Themed collection Journal of Materials Chemistry B Emerging Investigators

Journal of Materials Chemistry B profiles: Contributors to the Emerging Investigators 2018 issue
Journal of Materials Chemistry B profiles contributors to the Emerging Investigators issue.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7089-7095
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB90154F
Gel-based soft actuators driven by light
Gels that display light-induced motile, life-like actions are reviewed and their potential applications as light-driven soft actuators are also discussed.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2019,7, 4234-4242
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01893F
The benefits of macromolecular hydrogen sulfide prodrugs
The potential of H2S can be realised with design of macromolecular prodrugs.
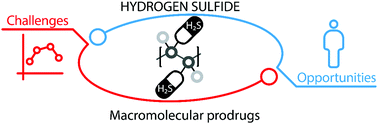
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7122-7128
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB02352B
Bioelectronics goes 3D: new trends in cell–chip interface engineering
Bioelectronic platforms can be used for electrophysiology, monitoring and stimulating specific cellular functions.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7096-7101
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01737A
Near-infrared light triggered drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles
Stimuli triggered drug delivery systems enable controlled release of drugs at the optimal space and time, thus achieving optimal therapeutic effects.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7112-7121
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01548A
Enhancing the sensitivity of colorimetric lateral flow assay (CLFA) through signal amplification techniques
This article highlights recent signal amplification techniques for enhancing the detection sensitivity of colorimetric lateral flow assay.
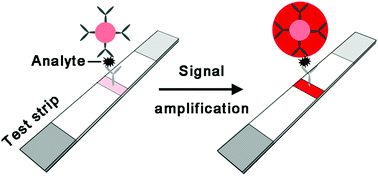
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7102-7111
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01603H
Mechanical determination of particle–cell interactions and the associated biomedical applications
Mechanical determination of particle–cell interactions and the associated biomedical applications.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7129-7143
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01590B
Bioelectronics with nanocarbons
Smart bioelectronics fabricated from nanocarbons have the potential to enable seamless integration with electrogenic cells and tissues.
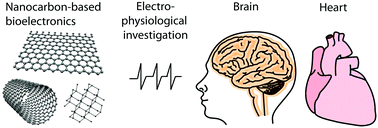
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7159-7178
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01600C
Nanostructured interfaces for probing and facilitating extracellular electron transfer
Probing and facilitating microbial extracellular electron transfer through nanotechnology enabled platforms are transforming bioenergetic, bioelectronic, and other related research areas.
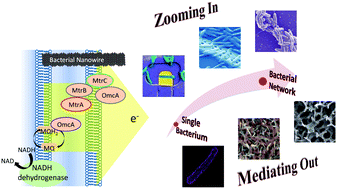
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7144-7158
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01598H
Design and fabrication of reduction-sensitive cell penetrating nanofibers for enhanced drug efficacy
In this work, we report the facile preparation of reduction-responsive cell penetrating nanofibers through the design and self-assembly of integrated multidomain peptides that have tunable surface charges and nanostructures in response to a chemically reducing environment. Stimuli-responsive cell penetrating activity was demonstrated for improved drug efficacy in HeLa cell culture compared with the non-responsive nanofibers.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7179-7184
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB00728D
Polymeric arsenicals as scaffolds for functional and responsive hydrogels
Here arsenohydrogels are introduced for the first time as functional, tuneable and responsive hydrogels.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2019,7, 4263-4271
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB02569J
Tuning HIV drug release from a nanogel-based in situ forming implant by changing nanogel size
This paper reports an in situ forming implant based on responsive nanogels that gives tuneable long-acting drug release.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2019,7, 373-383
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01597J
An injectable dipeptide–fullerene supramolecular hydrogel for photodynamic antibacterial therapy
An injectable dipeptide–fullerene supramolecular hydrogel is designed for photodynamic antibacterial therapy.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7335-7342
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01487F
Reversible encapsulations and stimuli-responsive biological delivery from a dynamically assembled cucurbit[7]uril host and nanoparticle guest scaffold
Dynamic host–guest scaffold utilizes bioorthogonal small molecule to achieve therapeutic control.
![Graphical abstract: Reversible encapsulations and stimuli-responsive biological delivery from a dynamically assembled cucurbit[7]uril host and nanoparticle guest scaffold](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C8TB01596A&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2018)
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7329-7334
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01596A
Pharmaceutical crystallization in surface-modified nanocellulose organogels
This study shows that it is possible to shift the polymorph of pharmaceuticals through crystallization in a nanocellulose gel. This is a demonstration of using natural materials that are readily surface modified to form a tailored environment for drug crystallization.
