Identification of new scaffolds with anti-tumor action toward human glioblastoma cells†
Abstract
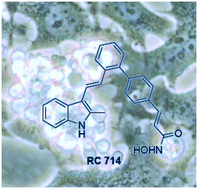
Glioblastoma (GBM), a malignant brain tumor, is one of the most aggressive human neoplasms due to its molecular heterogeneity, diffusive growth and multiple mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapeutics. Frequent dysfunctions of tumor suppressors and oncogenes, which lead to overactivation of prosurvival and antiapoptotic signals, are driven by genetics as well as epigenetic abnormalities. The epigenetic mechanisms are de-regulated in gliomas as a result of an aberrant activation or inactivation of enzymes maintaining and modifying the epigenome, such as histone deacetyltranferases (HDAC). Herein, we demonstrate the effects of new compounds from three structurally and functionally unrelated groups on two human glioblastoma cell lines, which are highly resistant to radiation and a majority of anticancer drugs. The first group was comprised of several potential HDAC inhibitors bearing a 4-vinylbiphenyl skeleton incorporating both hydroxyamic and non-hydroxyamic head groups, and the other two groups of compounds contain a 3-arylidene-oxindole scaffold and an isothiazolonaphthoquinone core, respectively. The results demonstrate the promising antitumor efficacy of some of the compounds and provides insight into molecular mechanisms of their cytotoxic action. The compounds containing an isothiazolonaphthoquinone core and HDAC inhibitors with an indolyl-substituted biphenyl-4-yl-acrylohydroxamic acid showed the highest efficacy against tumor cells. The observed proapoptotic effect of certain potential HDAC inhibitors on glioma cells provides a new therapeutic strategy based on the direct modulation of glioma growth using a specific HDAC inhibitor. These new and effective scaffolds can be considered as promising candidates for further investigation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...