Themed collection Electrostatics and Soft Matter

Electrostatics and Soft Matter: a Themed Collection in memory of Per Linse
Christos N. Likos and Joakim Stenhammar introduce this themed collection in Soft Matter on electrostatics and soft matter, in memory of Per Linse.

Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4019-4019
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM90077A
Hunting mermaids in real space: known knowns, known unknowns and unknown unknowns
We review efforts to realise so-called mermaid (or short-ranged attraction/long ranged repulsion) interactions in 3d real space.
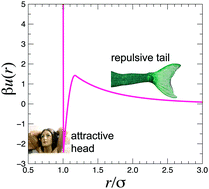
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4020-4028
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00400E
Ionic equilibria and swelling of soft permeable particles in electrolyte solutions
We report an analytical theory and coarse-grained simulations of electro-osmotic equilibria of uniformly charged soft permeable particles immersed in electrolyte solutions.

Soft Matter, 2020,16, 929-938
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SM01602C
The intimate relationship between the dielectric response and the decay of intermolecular correlations and surface forces in electrolytes
The simultaneous monotonic and oscillatory decay modes for interactions in ionic liquids and electrolyte solutions are analysed and physically explained.

Soft Matter, 2019,15, 5866-5895
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SM00712A
Tuning the order of colloidal monolayers: assembly of heterogeneously charged colloids close to a patterned substrate
We study the behavior of negatively charged colloids with two positively charged polar caps close to a planar patterned surface.

Soft Matter, 2018,14, 8119-8136
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00691A
Two time scales for self and collective diffusion near the critical point in a simple patchy model for proteins with floating bonds
In a simple patchy particle model for proteins with floating bonds, self and collective diffusion exhibits two time scales when approaching the critical point.
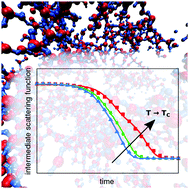
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 8006-8016
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00599K
Theory of polymer-electrolyte-composite electroactuator sensors with flat or volume-filling electrodes
In reverse actuation, a voltage/electrical-current signal can be generated from applying a mechanical force to an electroactuator.

