce a one-square-meter nanofiltration membrane, which demonstrates that the graphene nanofiltration membrane can be produced on a large scale with relatively low-cost. Min et al.172 designed an MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/MCE (mixed cellulose ester) composite membrane. Taking both the merits of the ultra-small interlayer distance of the MXene laminate and high porosity of the MCE layer, the MXene/MCE composite membrane shows high water permeability and excellent removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. The highest pure water flux of the MXene/MCE membrane is up to 119.83 ± 6.22 L m−2 h−1 and the rejection rate for methylene blue is 100%. Wang et al.173 reported the fabrication of Mxene membranes by filtering 2D Ti3C2Tx layers through an anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) substrate. Thanks to the short transport paths and large amount of nanochannels, the Ti3C2Tx MXene membrane shows a high water permeability of more than 1000 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 and a rejection rate of 90% for molecules larger than 2.5 nm. Peng et al.174 reported the assembly of chemically exfoliated WS2 nanosheets into a layered membrane and it was used to selectively separate small molecules from water. The thinnest WS2 membrane (300 nm) can reject more than 90% of Evans Blue (EB) with a molecular size around 3 nm. The water flux through the membrane can reach 730 L m−2 h−1 bar−1. Hong et al.175 assembled 2D Zn-TCP (Fe) nanosheets to obtain a defect-free ultra-thin 2D MOF membrane with a thickness of about 48 nm. The membrane can reject more than 90% of methyl red with a molecular size of 0.8 × 1.1 nm. Most importantly, this membrane shows an extremely high-water flux of 4243 L m−2 h−1 bar−1. This ultra-high water permeance is probably due to the large number of oxygen-containing groups in Zn-TCP (Fe) which makes the membrane more hydrophilic, and thus results in faster water transport speed.
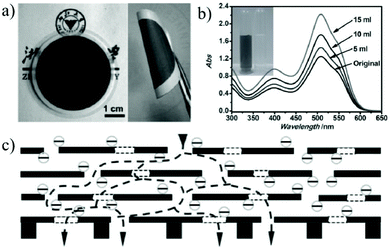 | ||
| Fig. 18 (a) Optical image of the uGNM membrane coated on an AAO substrate. (b) The absorbance changes of the upper stream of DR 81 solution when the permeation volumes were 5, 10, and 15 mL under a pressure of 5 bar. (c) Schematic illustration of the possible permeation route: water molecules go through both the interlayer space of the uGNMs and the nanoholes on the graphene nanosheets and finally reach the supporting membranes.31 Copyright, 2013 Wiley-VCH. | ||
Besides the wide applications in the aqueous phase, 2D material membranes also show their great potential in organic solvent nanofiltration, which represents an important separation process in the organic phase. The traditional OSN membranes are mostly polymeric materials with poor resistance to organic solvents. In contrast, the good stability of graphene and graphene derivatives in various organic solvents makes them ideal materials for OSN. Huang et al.176 prepared semi-permeable GO membranes by thermal annealing or solvent changing methods. The nanochannel of the as-prepared GO membrane is 0.98 nm in ethanol, which allows small molecules such as toluene, acetone, and pyrene to pass through, while blocking the passage of large molecules such as Lumogen Red 300. Shi et al.177 reported an 18 nm thick OSN membrane prepared by depositing solvent solvated reduced graphene oxide (S-rGO) on a microporous substrate. The membrane shows a high acetone permeance of 215 L m−2 h−1 bar−1, with good stability in various organic solvents such as methanol, acetone and dimethylformamide. It was found that the original rGO coating showed high rejection to small negatively charged molecules probably due to the negatively charged surface caused by the ionization of the residual carboxyl groups on the S-rGO surface. Neutral solutes with a molecular size larger than the interlayer space (about 3.4 nm) can also be completely rejected. In contrast, the S-rGO membrane can be functionalized with hyperbranched poly(ethylene imine) (HPEI), leading to a positively charged surface with high rejection of positively charged molecules (Fig. 19). Li et al.178 prepared a 1.5 μm thick GO membrane by depositing GO nanosheets on a ceramic hollow fiber membrane. The as-prepared GO hollow fiber membrane can reject molecules larger than 300 Da in acetone and methanol, with the permeance of methanol and acetone up to 3.97 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 and 6.35 L m−2 h−1 bar−1, respectively. In addition, the nanochannels of the GO membrane will not be blocked by macromolecules.
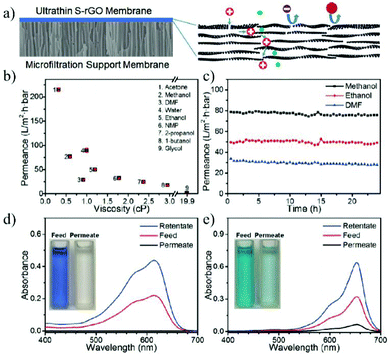 | ||
| Fig. 19 (a) Schematic illustration of the ultrathin S-rGO membrane coated on the surface of a microporous substrate and the separation mechanism of the S-rGO membrane. (b–e) The nanofiltration performance of S-rGO and HPEI/S-rGO membranes.177 Copyright, 2016 Wiley-VCH. | ||
4.3 Gas separation
Gas separations, such as H2/CH4 separation,179 olefin/paraffin separation180 and air purification,181 are significantly important in industry. Methods for separating gases in industry include distillation,182 absorption,183 and membrane separation.184 Among these, the first two are high energy-consuming processes that increase CO2 emissions and global pollution. While the membrane process is considered to be a more promising strategy due to its low energy consumption. At present, industrial gas separations are mostly realized with synthetic membranes made of traditional polymers.185 Although some rigid and microporous polymers, such as polymers with intrinsic microporosity (PIM)186 have been developed to increase the gas permeability and selectivity, the poor mass transport and separation performance caused by their small pore size, broad pore size distribution and poor thermal and chemical stability under harsh conditions still significantly restrict the overall separation efficiency of the polymer-based membranes. The 2D material membranes have been demonstrated to show great advantages over the traditional polymer-based membranes owing to their robustness, controllable pore size and facile functionalization.Molecular simulations have shown that nanopores in single layer graphene exhibit high gas permeance, which is orders of magnitude higher than that of traditional polymeric membranes.187 This high gas permeation can greatly reduce the membrane area required for gas separation. Agrawal et al.188 prepared a large-area single-layer graphene membrane by nanoporous-carbon-assisted transfer technology. On one hand, this membrane contains molecular level nanopores with a porosity of 0.025%, which can selectively transport H2 over larger gases. The H2 permeability is as high as 4.1 × 10−7 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1, and the separation coefficient of H2/CH4 is up to 25. On the other hand, the single-layer thickness can minimize gas transmission resistance and maximize gas permeance. Despite the high gas separation performance of the single-layer graphene membrane, the difficulty in large membrane fabrication and low density of nanopores greatly prohibit their practical application. In this context, the stacking GO membranes are further investigated (Fig. 20a and b). Yu et al.74 prepared an ultra-thin GO membrane with a thickness of approximately 1.8 nm by a simple filtration process. The selectivity of these membranes for H2/CO2 and H2/N2 mixtures are as high as 3400 and 900, respectively. Despite the high gas selectivity, the H2 permeance is relatively low (<3.0 × 10−7 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1), probably due to the low density of random defects in the ultrathin GO membrane. It is believed that the main transport route for gases in this membrane is through selective structural defects, rather than the stacking space between the GO nanosheets. However, when GO sheets are stacked into a thicker membrane, it is easy to form a random laminar flow structure, which will inevitably reduce the gas selectivity (Fig. 20c and b).
