Development of small particle speciation for nuclear forensics by soft X-ray scanning transmission spectromicroscopy
Abstract
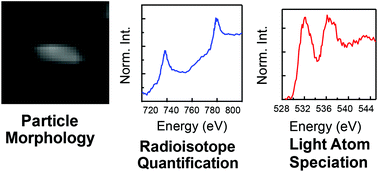
Synchrotron radiation spectromicroscopy provides a combination of submicron spatial resolution and chemical sensitivity that is well-suited to analysis of heterogeneous nuclear materials. The chemical and physical characteristics determined by scanning transmission X-ray microscopy (STXM) are complementary to information obtained from standard radiochemical analysis methods. In addition, microscopic quantities of radioactive material can be characterized rapidly by STXM with minimal sample handling and intrusion, especially in the case of particulate materials. The STXM can accommodate a diverse range of samples including wet materials, complex mixtures, and small quantities of material contained in a larger matrix. In these cases, the inventory of species present in a sample is likely to carry information on its process history; STXM has the demonstrated capability to identify contaminants and sample matrices. Operating in the soft X-ray regime provides particular sensitivity to the chemical state of specimens containing low-Z materials, via the K-edges of light elements. Here, recent developments in forensics-themed spectromicroscopy, sample preparation, and data acquisition methods at the Molecular Environmental Science Beamline 11.0.2 of the Advanced Light Source are described. Results from several initial studies are presented, demonstrating the capability to identify the distribution of the species present in heterogeneous uranium-bearing materials. Future opportunities for STXM forensic studies and potential methodology development are discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...