Molecularly imprinted polymers for the analysis and removal of polychlorinated aromatic compounds in the environment: a review
Abstract
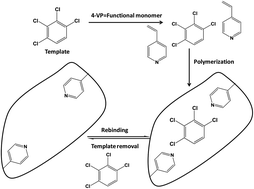
Synthetic receptors and in particular molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) are gaining relevance as selective sorbent materials and biomimetic recognition elements for analyzing polychlorinated aromatic compounds (PACs) in the environment. PACs are still ubiquitous toxic pollutants requiring their continuous environmental assessment for protecting humans and animals from exposure. Since nowadays most PACs occur at ultra-trace concentration levels and in complex matrices, the selectivity of MIPs renders them ideally suited for facilitating either sample pre-treatment and quantitative enrichment, or acting as biomimetic recognition elements as an integral component of corresponding sensing schemes. Due to the diversity of PACs, imprinting polymers for these constituents appears particularly challenging. This review focuses on prevalent strategies towards successfully templating polymer materials towards polychlorinated biphenyls and their hydroxy forms, chlorophenols, dioxins and furans, and organochlorine pesticides, and successful applications of the polymer materials in monitoring of these compounds at trace-levels in real-world environmental matrices. Discussed are also group-selective sorbents for facilitating simultaneous detection and quantification of PACs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...