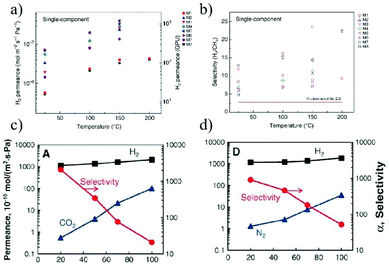 | ||
| Fig. 20 (a and b) Separation of H2/CH4 by single layer graphene membranes.188 (a) H2 permeance of eight graphene membranes (M1–M8) at different temperatures. (b) Ideal H2/CH4 selectivity as a function of temperature. (c and d) H2/N2 separation through stacking GO membranes.74 The separation performance of H2/CO2 through 1.8 nm (c) and 9 nm (d) thick GO membranes. Copyright, 2018 Springer Nature and 2013 American Association for the Advancement of Science. | ||
Due to their good chemical and thermal stability, MoS2 membranes are also used for high performance gas separation. Jin et al.189 for the first time reported the utilization of the MoS2 membrane for high-permeation H2/CO2 separation. The ultra-thin MoS2 membranes were successfully prepared via an ultrafiltration deposition method, with thicknesses of 17 ± 1 nm, 35 ± 2 nm, and 60 ± 2 nm. Among them, the 17 nm-thick MoS2 membrane shows the highest gas permeation rate, with H2 permeance up to 9.37 × 10−6 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1, and the H2/CO2 selectivity greater than 3. The ideal selectivity of the three membranes for H2/CO2 are all between 3 and 4. It is revealed that the transport pathway of gas molecules is the stacking space between MoS2 nanosheets in the membrane. Different from GO or MoS2, MXenes represent another 2D material, with a variety of groups (such as O, OH and F) distributed on the surface of the nanosheets, leading to nanochannels with a highly controllable pore surface. Gogotsi et al.83 reported the preparation of laminar MXene membranes with sub-nanometer channels, showing excellent gas separation performance. The permeance of H2 exceeds 3.68 × 10−7 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1, and the selectivity of H2/CO2 is greater than 160. Molecular dynamics simulations revealed that the sub-nanometer spacing between adjacent MXene nanosheets acts as molecular sieving channels for gas separation (Fig. 21a and b). Through high-temperature processing, the interlayer distance of the MXene can be adjusted to further improve its gas separation performance. Fan et al.190 prepared 2D laminar MXene membranes through vacuum filtration and a subsequent drying process. After high temperature treatment at 500 °C, the interlayer spacing of the MXene membrane was reduced from 3.4 Å to 2.7 Å. The reduction of the interlayer spacing improves the separation performance of gas molecules, with a H2 permeance up to 2.0 × 10−7 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1 and a H2/N2 mixture selectivity of 41.
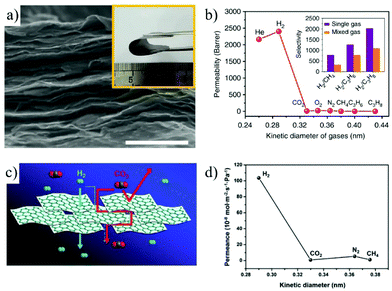 | ||
| Fig. 21 (a and b) Gas permeance through the MXene membrane.83 (a) SEM image of the MXene membrane surface (scale bar, 500 nm). Inset is a photograph of the MXene membrane. (b) Single gas permeance through the MXene membrane as a function of the gas kinetic diameter. (c and d) Schematic illustration of H2/CO2 separation with the porous Zn2(Bim)3 membrane and single gas permeation.191 Copyright, 2018 Springer Nature and 2017 Wiley-VCH. | ||
The intrinsic micropores with controllable pore size and surface, combined with diverse chemical structures of 2D MOFs make them particularly attractive for the preparation of molecular sieving membranes. Peng et al.136 prepared one-nanometer-thick Zn2(bim)4 nanosheets by ball milling, followed by vacuum-filtering to generate a Zn2(bim)4 molecular sieve membrane on an a-Al2O3 substrate. The resulting membrane shows a H2 permeance as high as 9.04 × 10−7 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1 and a H2/CO2 selectivity up to 291. Yang et al.191 reported an improved soft physical exfoliation method to exfoliate a few layered MOF, Zn2(Bim)3, into 2D nanoflakes, and successfully prepared sub-10 nm thick ultrathin MOF membranes. The as-prepared membranes exhibit excellent H2/CO2 separation performance, with a separation coefficient as high as 166, and a H2 permeance up to 8 × 10−7 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1. It was found that only small H2 molecules can pass through the intrinsic micropores of the nanosheets, while larger CO2 molecules transport through the tortuous interlayer channels of the membrane (Fig. 21c and d).
Caro et al.192 first synthesized vertical 2D COF layers as gas separation membranes by growing parallel to CoAl-layered double hydroxides (LDHs) and growing vertically on the substrate. The gas is transported through the vertical COF-LZU1 membrane interlayer space. These vertical COF membranes show ultra-high H2 permeance and excellent H2 transmission selectivity, with a high H2 permeance of 1.2 × 10−6 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1, and a separation factor of H2/C3H8 as high as 119.5 (Fig. 22).
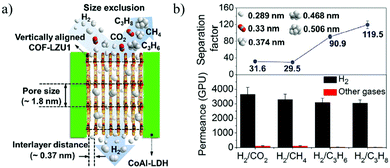 | ||
| Fig. 22 (a) Schematic illustration of the gas passing through the vertically arranged COF-LZU1 membrane. (b) Penetration and separation factors of the COF-LZU1 membrane for different mixed gases.192 Copyright, 2020 American Chemical Society. | ||
Beyond small gas molecules, 2D material membranes are also widely adopted for the separation of large organic gases, such as n-butane/isobutane. Tsapatsis et al.123 for the first time prepared a 4 nm thick MFI molecular sieve membrane by vacuum filtration for the separation of hydrocarbon isomers. In the single-component gas permeation measurement, the membrane displays an n-butane permeance of 3.5 × 10−7 mol m−2 s−1 Pa−1, with an ideal selectivity of 5.4 for the n-butane/isobutane mixture.
4.4 Chiral molecule separation
The chiral separation of enantiomers is of great importance in both life science and the pharmaceutical industry.193 Various separation techniques have been used for chiral molecule separation, such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC),194 gas chromatography (GC),195 high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)196 and membrane technology,197 among which, the membrane process has attracted growing research attention in recent years, due to its low cost and easy operation. Although traditional polymeric membranes have been widely used, chiral separations based on the 2D material membranes are still very limited.Liu et al.48 first reported the separation of chiral molecules using chiral selector (L-glutamic acid) functionalized GO membranes. The L-glutamic acid not only stabilizes the stacked GO nanosheets, but also acts as a spacing regulator to control the stacking distance of the GO layers. The enantiomeric separation performance of the L-glutamic acid modified GO (Glu-GO) membrane for 3,4-dihydroxy-D,L-phenylalanine (D-,L-DOPA) is 1–2 orders of magnitude higher than that of the ordinary chiral separation membrane, with a maximum selectivity exceeding 2.0. In addition to chiral resolution, the graphene membrane has also been used for chiral molecular sensing.198
Graphitic carbon nitride (GCN) is a new 2D layered material with defined distribution of nitrogen atoms. The solitary electrons on nitrogen can be protonated by a proton or functionalized by various anions; thus the interlayer spacing can be precisely regulated at the sub-nanometer scale. Liu et al.199 reported the preparation of a functionalized GCN membrane by introducing a chiral camphor sulfonic acid (CSA) in between the GCN interlayers. With the interlayer spacing being precisely controlled by protons or ions, the membrane shows a molecular weight cut-off of about 150 g mol−1 and high permeation for both water and organic solutions. More importantly, the membrane exhibits a strong enantioselectivity for limonene, with an ee value as high as 89% (Fig. 23). This work provides a new research idea for precisely regulating the interlayer spacing and chemical environment of 2D material membranes and broadening their further application in some specific fields, such as pharmaceutical and biological separations.
