Biochar-supported carbon nanotube and graphene oxide nanocomposites for Pb(ii) and Cd(ii) removal
Abstract
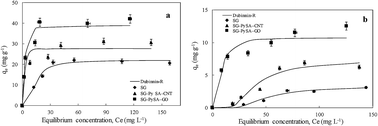
Carbon materials such as nanoparticles have provided new solutions for the removal of various environmental contaminants. In this work, two carbon nanomaterial–biochar nanocomposites (SG–PySA–CNT and SG–PySA–GO) were derived from sweetgum biomass pretreated with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene oxide (GO) through slow pyrolysis at 600 °C. Both SG–PySA–CNT and SG–PySA–GO had higher surface area but much lower pore volume than the pristine biochar (SG). Batch sorption experimental results showed that SG–PySA–CNT and SG–PySA–GO had greater sorption ability to Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution than SG. SG–PySA–GO was the best sorbent with maximum sorption capacities higher than 40 and 10 mg g−1 for Pb(II) and Cd(II), respectively. The enhanced metal sorption by the biochar nanocomposites could be mainly attributed to the excellent sorptive properties of the carbon nanoparticles (CNT/GO) distributed and stabilized on the biochar surfaces within the matrix. Because of its facile synthesis and good sorptive properties, biochar-supported CNT and GO nanocomposites have great potential to be used in various environmental applications for the removal of metal and metalloid contaminants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...