Soft Matter, 2018,14, 7996-8005
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01438H
Structure and properties of polydisperse polyelectrolyte brushes studied by self-consistent field theory
Two complementary self-consistent field theoretical approaches are used to analyze the equilibrium structure of binary and ternary brushes of polyions with different degrees of polymerization.
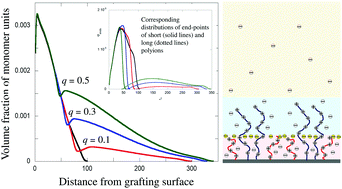
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 6230-6242
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01138A
Specific ion effects for polyelectrolytes in aqueous and non-aqueous media: the importance of the ion solvation behavior
We study the ion-specific counterion condensation behavior around charged polymers in distinct solvents. Our findings reveal the importance of ion solvation behavior in order to rationalize deviations from electrostatic mean field theories.
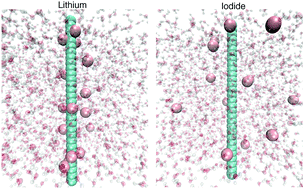
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 6243-6255
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00600H
Charge regulating macro-ions in salt solutions: screening properties and electrostatic interactions
We revisit the charge-regulation mechanism of macro-ions and apply it to mobile macro-ions in a bathing salt solution.
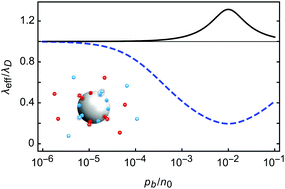
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 6058-6069
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00728D
Osmotic pressure in polyelectrolyte solutions: cell-model and bulk simulations
The osmotic pressure of polyelectrolyte solutions as a function of concentration has been calculated by simulations of a spherical cell model and by simulations with periodic boundary conditions.
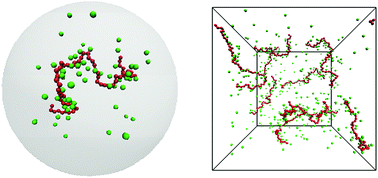
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 5832-5846
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00654G
Electrostatic interactions between charged dielectric particles in an electrolyte solution: constant potential boundary conditions
The problem of electrostatic interactions between colloidal particles in an electrolyte solution has been solved within the Debye–Hückel approximation using the boundary condition of constant potential.
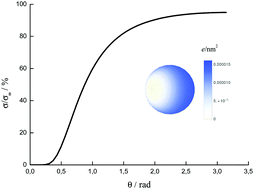
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 5480-5487
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01068D
Reappearance of slow mode in mixtures of polyethylene glycol and poly(sodium methacrylate)
After addition of poly(ethylene glycol) to a solution of poly(sodium methacrylate), the slow-mode dynamic light scattering signal reappears.
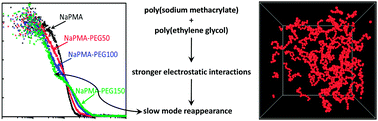
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 5039-5047
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00473K
Quenching of fully symmetric mixtures of oppositely charged microgels: the role of soft stiffness
Using molecular dynamics simulations, we investigate the self-assembly of a coarse-grained binary system of oppositely charged microgels, symmetric in size and concentration.
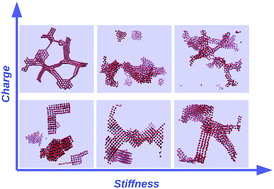
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 5106-5120
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00441B
Interactions between amphoteric surfaces with strongly overlapping double layers
The entropic repulsion between strongly overlapping electrical double-layers from two parallel amphoteric plates is described via the Donnan equilibrium in the limit of zero electric field.
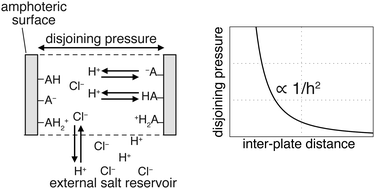
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4702-4710
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00662H
A diagrammatic analysis of the variational perturbation method for classical fluids
The statistical mechanics of classical fluids can be approached from the particle perspective, where the focus is on the positions of the particles, or from the field perspective, where the focus is on the form of the interaction fields generated by the particles. These two perspectives can be combined through the variational perturbation method.
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4721-4734
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00676H
Hydrodynamic simulations of charge-regulation effects in colloidal suspensions
Self-organization of charged soft matter is of crucial importance in biology.
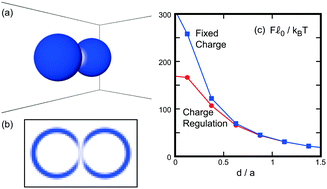
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4711-4720
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00579F
Field-induced dipolar attraction between like-charged colloids
The field induced anisotropic interactions between like-charged colloidal particles is studied using direct numerical simulations, where the polarization of the electric double layer is explicitly computed under external AC electric fields.
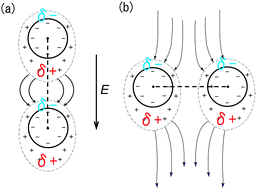
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4520-4529
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00395E
Concentration-dependent swelling and structure of ionic microgels: simulation and theory of a coarse-grained model
Swelling and structural properties of ionic microgel suspensions are described by a coarse-grained model that includes elastic and electrostatic interactions.
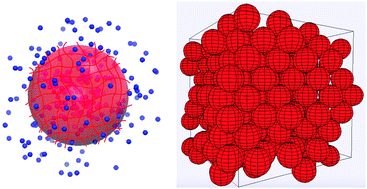
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4530-4540
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00799C
Charge and hydration structure of dendritic polyelectrolytes: molecular simulations of polyglycerol sulphate
Macromolecules based on dendritic or hyperbranched polyelectrolytes have been emerging as high potential candidates for biomedical applications.
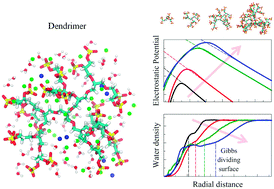
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4300-4310
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00714D
An anionic shell shields a cationic core allowing for uptake and release of polyelectrolytes within core–shell responsive microgels
MD-simulations and experimental investigations on uptake and release of anionic polyelectrolytes by cationic microgels surrounded by a soft anionic shell.