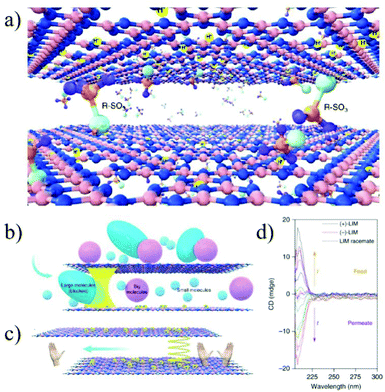 | ||
| Fig. 23 Schematic illustration of the GCN membrane with chiral nanochannels and its application for chiral separation.199 Copyright, 2019 Springer Nature. | ||
5. Conclusion and outlook
In this paper, we reviewed the 2D material membrane as an emerging material system for promising separation applications. Undoubtedly, 2D materials represent a unique choice for the construction of membranes with nanochannels that can selectively transport ions or organic molecules with very similar size. On one hand, the 2D material membrane can be fabricated on a large scale by a facile filtration process, endowing them with the capability of industrial application. On the other hand, the stacking channels are unique when compared with other porous materials with intrinsic microporosity. Specifically, the small stacking space, in some cases down to sub-nanometers, can afford higher resolution than other porous materials (such as COFs and MOFs) whose pore sizes are limited by the size of the organic monomers. Despite the advantages, the development of 2D material membranes for separation application is still in its infancy and further research studies are still needed in the following areas.To synthesize 2D material nanosheets with controllable and uniform thickness, as well as functionality. Although the exfoliation of a wide range of 2D materials has been intensively studied, the precise control on the thickness and surface properties of the exfoliated nanosheets is still far from satisfactory. On one hand, most of the current strategies can only afford nanosheets with broad thickness distribution. On the other hand, it is still highly challenging to functionalize the surface of the exfoliated nanosheets in a controllable way, such as precisely controlling the functional groups and their density on the surface. Considering that the 2D nanosheets are the basic building blocks for membrane fabrication, developing new methodologies to produce high-quality 2D materials with uniform thickness and surface functionality is of great significance for improving the separation performance of the 2D material-derived membrane.
The chemical and structural stability of the 2D material membrane needs to be further improved for further application. Long-term stability is one of the crucial features for a separation membrane. However, most of the 2D material membranes undergo structural deformation in solution, because the layered architecture is maintained by weak van der Waals forces, which usually result in dissociation of the 2D layers when the membrane is immersed in a solution for a long time. Thus, finding ways to maintain both the chemical and structural stability in various solvents is still a somewhat open challenge for 2D material membranes and need to be explored in more detail.
Developing new strategies to precisely control the stacking distance and surface properties of the nanochannels. Different from the intrinsic microporous materials, the selectivity of the 2D material membrane largely depends on the interlayer stacking distance. However, the controllability of the accuracy of the interlayer spacing is far from satisfactory, especially for some fine separations, in which discrimination of substances with very similar sizes is required. For example, it is still very challenging to separate mono- and double-valent ions or even isovalent ions with very similar hydrated radii. In this respect, the interlayer distance and surface properties are the two key parameters for the design of future 2D material membranes for fine separations.
Finally, understanding the mechanism of selective mass transport in confined channels will provide the guideline for rational design of 2D material membranes with remarkable separation performance. Currently, the separation in the stacking channels of 2D material membranes is generally ascribed to either size exclusion or chemical interactions. The investigation on the theory and models for mass transport in stacked channels is still very scarce, and represents a very important research direction in the future.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2016YFA0200700, Z. Y. T.), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21890381 and 21721002, Z. Y. T.), Frontier Science Key Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDJ-SSW-SLH038, Z. Y. T.), K.C. Wong Education Foundation (Z. Y. T.), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21922504, L. S. L.), Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2018046, L. S. L.) and the Program of Tianjin Science and Technology Major Project and Engineering (19ZXYXSY00090).Notes and references
- W. T. Choate, Energy and emission reduction opportunities for the cement industry, BCS, Incorporated, 2003 Search PubMed.
- D. S. Sholl and R. P. Lively, Seven chemical separations to change the world, Nat. News, 2016, 532, 435 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. L. Gin and R. D. Noble, Designing the next generation of chemical separation membranes, Science, 2011, 332, 674–676 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Huang, Y. Mao, Y. Ying, Y. Liu, L. Sun and X. Peng, Salt concentration, pH and pressure controlled separation of small molecules through lamellar graphene oxide membranes, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 5963–5965 RSC.
- M. Hu and B. Mi, Enabling graphene oxide nanosheets as water separation membranes, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 3715–3723 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Das, M. E. Ali, S. B. A. Hamid, S. Ramakrishna and Z. Z. Chowdhury, Carbon nanotube membranes for water purification: a bright future in water desalination, Desalination, 2014, 336, 97–109 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Matsuura, Progress in membrane science and technology for seawater desalination—a review, Desalination, 2001, 134, 47–54 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Shen, G. Liu, K. Huang, Z. Chu, W. Jin and N. Xu, Subnanometer two-dimensional graphene oxide channels for ultrafast gas sieving, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 3398–3409 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. B. Shinde, G. Sheng, X. Li, M. Ostwal, A. H. Emwas, K.-W. Huang and Z. Lai, Crystalline 2D covalent organic framework membranes for high-flux organic solvent Nanofiltration, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 14342–14349 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D.-Y. Koh, B. A. McCool, H. W. Deckman and R. P. Lively, Reverse osmosis molecular differentiation of organic liquids using carbon molecular sieve membranes, Science, 2016, 353, 804–807 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Cui and T. S. Chung, Pharmaceutical concentration using organic solvent forward osmosis for solvent recovery, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 1–9 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Y. Chan, H. Zhang, Y. Nolvachai, Y. Hu, H. Zhu, M. Forsyth, Q. Gu, D. E. Hoke, X. Zhang and P. J. Marriot, Incorporation of homochirality into a zeolitic imidazolate framework membrane for efficient chiral separation, Angew. Chem., 2018, 130, 17376–17380 CrossRef.
- X. Zhuang, F. Zhang, D. Wu and X. Feng, Graphene coupled Schiff-base porous polymers: towards nitrogen-enriched porous carbon nanosheets with ultrahigh electrochemical capacity, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 3081–3086 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. D. Guiver and Y. M. Lee, Polymer rigidity improves microporous membranes, Science, 2013, 339, 284–285 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Li, Y. Liu, J. Wang, J. Gascon, J. Li and B. Van der Bruggen, Metal–organic frameworks based membranes for liquid separation, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 7124–7144 RSC.
- K. Dey, M. Pal, K. C. Rout, S. Kunjattu H, A. Das, R. Mukherjee, U. K. Kharul and R. Banerjee, Selective molecular separation by interfacially crystallized covalent organic framework thin films, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 13083–13091 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Tan, X. Cao, X. J. Wu, Q. He, J. Yang, X. Zhang, J. Chen, W. Zhao, S. Han and G.-H. Nam, Recent advances in ultrathin two-dimensional nanomaterials, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 6225–6331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Gugliuzza, A. Politano and E. Drioli, The advent of graphene and other two-dimensional materials in membrane science and technology, Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng., 2017, 16, 78–85 CrossRef.
