Fluctuation spectra in polymer nematics and Frank elastic constants: a coarse-grained modelling study
Abstract
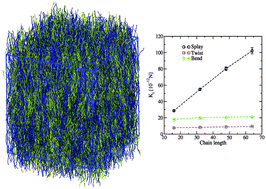
Monte Carlo simulations of uniaxial nematic polymer melts are performed, based on a discrete worm-like chain model combined with soft, anisotropic non-bonded potentials. Different chain lengths are considered, the contour length of the longest being an order of magnitude larger than the persistence length. From equilibrated melt configurations, density and director fluctuation spectra are calculated and compared with analytical predictions available in literature. The latter typically correspond to hydrodynamic treatments of correlations and assume that there is no chain backfolding along the nematic director. Nevertheless, it is demonstrated that the analytical theories capture several features of the spectra obtained in the current simulations, where moderate backfolding of polymer chains is observed. Based on the available analytical expressions for density and director fluctuation spectra, material properties, such as Frank elastic constants, are extracted. Their dependence on polymerisation degree is studied and found to reproduce theoretically expected trends. For example, evidence is provided that the splay constant increases linearly with chain length, when effects of hairpins are negligible.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...