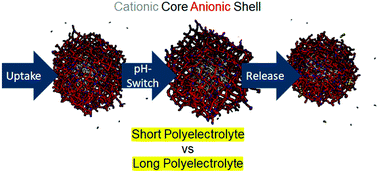
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4287-4299
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00397A
Electrostatic interactions in soft particle systems: mesoscale simulations of ionic liquids
Computer simulations provide a unique insight into the microscopic details, molecular interactions and dynamic behavior responsible for many distinct physicochemical properties of ionic liquids.
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4252-4267
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00387D
Deswelling behaviour of ionic microgel particles from low to ultra-high densities
The swelling of ionic microgel particles is measured at a wide range of concentrations using a combination of light, X-ray and neutron scattering techniques. Theoretical modeling as well as simulations are used to interpret the data.
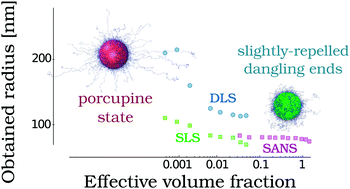
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4150-4159
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00390D
Strong-coupling theory of counterions between symmetrically charged walls: from crystal to fluid phases
We study thermal equilibrium of classical pointlike counterions confined between symmetrically charged walls at distance d.
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4040-4052
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00571K
Electrolyte solutions at heterogeneously charged substrates
Fluid density profiles sensitively depend on the type of interaction and on the lateral structure and distribution of interaction sites.
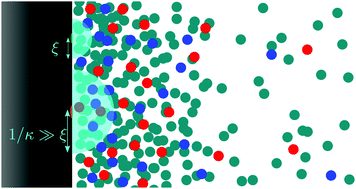
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4126-4140
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00497H
Molecular dynamics simulation of charged colloids confined between hard walls: pre-melting and pre-freezing across the BCC–fluid coexistence
Computer simulations of hard-core Yukawa systems confined between hard walls reveal pre-melting and pre-freezing transitions across the BCC–fluid coexistence.
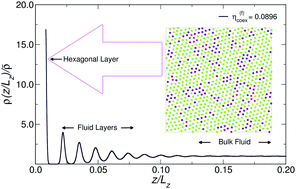
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4141-4149
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00398J
Overcharging and reentrant condensation of thermoresponsive ionic microgels
We investigated the complexation of thermoresponsive anionic poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNiPAM) microgels and cationic ε-polylysine chains. We show that the volume phase transition of the microgels triggers polyion adsorption and gives rise to a thermosensitive microgel overcharging and reentrant condensation.
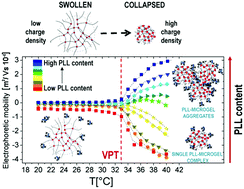
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4110-4125
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SM02357J
Many-body interactions between charged particles in a polymer solution: the protein regime
We study the phase behavior of charged particles in electrolyte solutions wherein non-adsorbing polymers are added to provide an attractive depletion interaction.
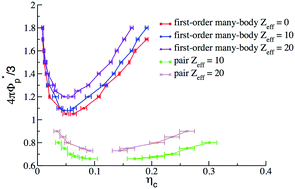
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4064-4073
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00471D
Ionic structure around polarizable metal nanoparticles in aqueous electrolytes
The high polarizability of neutral metal nanoparticles dictates their electrostatic character in electrolyte solutions.
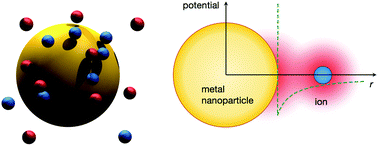
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4053-4063
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00399H
Making strong polyelectrolyte brushes pH-sensitive by incorporation of gold nanoparticles
Incorporation of pH-sensitive gold nanoparticles in an inert polymer brush triggers a pH-sensitive response.
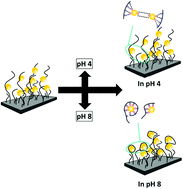
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4029-4039
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00411K
Clustering and assembly dynamics of a one-dimensional microphase former
We consider a one-dimensional model of short range attraction and long range repulsion interactions whose simplicity enables detailed analysis.
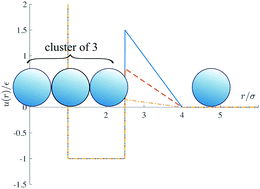
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4101-4109
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00315G
Monte Carlo simulations of weak polyelectrolyte microgels: pH-dependence of conformation and ionization
A Monte Carlo study of the pH-dependent ionization and swelling behavior of weak polyelectrolyte microgels.
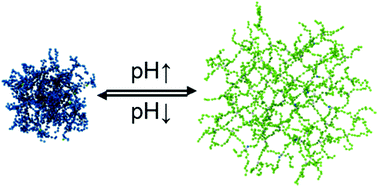
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4087-4100
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SM02528A
A bead–spring chain as a one-dimensional polyelectrolyte gel
The physical principles underlying expansion of a single-chain polyelectrolyte coil caused by Coulomb repulsions among its ionized groups, and the expansion of a cross-linked polyelectrolyte gel, are probably the same.
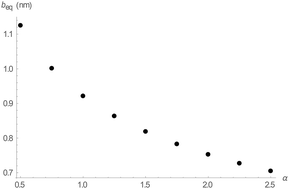
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4074-4080
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00156A
Efficient simulation method for nano-patterned charged surfaces in an electrolyte solution
We present a method to efficiently simulate nano-patterned charged surfaces inside an electrolyte solution.
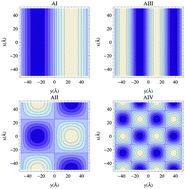
Soft Matter, 2018,14, 4081-4086
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00226F
About this collection
In spring 2017, our highly respected colleague Per Linse tragically passed away at the age of 61. Per was a prominent member of the soft matter community, and in particular made many key contributions within the field of soft matter electrostatics and polyelectrolytes.
To honor Per’s memory and his scientific contributions within this field, Soft Matter is pleased to present this themed collection on electrostatics and soft matter. The collection is Guest Edited by Christos Likos (University of Vienna, Austria) and Joakim Stenhammar (Lund University, Sweden), and contains contributions from many of Per’s former colleagues, as well as other leaders in the field.