- N. Song, X. Gao, Z. Ma, X. Wang, Y. Wei and C. Gao, A review of graphene-based separation membrane: Materials, characteristics, preparation and applications, Desalination, 2018, 437, 59–72 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Mi, Graphene oxide membranes for ionic and molecular sieving, Science, 2014, 343, 740–742 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Liu, J. Shen, Q. Liu, G. Liu, J. Xiong, J. Yang and W. Jin, Ultrathin two-dimensional MXene membrane for pervaporation desalination, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 548, 548–558 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Tan and H. Zhang, Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheet-based composites, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 2713–2731 RSC.
- M. Tsapatsis, 2-dimensional zeolites, AIChE J., 2014, 60, 2374–2381 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhao, Q. Lu, Q. Ma and H. Zhang, Two-Dimensional Metal–Organic Framework Nanosheets, Small Methods, 2017, 1, 1600030 CrossRef.
- Q. Lu, M. Zhao, J. Chen, B. Chen, C. Tan, X. Zhang, Y. Huang, J. Yang, F. Cao and Y. Yu, Synthesis of Metal Sulfide Nanoparticles Based on 2D Metal-Organic Framework Nanosheets, Small, 2016, 12, 4669–4674 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. A. Kuehl, J. Yin, P. H. Duong, B. Mastorovich, B. Newell, K. D. Li-Oakey, B. A. Parkinson and J. O. Hoberg, Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework with Modifiable Pores, and Its Application in Water Purification and Ion Sieving, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 18200–18207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Chen, G. Shi, J. Shen, B. Peng, B. Zhang, Y. Wang, F. Bian, J. Wang, D. Li and Z. Qian, Ion sieving in graphene oxide membranes via cationic control of interlayer spacing, Nature, 2017, 550, 380 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Sun, M. Zhu, K. Wang, M. Zhong, J. Wei, D. Wu, Z. Xu and H. Zhu, Selective ion penetration of graphene oxide membranes, ACS Nano, 2012, 7, 428–437 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. h. Song, H. W. Yu, M.-H. Ham and I. S. Kim, Tunable Ion Sieving of Graphene Membranes through the Control of Nitrogen-Bonding Configuration, Nano Lett., 2018, 18, 5506–5513 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Kang, Y. Peng, Y. Qian, D. Yuan, M. A. Addicoat, T. Heine, Z. Hu, L. Tee, Z. Guo and D. Zhao, Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising exfoliated 2D covalent organic frameworks (COFs) for efficient CO2 separation, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28, 1277–1285 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Han, Z. Xu and C. Gao, Ultrathin graphene nanofiltration membrane for water purification, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23, 3693–3700 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. You, V. Sahajwalla, M. Yoshimura and R. K. Joshi, Graphene and graphene oxide for desalination, Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 117–119 RSC.
- S. Garaj, W. Hubbard, A. Reina, J. Kong, D. Branton and J. Golovchenko, Graphene as a subnanometre trans-electrode membrane, Nature, 2010, 467, 190 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Fox, A. O'Neill, D. Zhou, M. Boese, J. Coleman and H. Zhang, Nitrogen assisted etching of graphene layers in a scanning electron microscope, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2011, 98, 243117 CrossRef.
- S. P. Koenig, L. Wang, J. Pellegrino and J. S. Bunch, Selective molecular sieving through porous graphene, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2012, 7, 728 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. C. O'Hern, M. S. Boutilier, J. C. Idrobo, Y. Song, J. Kong, T. Laoui, M. Atieh and R. Karnik, Selective ionic transport through tunable subnanometer pores in single-layer graphene membranes, Nano Lett., 2014, 14, 1234–1241 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Celebi, J. Buchheim, R. M. Wyss, A. Droudian, P. Gasser, I. Shorubalko, J. I. Kye, C. Lee and H. G. Park, Ultimate permeation across atomically thin porous graphene, Science, 2014, 344, 289–292 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. P. Surwade, S. N. Smirnov, I. V. Vlassiouk, R. R. Unocic, G. M. Veith, S. Dai and S. M. Mahurin, Water desalination using nanoporous single-layer graphene, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2015, 10, 459 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Diankov, M. Neumann and D. Goldhaber-Gordon, Extreme monolayer-selectivity of hydrogen-plasma reactions with graphene, ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 1324–1332 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. S. Safron, A. S. Brewer and M. S. Arnold, Semiconducting Two-Dimensional Graphene Nanoconstriction Arrays, Small, 2011, 7, 492–498 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Joshi, P. Carbone, F. C. Wang, V. G. Kravets, Y. Su, I. V. Grigorieva, H. Wu, A. K. Geim and R. R. Nair, Precise and ultrafast molecular sieving through graphene oxide membranes, Science, 2014, 343, 752–754 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Huang, X. Y. Kong, L. Wen and L. Jiang, Bioinspired ionic diodes: From unipolar to bipolar, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1801079 CrossRef.
- Z. Zhang, L. Wen and L. Jiang, Bioinspired smart asymmetric nanochannel membranes, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 322–356 RSC.
- P. Liu, Y. Sun, C. Zhu, B. Niu, X. Huang, X.-Y. Kong, L. Jiang and L. Wen, Neutralization Reaction Assisted Chemical-Potential-Driven Ion Transport through Layered Titanium Carbides Membrane for Energy Harvesting, Nano Lett., 2020, 20, 3593–3601 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Sun, H. Huang and X. Peng, Laminar MoS2 membranes for molecule separation, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 10718–10720 RSC.
- F. Xu, M. Wei, X. Zhang and Y. Wang, Ion Rejection in Covalent Organic Frameworks: Revealing the Overlooked Effect of In-Pore Transport, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 45246–45255 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Shen, G. Liu, K. Huang, W. Jin, K. R. Lee and N. Xu, Membranes with fast and selective gas-transport channels of laminar graphene oxide for efficient CO2 capture, Angew. Chem., 2015, 127, 588–592 CrossRef.
- C. Meng, Y. Sheng, Q. Chen, H. Tan and H. Liu, Exceptional chiral separation of amino acid modified graphene oxide membranes with high-flux, J. Membr. Sci., 2017, 526, 25–31 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Nair, H. Wu, P. Jayaram, I. Grigorieva and A. Geim, Unimpeded permeation of water through helium-leak–tight graphene-based membranes, Science, 2012, 335, 442–444 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Huang, Z. Song, N. Wei, L. Shi, Y. Mao, Y. Ying, L. Sun, Z. Xu and X. Peng, Ultrafast viscous water flow through nanostrand-channelled graphene oxide membranes, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 2979 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Xie, P. Li, Z. Zhao, Z. Zhu, X.-Y. Kong, Z. Zhang, K. Xiao, L. Wen and L. Jiang, Light-and electric-field-controlled wetting behavior in nanochannels for regulating nanoconfined mass transport, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 4552–4559 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Torres, Graphene chemistry, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 4385–4386 RSC.
- K. S. Novoselov, A. K. Geim, S. V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S. V. Dubonos, I. V. Grigorieva and A. A. Firsov, Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films, Science, 2004, 306, 666–669 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Gupta, T. Sakthivel and S. Seal, Recent development in 2D materials beyond graphene, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2015, 73, 44–126 CrossRef CAS.
- A. T. Smith, A. M. LaChance, S. Zeng, B. Liu and L. Sun, Synthesis, properties, and applications of graphene oxide/reduced graphene oxide and their nanocomposites, Nano Mater. Sci., 2019, 1, 31–47 CrossRef.
- K. Erickson, R. Erni, Z. Lee, N. Alem, W. Gannett and A. Zettl, Determination of the local chemical structure of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 4467–4472 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Suk, R. D. Piner, J. An and R. S. Ruoff, Mechanical properties of monolayer graphene oxide, ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 6557–6564 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. R. Dreyer, S. Park, C. W. Bielawski and R. S. Ruoff, The chemistry of graphene oxide, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 228–240 RSC.
