Themed collection Bio-inspired and natural materials

Naturally-derived and bioinspired materials
Guest editors Jennie B. Leach and Molly S. Shoichet introduce this Journal of Materials Chemistry B themed issue on Bio-inspired and Natural Materials.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7814-7817
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB90130H
Strategies for skeletal muscle tissue engineering: seed vs. soil
The most commonly used tissue engineering approach includes the ex vivo combination of site-appropriate cell(s) and scaffold material(s) to create three-dimensional constructs for tissue replacement or reconstruction. Biologic scaffold materials facilitate endogenous cell recruitment.
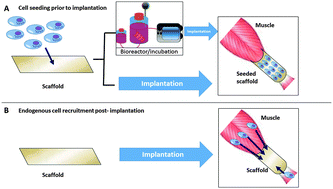
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7881-7895
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01714A
Mimicking biological phenomena in hydrogel-based biomaterials to promote dynamic cellular responses
Novel methods to endow cell-responsiveness into hydrogels are explored and successful work is summarized.
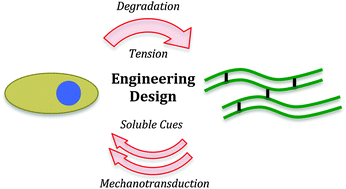
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7867-7880
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01045D
Hydrogels that allow and facilitate bone repair, remodeling, and regeneration
Bone defects can originate from a variety of causes, including trauma, cancer, congenital deformity, and surgical reconstruction. Success of the current “gold standard” treatment (i.e., autologous bone grafts) is greatly influenced by insufficient or inappropriate bone stock.
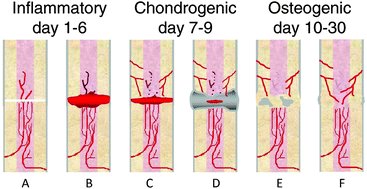
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7818-7830
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01043H
Hyaluronic acid and neural stem cells: implications for biomaterial design
While in the past hyaluronic acid (HA) was considered a passive structural component, research over the past few decades has revealed its diverse and complex biological functions resulting in a major ideological shift. This review describes recent advances in biological interactions of HA with neural stem cells, with a focus on leveraging these interactions to develop advanced biomaterials that aid regeneration of the central nervous system.
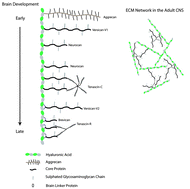
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7850-7866
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00974J
Synthesis and design of biologically inspired biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications
Synthesis and design of biologically inspired biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles.
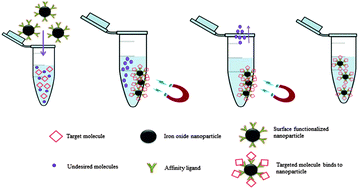
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7831-7849
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00931F
Surface modification of uniaxial cyclic strain cell culture platform with temperature-responsive polymer for cell sheet detachment
Because current cell sheet-based blood vessels lack biomimetic structure and require excessively long culture times that may compromise smooth muscle cell phenotype, we modified a cell culture platform with thermoresponsive copolymers to allow intact cell sheet detachment after uniaxial conditioning.
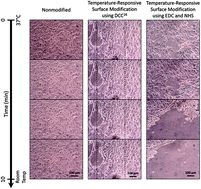
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7899-7902
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01171J
Spatially defined stem cell-laden hydrogel islands for directing endothelial tubulogenesis
Patterning of encapsulated MSCs for the spatio-temporal guidance of angiogenesis for modelling and design of therapeutic biomaterials.
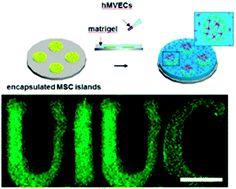
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7896-7898
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01294E
Photocrosslinkable, biodegradable hydrogels with controlled cell adhesivity for prolonged siRNA delivery to hMSCs to enhance their osteogenic differentiation
Sustained and localized delivery of siRNA from photocrosslinked dextran hydrogels can enhance human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 485-495
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB01739H
Physically crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol and gelatin interpenetrating polymer network theta-gels for cartilage regeneration
Theta-gels are hydrogels that form during the solidification and phase separation of two dislike polymers, in which a low molecular weight polymer behaves as a porogen and is removed through dialysis.
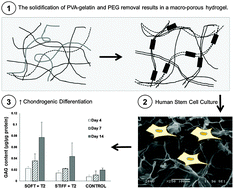
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 9242-9249
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00989H
Sustained small molecule delivery from injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogels through host–guest mediated retention
Shear-thinning hyaluronic acid hydrogels based on modifications of β-cyclodextrin and adamantane were developed for the tunable, sustained release of small molecules, through regulation of cyclodextrin content and affinity for cyclodextrin.