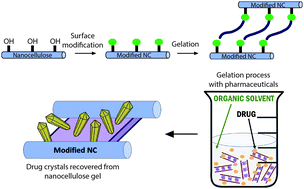
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7317-7328
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01554F
Lipid nanoemulsion passive tumor accumulation dependence on tumor stage and anatomical location: a new mathematical model for in vivo imaging biodistribution studies
Nanoparticle delivery to tumor tissue is one of the most important applications of nanomedicine.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7306-7316
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01577E
Barcoding chemical modifications into nucleic acids improves drug stability in vivo
The efficacy of nucleic acid therapies can be limited by unwanted degradation.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7197-7203
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01642A
Binding of an amphiphilic phthalocyanine to pre-formed liposomes confers light-triggered cargo release
Liposomes are able to load a range of cargos and have been used for drug delivery applications, including for stimuli-triggered drug release.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7298-7305
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01602J
Enhancing anti-thrombogenicity of biodegradable polyurethanes through drug molecule incorporation
An anti-thrombogenic, elastic, biodegradable polyurethane with covalently incorporated drug can reduce blood platelet deposition on the surface.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7288-7297
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01582A
Sub-zero temperature mechanically stable low molecular weight hydrogels
We show here a low molecular weight hydrogelator based on a functionalised dipeptide which is stable down to temperatures of −12 °C despite being made from >99% water. With the addition of glycerol this can be lowered further to −40 °C. At these colder temperatures there is no effect on the mechanical properties of the gels.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7274-7279
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01668B
Plasmonic Janus hybrids for the detection of small metabolites
Janus hybrids with amphiphilic structures were used for the sensitive detection of small metabolites.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7280-7287
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01587B
A biodegradable polyphosphoester-functionalized poly(disulfide) nanocarrier for reduction-triggered intracellular drug delivery
A reduction-cleavable polyphosphoester-functionalized poly(disulfide) nanoparticle has been constructed for the intracellular triggered release of doxorubicin in tumor chemotherapy.
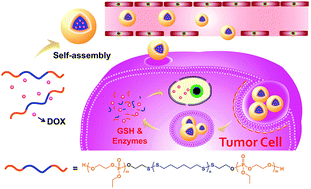
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7263-7273
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01566J
Biomolecular dynamic covalent polymers for DNA complexation and siRNA delivery
Dynamic covalent polymers made from modified amino acids complex nucleic acids and deliver siRNA in living cells.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7239-7246
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01278D
Quantum-dot-encapsulated core–shell barcode particles from droplet microfluidics
A new class of QD-encapsulated core–shell barcode particles for biomedical applications were generated using a capillary microfluidic device.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7257-7262
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB00946E
Highly selective, red emitting BODIPY-based fluorescent indicators for intracellular Mg2+ imaging
New fluorescent sensors with excellent turn-on ratio and low energy excitation provide Mg2+ detection in live cells with high selectivity.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7247-7256
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01599F
Statistical versus block fluoropolymers in gene delivery
A statistical fluorocopolymer shows dramatically higher transfection efficiency in gene delivery than a block one.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7230-7238
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01470A
Self-immolative polymers with potent and selective antibacterial activity by hydrophilic side chain grafting
Self-immolative polymers, which exert potent antibacterial activity with low hemolytic toxicity to red blood cells, are triggered to unzip into small molecules by a chemical stimulus.
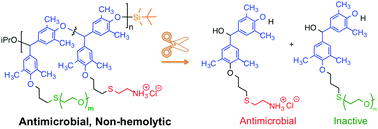
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7217-7229
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01632A
In vitro and in vivo toxicity evaluation of halloysite nanotubes
Halloysite is weakly toxic to cells and can be excreted out through the gastrointestinal metabolism of zebrafish.
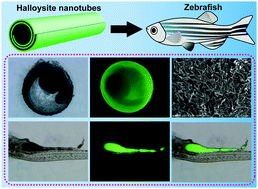
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7204-7216
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01382A
Conductive silk–polypyrrole composite scaffolds with bioinspired nanotopographic cues for cardiac tissue engineering
Imparting electroconductive and nanotopographical cues to biodegradable silk–fibroin films enhanced the maturation of cultured human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018,6, 7185-7196
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01116H
About this collection
Journal of Materials Chemistry B is proud to present this themed issue highlighting 2018’s rising stars of materials chemistry research. This issue gathers the very best work from materials chemists in the early stages of their independent career.
Each contributor was recommended by experts in their fields as carrying out work with the potential to influence future directions in materials chemistry. Congratulations to all of those who feature on their important work so far in the field of materials for biology and medicine.