Effective removal of Cr(vi) through adsorption and reduction by magnetic mesoporous carbon incorporated with polyaniline†
Abstract
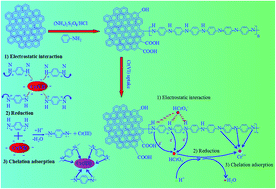
Magnetic mesoporous carbon incorporated with polyaniline (PANI–Fe/OMC) is developed for enhanced adsorption and reduction of toxic Cr(VI) to non-toxic Cr(III). Several physicochemical techniques including TEM, FTIR and XPS analyses confirmed that magnetic iron nanoparticles and amino groups have been successfully bound on the mesoporous matrix. The adsorption capacity of the functionalized material is two- and ten-fold that of the magnetic mesoporous carbon (Fe/OMC) and pristine mesoporous silicon (SBA-15), respectively. Solution pH exhibited a remarkable impact on the Cr(VI) adsorption and the maximum uptake amount (172.33 mg g−1) occurred at pH 2.0. The good fitting of adsorption process using pseudo-second-order and Langmuir models indicated the chemisorption process of Cr(VI) removal. The regeneration study revealed that PANI–Fe/OMC can be reused without loss of their activity in repetitive adsorption tests. Moreover, the resultant adsorbent can be effectively applied in actual wastewater treatment due to the excellent removal performance in fixed-bed column and real water samples. The interaction between Cr(VI) and PANI–Fe/OMC was investigated by FTIR and XPS analyses. The results indicate that the amino groups on the surface of PANI–Fe/OMC are involved in Cr(VI) uptake, and simultaneously some toxic Cr(VI) are reduced to non-toxic Cr(III) during the removal process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...