Classification of carbon nanostructure families occurring in a chemically activated arc discharge reaction†
Abstract
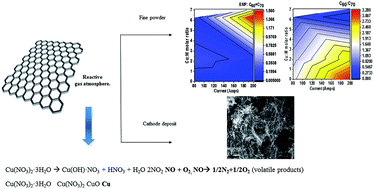
Controlling the generation of empty cages, endohedral metallofullerenes and carbon nanotubes is an important challenge for the tailored synthesis of functional materials and their scaled up production. However, the reaction yields for fullerenes are low and their formation mechanism is far from being elucidated thus hampering their targeted, scaled up production and potential applications. We present a systematic study on the effect of the addition of copper nitrate as a doping agent during an arc discharge vaporization of Gd and Nd doped rods for the production of a series of fullerenes and carbon nanotubes. The incorporation of copper nitrate at a Cu/M molar ratio in the range of 6 to 7 leads to a higher yield for the high molecular weight fullerenes and endohedral fullerenes compared to small empty cages. We distinguished three different families of nanomaterials: (1) small empty cage fullerenes, (2) endohedral metallofullerenes and empty cage fullerenes with more than 88 atoms, and (3) multi-wall carbon nanotubes which were deposited on the cathode and their yield appeared to be influenced by the different reaction conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...