Investigation of the effects of nanoAg on the enzyme lysozyme at the molecular level†
Abstract
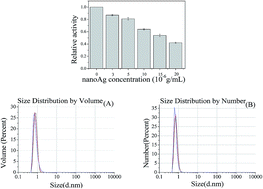
NanoAg is almost the most widely used nanoparticle material, and the potential toxicity of nanoAg has aroused widespread concerns regarding its effect on human health. However, because previous studies differed in the preparation of the nanoAg as well as its size, exposure mode and targets, coating and so on, it is difficult to compare the experimental results of these reports and to arrive at an accurate and comprehensive conclusion. Further systematic study of the mechanism underlying the toxicity of nanoAg at the molecular level is necessary and important. Lysozyme was selected to investigate the mechanism underlying the toxicity of nanoAg at the molecular level, and this analysis included transmission electron microscopy, enzyme activity assays, and various spectroscopic methods including fluorescence spectroscopy, synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy, light scattering spectroscopy, UV absorption spectroscopy and circular dichroism spectroscopy. Multi-spectroscopic experiments indicated that nanoAg quenched the fluorescence of lysozyme at the concentrations of nanoAg ranging from 1.0 × 10−6 g mL−1 to 200.0 × 10−6 g mL−1 in the quenching mode of exponential decay using both dynamic and static processes, and was accompanied by complex conformational changes of lysozyme. The interaction between lysozyme and nanoAg inhibited the function of lysozyme. The toxicity of nanoAg was attributed to the smaller lysozyme being surrounded by nanoAg and that nanoAg released silver ions. The results will help provide a strong biophysical basis for research into the toxicity of nanoAg.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...