Molecular basis of 5-hydroxytryptophan synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae†
Abstract
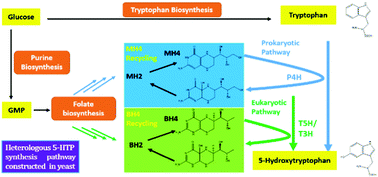
We report for the first time that 5-hydroxytryptophan can be synthesized in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by heterologously expressing prokaryotic phenylalanine 4-hydroxylase or eukaryotic tryptophan 3/5-hydroxylase, together with enhanced synthesis of MH4 or BH4 cofactors. The innate DFR1 gene in the folate synthesis pathway was found to play pivotal roles in 5-hydroxytryptophan synthesis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in Molecular BioSystems

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...