Neurospora crassa transcriptomics reveals oxidative stress and plasma membrane homeostasis biology genes as key targets in response to chitosan†
Abstract
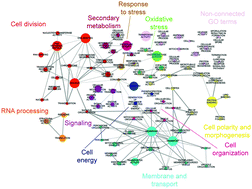
Chitosan is a natural polymer with antimicrobial activity. Chitosan causes plasma membrane permeabilization and induction of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Neurospora crassa. We have determined the transcriptional profile of N. crassa to chitosan and identified the main gene targets involved in the cellular response to this compound. Global network analyses showed membrane, transport and oxidoreductase activity as key nodes affected by chitosan. Activation of oxidative metabolism indicates the importance of ROS and cell energy together with plasma membrane homeostasis in N. crassa response to chitosan. Deletion strain analysis of chitosan susceptibility pointed NCU03639 encoding a class 3 lipase, involved in plasma membrane repair by lipid replacement, and NCU04537 a MFS monosaccharide transporter related to assimilation of simple sugars, as main gene targets of chitosan. NCU10521, a glutathione S-transferase-4 involved in the generation of reducing power for scavenging intracellular ROS is also a determinant chitosan gene target. Ca2+ increased tolerance to chitosan in N. crassa. Growth of NCU10610 (fig 1 domain) and SYT1 (a synaptotagmin) deletion strains was significantly increased by Ca2+ in the presence of chitosan. Both genes play a determinant role in N. crassa membrane homeostasis. Our results are of paramount importance for developing chitosan as an antifungal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...