Characterization and control of surfactant-mediated Norovirus interactions†
Abstract
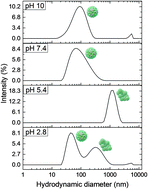
Understanding of the colloidal interactions of Norovirus particles in aqueous medium could provide insights on the origins of the notorious stability and infectivity of these widespread viral agents. We characterized the effects of solution pH and surfactant type and concentration on the aggregation, dispersion, and disassembly of Norovirus virus-like particles (VLPs) using dynamic light scattering, electrophoretic light scattering, and transmission electron microscopy. Owing to net negative surface charge of the VLPs at neutral pH, low concentrations of cationic surfactant tend to aggregate the VLPs, whereas low concentrations of anionic surfactant tend to disperse the particles. Increasing the concentration of these surfactants beyond their critical micelle concentration leads to virus capsid disassembly and breakdown of aggregates. Non-ionic surfactants, however, had little effect on virus interactions and likely stabilized them additionally in suspension. The data were interpreted on the basis of simple models for surfactant binding and re-charging of the virus capsid. We used zeta potential data to characterize virus surface charge and interpret the mechanisms behind these demonstrated surfactant–virus interactions. The fundamental understanding and control of these interactions will aid in practical formulations for virus inactivation and removal from contaminated surfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...