- R. Zbořil, F. Karlický, A. B. Bourlinos, T. A. Steriotis, A. K. Stubos, V. Georgakilas, K. Šafářová, D. Jančík, C. Trapalis and M. Otyepka, Graphene fluoride: a stable stoichiometric graphene derivative and its chemical conversion to graphene, Small, 2010, 6, 2885–2891 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Long, L. Tang, D. Wang, Y. Li and Z. Shuai, Electronic structure and carrier mobility in graphdiyne sheet and nanoribbons: theoretical predictions, ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 2593–2600 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Liu, W. Jin and N. Xu, Graphene-based membranes, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 5016–5030 RSC.
- D. Cohen-Tanugi and J. C. Grossman, Water desalination across nanoporous graphene, Nano Lett., 2012, 12, 3602–3608 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Jiang, V. R. Cooper and S. Dai, Porous graphene as the ultimate membrane for gas separation, Nano Lett., 2009, 9, 4019–4024 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Li, W. Cai, J. An, S. Kim, J. Nah, D. Yang, R. Piner, A. Velamakanni, I. Jung and E. Tutuc, Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils, Science, 2009, 324, 1312–1314 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. S. Kim, Y. Zhao, H. Jang, S. Y. Lee, J. M. Kim, K. S. Kim, J.-H. Ahn, P. Kim, J.-Y. Choi and B. H. Hong, Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes, Nature, 2009, 457, 706 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hernandez, V. Nicolosi, M. Lotya, F. M. Blighe, Z. Sun, S. De, I. McGovern, B. Holland, M. Byrne and Y. K. Gun'Ko, High-yield production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008, 3, 563 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Shams, R. Zhang and J. Zhu, Graphene synthesis: a Review, Mater. Sci. Polym., 2015, 33, 566–578 CAS.
- J. H. Lee, E. K. Lee, W. J. Joo, Y. Jang, B. S. Kim, J. Y. Lim, S. H. Choi, S. J. Ahn, J. R. Ahn and M. H. Park, Wafer-scale growth of single-crystal monolayer graphene on reusable hydrogen-terminated germanium, Science, 2014, 344, 286–289 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Yi and Z. Shen, A review on mechanical exfoliation for the scalable production of graphene, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 11700–11715 RSC.
- R. Joshi, S. Alwarappan, M. Yoshimura, V. Sahajwalla and Y. Nishina, Graphene oxide: the new membrane material, Appl. Mater. Today, 2015, 1, 1–12 CrossRef.
- W. S. Hummers Jr. and R. E. Offeman, Preparation of graphitic oxide, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1958, 80, 1339–1339 CrossRef.
- D. C. Marcano, D. V. Kosynkin, J. M. Berlin, A. Sinitskii, Z. Sun, A. Slesarev, L. B. Alemany, W. Lu and J. M. Tour, Improved synthesis of graphene oxide, ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 4806–4814 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Hou, H. Wang, Q. Zhang, Y. Li and M. Zhu, Highly conductive, flexible, and compressible all-graphene passive electronic skin for sensing human touch, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 5018–5024 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Li, Z. Song, X. Zhang, Y. Huang, S. Li, Y. Mao, H. J. Ploehn, Y. Bao and M. Yu, Ultrathin, molecular-sieving graphene oxide membranes for selective hydrogen separation, Science, 2013, 342, 95–98 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. W. Kim, H. W. Yoon, S. M. Yoon, B. M. Yoo, B. K. Ahn, Y. H. Cho, H. J. Shin, H. Yang, U. Paik and S. Kwon, Selective gas transport through few-layered graphene and graphene oxide membranes, Science, 2013, 342, 91–95 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Sun, M. Zhu, K. Wang, M. Zhong, J. Wei, D. Wu, Z. Xu and H. Zhu, Selective ion penetration of graphene oxide membranes, ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 428–437 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Hu and B. Mi, Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide membranes via electrostatic interaction, J. Membr. Sci., 2014, 469, 80–87 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Naguib, V. N. Mochalin, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, 25th anniversary article: MXenes: a new family of two-dimensional materials, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 992–1005 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Anasori, M. R. Lukatskaya and Y. Gogotsi, 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2017, 2, 16098 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Naguib, M. Kurtoglu, V. Presser, J. Lu, J. Niu, M. Heon, L. Hultman, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2, Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 4248–4253 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Naguib, O. Mashtalir, J. Carle, V. Presser, J. Lu, L. Hultman, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Two-dimensional transition metal carbides, ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 1322–1331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, H. B. Zhang, R. Sun, Y. Liu, Z. Liu, A. Zhou and Z. Z. Yu, Hydrophobic, flexible, and lightweight MXene foams for high-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1702367 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Ding, Y. Wei, L. Li, T. Zhang, H. Wang, J. Xue, L. X. Ding, S. Wang, J. Caro and Y. Gogotsi, MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 155 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Ghidiu, J. Halim, S. Kota, D. Bish, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Ion-exchange and cation solvation reactions in Ti3C2 MXene, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28, 3507–3514 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ghidiu, M. R. Lukatskaya, M. Q. Zhao, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay'with high volumetric capacitance, Nature, 2014, 516, 78 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Lipatov, M. Alhabeb, M. R. Lukatskaya, A. Boson, Y. Gogotsi and A. Sinitskii, Effect of synthesis on quality, electronic properties and environmental stability of individual monolayer Ti3C2 MXene flakes, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2016, 2, 1600255 CrossRef.
- O. Mashtalir, M. R. Lukatskaya, M. Q. Zhao, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, Amine-assisted delamination of Nb2C MXene for Li-ion energy storage devices, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 3501–3506 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhou, X. Zha, F. Y. Chen, Q. Ye, P. Eklund, S. Du and Q. Huang, A two-dimensional zirconium carbide by Selective etching of Al3C3 from nanolaminated Zr3Al3C5, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 5008–5013 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Shen, G. Liu, Y. Ji, Q. Liu, L. Cheng, K. Guan, M. Zhang, G. Liu, J. Xiong and J. Yang, 2D MXene nanofilms with tunable gas transport channels, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1801511 CrossRef.
- S. Manzeli, D. Ovchinnikov, D. Pasquier, O. V. Yazyev and A. Kis, 2D transition metal dichalcogenides, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2017, 2, 17033 CrossRef CAS.
- R. G. Dickinson and L. Pauling, The crystal structure of molybdenite, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1923, 45, 1466–1471 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Radisavljevic, A. Radenovic, J. Brivio, V. Giacometti and A. Kis, Single-layer MoS2 transistors, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2011, 6, 147 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Chhowalla, H. S. Shin, G. Eda, L. J. Li, K. P. Loh and H. Zhang, The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets, Nat. Chem., 2013, 5, 263 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Frindt and A. Yoffe, Physical properties of layer structures: optical properties and photoconductivity of thin crystals of molybdenum disulphide, Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1963, 273, 69–83 Search PubMed.
- P. Joensen, R. Frindt and S. R. Morrison, Single-layer MoS2, Mater. Res. Bull., 1986, 21, 457–461 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Wei, B. Li, C. Xia, Y. Cui, J. He, J. B. Xia and J. Li, Various Structures of 2D Transition-Metal Dichalcogenides and Their Applications, Small Methods, 2018, 2, 1800094 CrossRef.