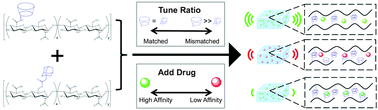
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 8010-8019
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00981B
Hydrolysis and sulfation pattern effects on release of bioactive bone morphogenetic protein-2 from heparin-based microparticles
Microparticles fabricated with more highly sulfated heparin species are able to release bioactive bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), making these microparticles a promising method for growth factor delivery.
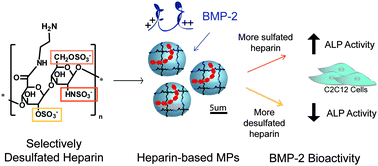
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 8001-8009
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00933B
Systematic evaluation of natural scaffolds in cutaneous wound healing
In this report, we show the tissue healing capacity for solely conductive scaffolds composed of fibrin and/or hyaluronic acid and compared them to scaffolds that deliver a proangiogenic protein signal.
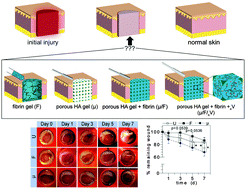
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7986-7992
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00807G
Spontaneous helical structure formation in laminin nanofibers
Surface-initiated assembly is used to engineer laminin nanofibers that spontaneously adopt a helical conformation.
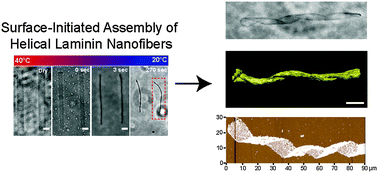
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7993-8000
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01003A
Tunable controlled release of bioactive SDF-1α via specific protein interactions within fibrin/nanoparticle composites
Control over burst release from SDF-1α-loaded PLGA nanoparticles when embedded in varying densities of fibrin matrices using specific protein/protein interactions.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7963-7973
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00935A
Development and characterization of polyethylene glycol–carbon nanotube hydrogel composite
Polyethylene–glycol–carbon nanotube composite was developed where carbon nanotubes altered the hydrogel mechanical and physical properties and aided neuronal cell viability.
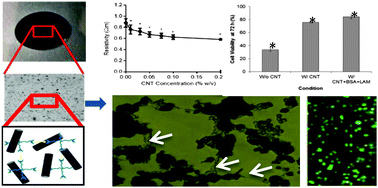
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7950-7962
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01047K
Designer hydrogels for precision control of oxygen tension and mechanical properties
Controlled oxygen levels and mechanical properties in hydrogels provide cellular cues.
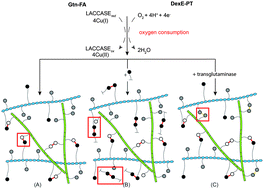
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7939-7949
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01038A
In situ crosslinking of electrospun gelatin for improved fiber morphology retention and tunable degradation
In situ crosslinking provides a method to crosslink gelatin during electrospinning enabling tunable degradation rates and displaying improved fiber morphology retention after implantation.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7930-7938
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00937E
Development of a glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor-releasing artificial dura for neural tissue engineering applications
Develop a scaffold consisting of aligned, drug releasing nanofiber to serve as a replacement for damaged dura mater.
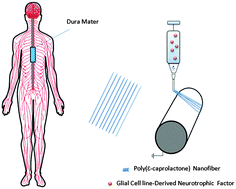
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7974-7985
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00871A
Biomimetic microbeads containing a chondroitin sulfate/chitosan polyelectrolyte complex for cell-based cartilage therapy
Cell-encapsulating microbeads containing a biomimetic chondroitin sulfate–chitosan polyelectrolyte complex for cartilage tissue engineering.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7920-7929
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00934K
Collagen-mimetic hydrogels promote human endothelial cell adhesion, migration and phenotypic maturation
This work evaluates the response of human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) to thromboresistant collagen-mimetic hydrogel coatings.
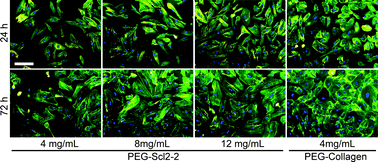
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7912-7919
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00990A
Hydrogel-based engineering of beige adipose tissue
Brown and beige adipose tissues have a significant capacity for energy expenditure that may be exploited as a treatment for obesity and metabolic disease.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 7903-7911
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00952A
About this collection
Bio-inspired and naturally-derived materials may derive their structure, crosslinking, fabrication or application from biological sources. Of particular interest are materials that are self-assembled, hierarchically structured, biologically active, dynamic, responsive or adaptable. Potential applications are diverse and include the medical, bioprocessing, environmental, energy, consumer or military fields. This themed issue aims to cover the most recent progress in the synthesis, processing and characterization of bio-inspired and natural materials, to highlight the new development in synthesis, engineering, and application of these materials.