Effects of atmospheric deposition nitrogen flux and its composition on soil solution chemistry from a red soil farmland, southeast China
Abstract
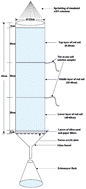
A detailed study on the solution chemistry of red soil in South China is presented. Data are collected from two simulated column-leaching experiments with an improved setup to evaluate the effects of atmospheric N deposition (ADN) composition and ADN flux on agricultural soil acidification using a 15N tracer technique and an in situ soil solution sampler. The results show that solution pH values decline regardless of the increase of the NH4+/NO3− ratio in the ADN composition or ADN flux, while exchangeable Al3+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and K+ concentrations increase at different soil depths (20, 40, and 60 cm). Compared with the control, ADN (60 kg per ha per year N, NH4+/NO3− ratio of 2 : 1) decreases solution pH values, increases solution concentrations of NO3−–N, Al3+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ at the middle and lower soil depths, and promotes their removal. NH4+–N was not detected in red soil solutions of all the three soil layers, which might be attributed to effects of nitrification, absorption and fixation in farmland red soil. Some of the NO3−–N concentrations at 40–60 cm soil depth exceed the safe drinking level of 10 mg L−1, especially when the ADN flux is beyond 60 kg ha−1 N. These features are critical for understanding the ADN agro-ecological effects, and for future assessment of ecological critical loads of ADN in red soil farmlands.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...