- X. Cui, G. H. Lee, Y. D. Kim, G. Arefe, P. Y. Huang, C. H. Lee, D. A. Chenet, X. Zhang, L. Wang and F. Ye, Multi-terminal transport measurements of MoS2 using a van der Waals heterostructure device platform, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2015, 10, 534 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. C. Knirsch, N. C. Berner, H. C. Nerl, C. S. Cucinotta, Z. Gholamvand, N. McEvoy, Z. Wang, I. Abramovic, P. Vecera and M. Halik, Basal-plane functionalization of chemically exfoliated molybdenum disulfide by diazonium salts, ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 6018–6030 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhou, J. Lin, X. Huang, Y. Zhou, Y. Chen, J. Xia, H. Wang, Y. Xie, H. Yu and J. Lei, A library of atomically thin metal chalcogenides, Nature, 2018, 556, 355–359 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Frindt, Single crystals of MoS2 several molecular layers thick, J. Appl. Phys., 1966, 37, 1928–1929 CrossRef CAS.
- R. J. Smith, P. J. King, M. Lotya, C. Wirtz, U. Khan, S. De, A. O'Neill, G. S. Duesberg, J. C. Grunlan and G. Moriarty, Large-scale exfoliation of inorganic layered compounds in aqueous surfactant solutions, Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 3944–3948 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. J. Carey, T. Daeneke, E. P. Nguyen, Y. Wang, J. Z. Ou, S. Zhuiykov and K. Kalantar-Zadeh, Two solvent grinding sonication method for the synthesis of two-dimensional tungsten disulphide flakes, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 3770–3773 RSC.
- J. N. Coleman, M. Lotya, A. O'Neill, S. D. Bergin, P. J. King, U. Khan, K. Young, A. Gaucher, S. De and R. J. Smith, Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials, Science, 2011, 331, 568–571 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. B. Dines, Lithium intercalation via n-butyllithium of the layered transition metal dichalcogenides, Mater. Res. Bull., 1975, 10, 287–291 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zeng, Z. Yin, X. Huang, H. Li, Q. He, G. Lu, F. Boey and H. Zhang, Single-Layer Semiconducting Nanosheets: High-yield preparation and device fabrication, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 11093–11097 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhan, Z. Liu, S. Najmaei, P. M. Ajayan and J. Lou, Large-area vapor-phase growth and characterization of MoS2 atomic layers on a SiO2 substrate, Small, 2012, 8, 966–971 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Choi, H. K. Jeong, M. A. Snyder, J. A. Stoeger, R. I. Masel and M. Tsapatsis, Grain boundary defect elimination in a zeolite membrane by rapid thermal processing, Science, 2009, 325, 590–593 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. J. Roth, P. Nachtigall, R. E. Morris and J. Cejka, Two-dimensional zeolites: current status and perspectives, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 4807–4837 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Přech, P. Pizarro, D. Serrano and J. Čejka, From 3D to 2D zeolite catalytic materials, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 8263–8306 RSC.
- M. Hong, L. Yu, Y. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Chen, L. Dong, Q. Zan and R. Li, Heavy metal adsorption with zeolites: The role of hierarchical pore architecture, Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 359, 363–372 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Li, V. A. Tuan, J. L. Falconer and R. D. Noble, Separation of 1, 3-propanediol from aqueous solutions using pervaporation through an X-type zeolite membrane, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2001, 40, 1952–1959 CrossRef CAS.
- S. L. Wee, C. T. Tye and S. Bhatia, Membrane separation process—pervaporation through zeolite membrane, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2008, 63, 500–516 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhong, J. Yao, R. Chen, Z. Low, M. He, J. Z. Liu and H. Wang, Oriented two-dimensional zeolitic imidazolate framework-L membranes and their gas permeation properties, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 15715–15722 RSC.
- Z. Lai, G. Bonilla, I. Diaz, J. G. Nery, K. Sujaoti, M. A. Amat, E. Kokkoli, O. Terasaki, R. W. Thompson and M. Tsapatsis, Microstructural optimization of a zeolite membrane for organic vapor separation, Science, 2003, 300, 456–460 CAS.
- A. R. Teixeira, X. Qi, W. C. Conner, T. Mountziaris, W. Fan and P. J. Dauenhauer, 2D surface structures in small zeolite MFI crystals, Chem. Mater., 2015, 27, 4650–4660 CrossRef CAS.
- W. J. Roth, B. Gil, W. Makowski, B. Marszalek and P. Eliášová, Layer like porous materials with hierarchical structure, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 3400–3438 RSC.
- M. Y. Jeon, D. Kim, P. Kumar, P. S. Lee, N. Rangnekar, P. Bai, M. Shete, B. Elyassi, H. S. Lee and K. Narasimharao, Ultra-selective high-flux membranes from directly synthesized zeolite nanosheets, Nature, 2017, 543, 690 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Na, M. Choi, W. Park, Y. Sakamoto, O. Terasaki and R. Ryoo, Pillared MFI zeolite nanosheets of a single-unit-cell thickness, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 4169–4177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Eliášová, M. Opanasenko, P. S. Wheatley, M. Shamzhy, M. Mazur, P. Nachtigall, W. J. Roth, R. E. Morris and J. Čejka, The ADOR mechanism for the synthesis of new zeolites, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 7177–7206 RSC.
- K. V. Agrawal, B. Topuz, Z. Jiang, K. Nguenkam, B. Elyassi, L. F. Francis, M. Tsapatsis and M. Navarro, Solution-processable exfoliated zeolite nanosheets purified by density gradient centrifugation, AIChE J., 2013, 59, 3458–3467 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Choi, K. Na, J. Kim, Y. Sakamoto, O. Terasaki and R. Ryoo, Stable single-unit-cell nanosheets of zeolite MFI as active and long-lived catalysts, Nature, 2009, 461, 246 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Varoon, X. Zhang, B. Elyassi, D. D. Brewer, M. Gettel, S. Kumar, J. A. Lee, S. Maheshwari, A. Mittal, C.-Y. Sung, M. Cococcioni, L. Franxis, A. McCormick, K. Mkhoyan and M. Tsapatsis, Dispersible exfoliated zeolite nanosheets and their application as a selective membrane, Science, 2011, 334, 72–75 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang, Q. Xiao, X. Guo, N. Li, P. Kumar, N. Rangnekar, M. Y. Jeon, S. Thabaiti, K. Narasimharao, S. N. Basahel, B. Topuz, F. J. Onorato, C. W. Macosko, K. A. Mkhoyan and M. Tsapatsis, Open-Pore Two-Dimensional MFI Zeolite Nanosheets for the Fabrication of Hydrocarbon-Isomer-Selective Membranes on Porous Polymer Supports, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 7184–7187 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. J. Roth, P. Nachtigall, R. E. Morris, P. S. Wheatley, V. R. Seymour, S. E. Ashbrook, P. Chlubná, L. Grajciar, M. Položij and A. Zukal, A family of zeolites with controlled pore size prepared using a top-down method, Nat. Chem., 2013, 5, 628 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mazur, P. S. Wheatley, M. Navarro, W. J. Roth, M. Položij, A. Mayoral, P. Eliášová, P. Nachtigall, J. Čejka and R. E. Morris, Synthesis of ‘unfeasible’ zeolites, Nat. Chem., 2016, 8, 58 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Furukawa, K. E. Cordova, M. O'Keeffe and O. M. Yaghi, The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks, Science, 2013, 341, 1230444 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Rodenas, I. Luz, G. Prieto, B. Seoane, H. Miro, A. Corma, F. Kapteijn, F. X. L. Xamena and J. Gascon, Metal–organic framework nanosheets in polymer composite materials for gas separation, Nat. Mater., 2015, 14, 48–55 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Li, K. Wang, Y. Sun, C. T. Lollar, J. Li and H. C. Zhou, Recent advances in gas storage and separation using metal–organic frameworks, Mater. Today, 2018, 21, 108–121 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhao, K. Yuan, Y. Wang, G. Li, J. Guo, L. Gu, W. Hu, H. Zhao and Z. Tang, Metal–organic frameworks as selectivity regulators for hydrogenation reactions, Nature, 2016, 539, 76–80 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. B. Wu and X. W. D. Lou, Metal-organic frameworks and their derived materials for electrochemical energy storage and conversion: Promises and challenges, Sci. Adv., 2017, 3, eaap9252 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Motoyama, R. Makiura, O. Sakata and H. Kitagawa, Highly crystalline nanofilm by layering of porphyrin metal−organic framework sheets, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 5640–5643 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Pfeffermann, R. Dong, R. Graf, W. Zajaczkowski, T. Gorelik, W. Pisula, A. Narita, K. Müllen and X. Feng, Free-standing monolayer two-dimensional supramolecular organic framework with good internal order, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 14525–14532 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Sakamoto, K. Hoshiko, Q. Liu, T. Yagi, T. Nagayama, S. Kusaka, M. Tsuchiya, Y. Kitagawa, W. Y. Wong and H. Nishihara, A photofunctional bottom-up bis (dipyrrinato) zinc(II) complex nanosheet, Chem. Commun., 2015, 6, 6713 CAS.
