Themed collection Environmental effects of ozone depletion and its interactions with climate change: 2014 Assessment

Preface
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 7-8
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90039A
Environmental effects of ozone depletion and its interactions with climate change: 2014 assessment
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 14-18
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90042A
Abbreviations and glossary
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 10-13
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90041C
Environmental effects of ozone depletion and its interactions with climate change: 2014 assessment
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 9-9
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90040E
Solar ultraviolet radiation and ozone depletion-driven climate change: effects on terrestrial ecosystems
We summarise advances in our knowledge of how UV-B radiation (280–315 nm) together with other climate change factors interact in their influence on terrestrial organisms and ecosystems.
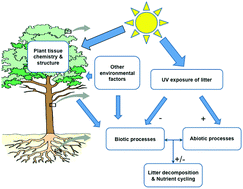
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 88-107
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90034K
Consequences of stratospheric ozone depletion and climate change on the use of materials
Materials used in the exterior of buildings and in construction are routinely exposed to solar UV radiation. Especially in the case of wood and plastic building materials, the service life is determined by their weather-induced deterioration.

Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 170-184
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90038C
Effects of UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with other environmental factors
Combined effects of anthropogenic changes in the environmental condition in marine ecosystems, including UV, CO2 and temperature.
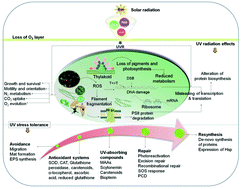
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 108-126
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90035A
The consequences for human health of stratospheric ozone depletion in association with other environmental factors
Ozone depletion, climate and human health.
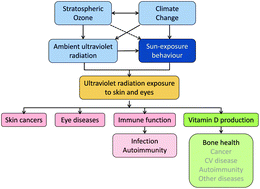
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 53-87
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90033B
Ozone depletion and climate change: impacts on UV radiation
Percentage changes in the UV Index (UVI) for 2090 relative to 2015 due to changes in ozone (left) and aerosols (right) only. Large decreases are projected over Antarctica due to stratospheric ozone recovery. Increases are projected for parts of Asia due to decreases in aerosols, partly reversing the possible large reductions in UVI after the 1950s.
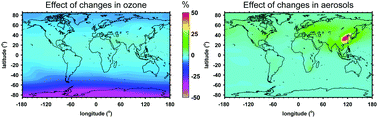
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 19-52
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90032D
Effects of stratospheric ozone depletion, solar UV radiation, and climate change on biogeochemical cycling: interactions and feedbacks
Solar UV radiation and climate change interact to influence and determine the environmental conditions for humans on planet Earth.
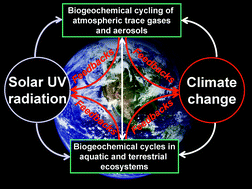
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 127-148
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90036G
Changes in air quality and tropospheric composition due to depletion of stratospheric ozone and interactions with changing climate: implications for human and environmental health
UV radiation is an essential driver for the formation of photochemical smog, which includes ground-level ozone and particulate matter (PM).

Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2015,14, 149-169
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PP90037E
About this collection
The assessments presented in the seven papers published in this journal deal with the effects of ozone depletion on human health and the environment and the consequences of interactions between ozone depletion and global climate change.