Binuclear nickel complexes with an edge sharing bis(square-pyramidal) N3Ni(μ-S2)NiN3 core: synthesis, characterization, crystal structure and magnetic properties†
Abstract
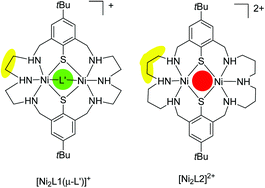
The synthesis of the novel macrocyclic octadentate amino-thiophenolate ligand H2L2 (3,7,11,19,23,27-hexaaza-33,34-dithiol-15,31-di(tert-butyl)-tricyclo[27,3,113.17]-tetratriaconta-1(32),13,15,17(34),29,30-hexane) and its ability to support binuclear nickel(II) complexes with dithiolato-bridged square-pyramidal NiII ions are reported. H2L2 is obtained as the hexahydrobromide salt from a Schiff-base condensation reaction between 1,2-bis(4-tert-butyl-2,6-diformylphenylthio)ethane and bis(3-aminopropyl)amine followed by two successive reductions with NaBH4 and Na/NH3. The ligand forms a green, paramagnetic, binuclear nickel(II) complex dication [NiII2L2]2+, which can be isolated as a ClO4− (4) or BPh4− salt (5). The binuclear nickel(II) complex contains a central N3Ni(μ-S)2NiN3 core with two square-pyramidal coordinated NiII ions. The [Ni2L2]2+ dication does not bind further coligands, in striking contrast to the behaviour of the parent [Ni2L1]2+ dication supported by the smaller (L1)2− macrocycle (containing diethylenetriamine in place of the dipropylenetriamine units) which readily binds a variety of other coligands (L′) to form bisoctahedral [Ni2L1(L′)]+ structures. The unusual behaviour of 4 relates to two different N configurations which leads to a steric shielding of the third bridging position by the CH2-groups of the dipropylenetriamine chains. An analysis of the temperature-dependent magnetic susceptibility data of 5 reveals the presence of a weak antiferromagnetic exchange interaction between the spins of the nickel(II) ions with a value for the magnetic exchange coupling constant J of −23.5 cm−1 (H = −2JS1S2). These results are further substantiated by DFT calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...