- T. Kambe, R. Sakamoto, K. Hoshiko, K. Takada, M. Miyachi, J.-H. Ryu, S. Sasaki, J. Kim, K. Nakazato and M. Takata, π-Conjugated nickel bis (dithiolene) complex nanosheet, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 2462–2465 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Gallego, C. Hermosa, O. Castillo, I. Berlanga, C. J. Gómez-García, E. Mateo-Martí, J. I. Martínez, F. Flores, C. Gómez-Navarro and J. Gómez-Herrero, Solvent-Induced Delamination of a Multifunctional Two-Dimensional Coordination Polymer, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 2141–2146 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Peng, Y. Li, Y. Ban, H. Jin, W. Jiao, X. Liu and W. Yang, Metal-organic framework nanosheets as building blocks for molecular sieving membranes, Science, 2014, 346, 1356–1359 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, C. Chi, K. Zhang, Y. Qian, K. M. Gupta, Z. Kang, J. Jiang and D. Zhao, Reversed thermo-switchable molecular sieving membranes composed of two-dimensional metal-organic nanosheets for gas separation, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 14460 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Makiura, S. Motoyama, Y. Umemura, H. Yamanaka, O. Sakata and H. Kitagawa, Surface nano-architecture of a metal–organic framework, Nat. Mater., 2010, 9, 565 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zhao, Y. Wang, Q. Ma, Y. Huang, X. Zhang, J. Ping, Z. Zhang, Q. Lu, Y. Yu and H. Xu, Ultrathin 2D metal–organic framework nanosheets, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 7372–7378 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhao, Y. Wang, J. Dong, C. T. He, H. Yin, P. An, K. Zhao, X. Zhang, C. Gao, L. Zhang, J. Lv, J. Wang, J. Zhang, A. M. Khattak, N. A. Khan, Z. Wei, J. Zhang, S. Liu, H. Zhao and Z. Tang, Ultrathin metal–organic framework nanosheets for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution, Nat. Energy, 2016, 1, 16184 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kim and H. C. Choi, Recent Advances in Covalent Organic Frameworks for Molecule-Based Two-Dimensional Materials, ACS Omega, 2020, 5, 948–958 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Song, Q. Sun, B. Aguila and S. Ma, Opportunities of covalent organic frameworks for advanced applications, Adv. Sci., 2019, 6, 1801410 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, X. S. Shi, R. Wang, A. K. Xiao and Y. Wang, Ultra-permeable polyamide membranes harvested by covalent organic framework nanofiber scaffolds: a two-in-one strategy, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 9077–9083 RSC.
- R. Wang, M. Wei and Y. Wang, Secondary Growth of Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) on Porous Substrates for Fast Desalination, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 604, 118090 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yao, C. Liu, X. Liu, J. Guo, S. Zhang, J. Zheng and S. Li, Azobenzene-assisted exfoliation of 2D covalent organic frameworks into large-area, few-layer nanosheets for high flux and selective molecular separation membrane, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 601, 117864 CrossRef.
- H. Fan, A. Mundstock, A. Feldhoff, A. Knebel, J. Gu, H. Meng and J. r. Caro, Covalent Organic Framework–Covalent Organic Framework Bilayer Membranes for Highly Selective Gas Separation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 10094–10098 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Rodríguez-San-Miguel, C. Montoro and F. Zamora, Covalent organic framework nanosheets: preparation, properties and applications, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 2291–2302 RSC.
- S. Yuan, X. Li, J. Zhu, G. Zhang, P. Van Puyvelde and B. Van der Bruggen, Covalent organic frameworks for membrane separation, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 2665–2681 RSC.
- I. Berlanga, M. L. Ruiz-González, J. M. González-Calbet, J. L. G. Fierro, R. Mas-Ballesté and F. Zamora, Delamination of layered covalent organic frameworks, Small, 2011, 7, 1207–1211 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chandra, S. Kandambeth, B. P. Biswal, B. Lukose, S. M. Kunjir, M. Chaudhary, R. Babarao, T. Heine and R. Banerjee, Chemically stable multilayered covalent organic nanosheets from covalent organic frameworks via mechanical delamination, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 17853–17861 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, Q. Chen, T. Xu, Z. Xie, J. Liu, X. Yu, S. Ma, T. Qin and L. Chen, De novo design and facile synthesis of 2D covalent organic frameworks: a two-in-one strategy, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 13822–13828 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Zhang, L. Zhang, H. Zhao, B. Li and H. Ma, A two-dimensional cationic covalent organic framework membrane for selective molecular sieving, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 13331–13339 RSC.
- J. Gao, W. Guo, D. Feng, H. Wang, D. Zhao and L. Jiang, High-performance ionic diode membrane for salinity gradient power generation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 12265–12272 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Werber, C. O. Osuji and M. Elimelech, Materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2016, 1, 1–15 Search PubMed.
- Y. J. Zhang, H. Chen, P. Y. He and C. J. Li, Developing silica fume-based self-supported ECR-1 zeolite membrane for seawater desalination, Mater. Lett., 2019, 236, 538–541 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Van Den Bergh, M. Mittelmeijer-Hazeleger and F. Kapteijn, Modeling permeation of CO2/CH4, N2/CH4, and CO2/air mixtures across a DD3R zeolite membrane, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 9379–9389 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sakai, Y. Sasaki, T. Tomono, M. Seshimo and M. Matsukata, Olefin Selective Ag-Exchanged X-Type Zeolite Membrane for Propylene/Propane and Ethylene/Ethane Separation, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 4145–4151 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Wei, K. M. Gupta, J. Liu and J. Jiang, Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration: A Molecular Simulation Exploration, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 33135–33143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yang, X. Yang, L. Liang, Y. Gao, H. Cheng, X. Li, M. Zou, R. Ma, Q. Yuan and X. Duan, Large-area graphene-nanomesh/carbon-nanotube hybrid membranes for ionic and molecular nanofiltration, Science, 2019, 364, 1057–1062 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Abraham, K. S. Vasu, C. D. Williams, K. Gopinadhan, Y. Su, C. T. Cherian, J. Dix, E. Prestat, S. J. Haigh and I. V. Grigorieva, Tunable sieving of ions using graphene oxide membranes, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2017, 12, 546 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Heiranian, A. B. Farimani and N. R. Aluru, Water desalination with a single-layer MoS2 nanopore, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 8616 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Ries, E. Petit, T. Michel, C. C. Diogo, C. Gervais, C. Salameh, M. Bechelany, S. Balme, P. Miele and N. Onofrio, Enhanced sieving from exfoliated MoS2 membranes via covalent functionalization, Nat. Mater., 2019, 18, 1112–1117 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. E. Ren, K. B. Hatzell, M. Alhabeb, Z. Ling, K. A. Mahmoud and Y. Gogotsi, Charge-and size-selective ion sieving through Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6, 4026–4031 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Ding, L. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Wu, Z. Lu, J. Deng, Y. Wei, J. Caro and H. Wang, Effective ion sieving with Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes for production of drinking water from seawater, Nat. Sustain., 2020, 3, 296–302 CrossRef.
