Oxygen vacancy formation and migration in double perovskite Sr2CrMoO6: a first-principles study
Abstract
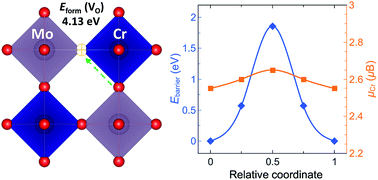
The perovskite-type oxide ABO3 with mixed ionic and electronic conductivity (MIEC) is a promising candidate for electrode materials of the intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells (IT-SOFCs). The strontium molybdate SrMoO3 shows high electrical conductivity but low oxygen ionic conductivity due to the stoichiometric features of oxygen. To enhance the oxygen ions diffusion rate, B-site Mo4+ cation was partially substituted by trivalent transition metals (TM) to generate the oxygen-deficient double perovskite Sr2BMoO6−δ. In this study, we present the theoretical investigation of the oxygen vacancy properties of Sr2CrMoO6 (SCM) using density functional theory (DFT) with on-site Coulomb potential U for the Cr 3d electrons. The oxygen vacancy formation and migration were investigated for the B-site-ordered SCM, as well as the SCM with Cr/Mo antisite defects (ADs). The oxygen ion migration was optimized by the climbing image nudged elastic band (CINEB) method to identify the minimum energy pathway. The B-site Cr/Mo ADs allow various TM–O bond types in the double perovskite SCM. The calculated formation energy and migration barrier suggests that the B-site Cr/Mo ADs are favorable to enhance the oxygen ionic conductivity of the SCM. These results elucidate the influence of B-site Cr and Mo cations on the oxygen vacancy formation and migration in the double perovskite SCM, which can be useful for investigating Cr-doped SrMoO3 as an IT-SOFCs anode.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...