15N isotopic labelling for in-cell protein studies by NMR spectroscopy and single-cell IR synchrotron radiation FTIR microscopy: a correlative study
Abstract
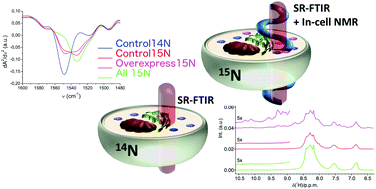
The ultimate goal of modern structural biology is to probe protein structures and dynamics in their physiological microenvironment. In-cell NMR spectroscopy is an ideal technique for achieving this goal, being able to investigate proteins at atomic-resolution in living cells. The reliability of the results provided by in-cell NMR relies on the selectivity of the labelling methodology coupled with the filtering capabilities offered by heteronuclear NMR experiments. However, solution NMR is not well-suited either for measuring to what extent the non-specific labelling occurs, or to evaluate how it is affected by cell-to-cell variability and, eventually, whether the labelling procedure affects the cellular macromolecular content in general. To answer these questions, we correlated in-cell 1D 1H and 2D 1H–15N NMR experiments on HEK293T cells overexpressing superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) with single-cell Synchrotron Radiation FTIR Microscopy (FTIRM) experiments on the same samples. We verified that SOD1 overexpression in 15N-enriched media does not induce modifications in the overall cellular profile, and that the cell-to-cell labelling variability is independent of SOD1 overexpression and is likely cell cycle-related. We concluded that the non-specific incorporation of 15N into cellular components other than the protein of interest is one of the main factors that hinder the possibility of in-cell conformational studies by FTIRM at the single-cell level. Improving labelling selectivity by employing protein insertion approaches, and increasing FTIRM sensitivity by plasmonic enhancement, would open new perspectives for in-cell ultra-sensitive single-protein conformational studies complementing NMR and vibrational analyses.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...