- Z. Cao, V. Liu and A. Barati Farimani, Water Desalination with Two-Dimensional Metal–Organic Framework Membranes, Nano Lett., 2019, 19, 8638–8643 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Marchetti, M. F. Jimenez Solomon, G. Szekely and A. G. Livingston, Molecular separation with organic solvent nanofiltration: a critical review, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 10735–10806 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Q. Ma, C. Zhang, C. Y. Zhu, S. Huang, J. Yang and Z. K. Xu, Nanocomposite membranes embedded with functionalized MoS2 nanosheets for enhanced interfacial compatibility and nanofiltration performance, J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 591, 117316 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang and T. S. Chung, Graphene oxide membranes for nanofiltration, Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng., 2017, 16, 9–15 CrossRef.
- R. Han and P. Wu, High-performance graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane with continuous nanochannels prepared by the in situ oxidation of MXene, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 6475–6481 RSC.
- W. Hirunpinyopas, E. Prestat, S. D. Worrall, S. J. Haigh, R. A. Dryfe and M. A. Bissett, Desalination and nanofiltration through functionalized laminar MoS2 membranes, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 11082–11090 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Cheng, Y. Chen, Y. H. Gu, X. Yan and W.-Z. Lang, Hybrid 2D WS2/GO nanofiltration membranes for finely molecular sieving, J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 591, 117308 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Zhang, S. Liao, F. Qi, R. Liu, T. Xiao, J. Hu, K. Li, R. Wang and Y. Min, Direct deposition of two-dimensional MXene nanosheets on commercially available filter for fast and efficient dye removal, J. Hazard. Mater., 2019, 384, 121367 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Ding, Y. Wei, Y. Wang, H. Chen, J. Caro and H. Wang, A two-dimensional lamellar membrane: MXene nanosheet stacks, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 1825–1829 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Sun, Y. Ying, H. Huang, Z. Song, Y. Mao, Z. Xu and X. Peng, Ultrafast molecule separation through layered WS2 nanosheet membranes, ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 6304–6311 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Ang and L. Hong, Polycationic polymer-regulated assembling of 2D MOF nanosheets for high-performance nanofiltration, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 28079–28088 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Huang, Y. Li, Q. Zhou, W. Yuan and G. Shi, Graphene oxide membranes with tunable semipermeability in organic solvents, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 3797–3802 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Huang, J. Chen, T. Gao, M. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Dai, L. Qu and G. Shi, Reduced graphene oxide membranes for ultrafast organic solvent nanofiltration, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 8669–8674 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. F. D. Aba, J. Y. Chong, B. Wang, C. Mattevi and K. Li, Graphene oxide membranes on ceramic hollow fibers–Microstructural stability and nanofiltration performance, J. Membr. Sci., 2015, 484, 87–94 CrossRef CAS.
- T. H. Weng, H. H. Tseng and M.-Y. Wey, Preparation and characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotube/PBNPI nanocomposite membrane for H2/CH4 separation, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34, 8707–8715 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Hou, P. Liu, M. Jiang, L. Yu, L. Li and Z. Tang, Olefin/paraffin separation through membranes: from mechanisms to critical materials, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 23489–23511 RSC.
- A. H. Mamaghani, F. Haghighat and C.-S. Lee, Photocatalytic oxidation technology for indoor environment air purification: the state-of-the-art, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 203, 247–269 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Tuinier, M. van Sint Annaland, G. J. Kramer and J. Kuipers, Cryogenic CO2 capture using dynamically operated packed beds, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2010, 65, 114–119 CrossRef CAS.
- G. T. Rochelle, Amine scrubbing for CO2 capture, Science, 2009, 325, 1652–1654 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Kosinov, J. Gascon, F. Kapteijn and E. J. Hensen, Recent developments in zeolite membranes for gas separation, J. Membr. Sci., 2016, 499, 65–79 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Duan, W. Jin and S. Kitagawa, Water-resistant porous coordination polymers for gas separation, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2017, 332, 48–74 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Hou, S. J. Smith, C. D. Wood, R. J. Mulder, C. H. Lau, H. Wang and M. R. Hill, Solvation effects on the permeation and aging performance of PIM-1-based MMMs for gas separation, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 6502–6511 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Blankenburg, M. Bieri, R. Fasel, K. Müllen, C. A. Pignedoli and D. Passerone, Porous graphene as an atmospheric nanofilter, Small, 2010, 6, 2266–2271 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Huang, M. Dakhchoune, W. Luo, E. Oveisi, G. He, M. Rezaei, J. Zhao, D. T. Alexander, A. Züttel, M. S. Strano and K. V. Agrawal, Single-layer graphene membranes by crack-free transfer for gas mixture separation, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 2632 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Wang, Z. Wang, L. Wang, L. Hu and J. Jin, Ultrathin membranes of single-layered MoS2 nanosheets for high-permeance hydrogen separation, Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 17649–17652 RSC.
- Y. Fan, L. Wei, X. Meng, W. Zhang, N. Yang, Y. Jin, X. Wang, M. Zhao and S. Liu, An unprecedented high-temperature-tolerance 2D laminar MXene membrane for ultrafast hydrogen sieving, J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 569, 117–123 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Peng, Y. Li, Y. Ban and W. Yang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 9757–9761 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Fan, M. Peng, I. Strauss, A. Mundstock, H. Meng and J. Caro, High-Flux Vertically Aligned 2D Covalent Organic Framework Membrane with Enhanced Hydrogen Separation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 6872–6877 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. J. Ward and K. D. Ward, Chiral separations: a review of current topics and trends, Anal. Chem., 2012, 84, 626–635 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Y. Aboul-Enein, M. I. El-Awady, C. M. Heard and P. J. Nicholls, Application of thin-layer chromatography in enantiomeric chiral analysis—an overview, Biomed. Chromatogr., 1999, 13, 531–537 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Xie, Z. J. Zhang, Z.-Y. Wang and L. M. Yuan, Chiral metal–organic frameworks for high-resolution gas chromatographic separations, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 11892–11895 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, M. Wu, R. a. Wu, J. Dong, J. Ou and H. Zou, Preparation of perphenylcarbamoylated β-cyclodextrin-silica hybrid monolithic column with “one-pot” approach for enantioseparation by capillary liquid chromatography, Anal. Chem., 2011, 83, 3616–3622 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Fernandes, M. E. Tiritan and M. M. Pinto, Chiral separation in preparative scale: A brief overview of membranes as tools for enantiomeric separation, Symmetry, 2017, 9, 206 CrossRef.
- Y. Zhang, X. Liu, S. Qiu, Q. Zhang, W. Tang, H. Liu, Y. Guo, Y. Ma, X. Guo and Y. Liu, A Flexible Acetylcholinesterase-Modified Graphene for Chiral Pesticide Sensor, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 14643–14649 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, N. Wu, Y. Wang, H. Ma, J. Zhang, L. Xu, M. K. Albolkany and B. Liu, Graphite phase carbon nitride-based membrane for selective permeation, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 2500 CrossRef PubMed.
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2020 |



